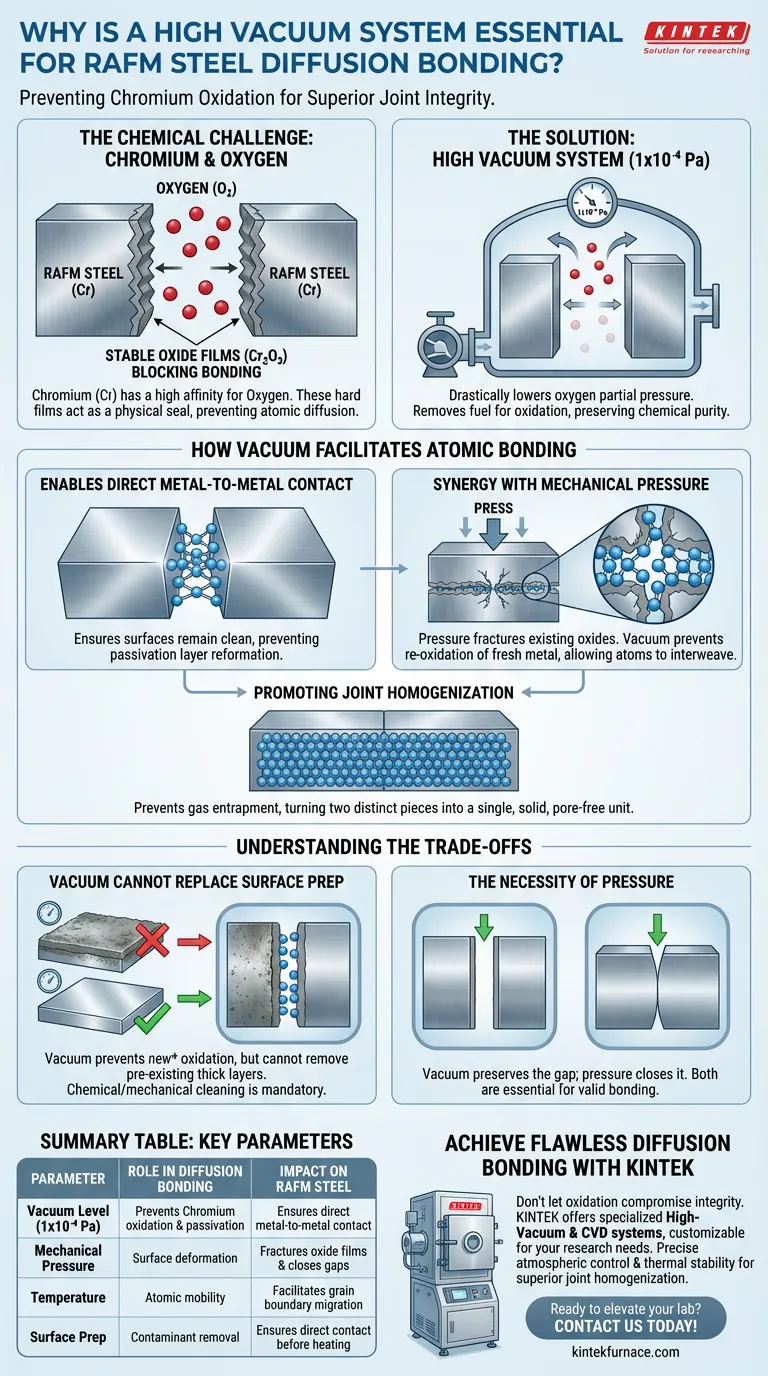
A high vacuum system is strictly necessary to prevent the rapid oxidation of Chromium within Reduced Activation Ferritic/Martensitic (RAFM) steel during the heating process. By maintaining a vacuum level of approximately 1x10^-4 Pa, the system eliminates residual oxygen that would otherwise react with the steel's surface, ensuring that metal atoms can make the direct contact required for successful solid-state diffusion.
The presence of oxygen is the single greatest barrier to bonding RAFM steel. A high vacuum environment serves as the primary defense mechanism, preventing the Chromium content from creating stable oxide films that block atomic diffusion and compromise joint integrity.
The Chemical Challenge: Chromium and Oxygen
The Vulnerability of RAFM Steel
RAFM steel contains significant amounts of Chromium (Cr). While beneficial for the steel's properties, Chromium presents a specific challenge during bonding: it possesses a high affinity for oxygen.
The Formation of Oxide Barriers
Even trace amounts of oxygen in the bonding chamber will react with the Chromium on the steel's surface.
This reaction creates hard, stable oxide films. These films act as a physical barrier, effectively "sealing" the metal and preventing the grain boundaries from merging across the interface.
Reducing the Oxidation Rate
A high vacuum environment (1x10^-4 Pa) drastically lowers the partial pressure of oxygen.
By removing the fuel (oxygen) for this reaction, the vacuum significantly reduces the oxidation rate at the bonding interface, preserving the chemical purity of the surface.
How Vacuum Facilitates Atomic Bonding
Enabling Direct Metal-to-Metal Contact
For diffusion bonding to occur, raw metal atoms from one surface must touch raw metal atoms from the other.
The vacuum environment ensures that once the surfaces are cleaned or mechanically abraded, they remain clean. It prevents the reformation of passivation layers that would interrupt the continuity of the bulk material.
Synergy with Mechanical Pressure
Vacuum alone is not enough; it must work in concert with mechanical pressure.
As pressure is applied to the joint, existing surface oxide films are fractured. The vacuum environment ensures that the freshly exposed metal within these fractures does not immediately oxidize, allowing for valid atomic bonding.
Promoting Joint Homogenization
The ultimate goal of this process is to eliminate pores and achieve a homogeneous joint.
Vacuum aids this by preventing gas entrapment at the interface. This allows atoms to interweave freely across the contact zone, turning two distinct pieces of metal into a single, solid unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Vacuum Cannot Replace Surface Preparation
While a high vacuum prevents new oxidation, it cannot always remove thick, pre-existing oxide layers formed before the material entered the chamber.
Relying solely on the vacuum to "clean" the surface is a common pitfall. The steel must be chemically or mechanically cleaned prior to insertion to ensure the vacuum is effective.
The Necessity of Pressure
A high vacuum does not negate the need for substantial mechanical force.
Without sufficient pressure (often breaking oxide films via plastic deformation), the vacuum only preserves the gap between the materials rather than closing it. The system must balance atmospheric control with mechanical stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve optimal diffusion bonding results with RAFM steel, align your process parameters with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is preventing interface failure: Prioritize achieving a vacuum of at least 1x10^-4 Pa to specifically inhibit Chromium oxide formation.
- If your primary focus is pore elimination: Ensure your vacuum system is paired with sufficient axial pressure to induce plastic deformation of surface asperities.
Success in diffusion bonding RAFM steel lies in the precise synchronization of a contaminant-free vacuum environment and the mechanical force required to merge atomic structures.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Diffusion Bonding | Impact on RAFM Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Level | 1x10^-4 Pa | Prevents Chromium oxidation and surface passivation |
| Mechanical Pressure | Surface deformation | Fractures oxide films and closes interface gaps |
| Temperature | Atomic mobility | Facilitates grain boundary migration across the joint |
| Surface Prep | Contaminant removal | Ensures direct metal-to-metal contact before heating |
Achieve Flawless Diffusion Bonding with KINTEK
Don't let oxidation compromise your structural integrity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized High-Vacuum and CVD systems, along with other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for your unique material research needs.
Whether you are bonding RAFM steel or advanced alloys, our systems provide the precise atmospheric control and thermal stability required for superior joint homogenization.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Jin‐Gui Chen, Yushun Wei. Diffusion bonding of RAFM steels: Evolution of interfacial oxide layer with pressure and microstructure and mechanical property after post bonding heat treatment. DOI: 10.2298/jmmb231011007c
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- Ultra High Vacuum Stainless Steel KF ISO CF Flange Pipe Straight Pipe Tee Cross Fitting
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of vacuum hot pressing? Essential for High-Performance Materials
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- How does temperature control precision of a vacuum hot press affect SiC fiber/TB8 matrix? Optimize Interface Quality
- What are the advantages of a high-pressure vacuum induction hot press furnace? Boost SiGe Thermoelectric Performance
- What is the necessity of maintaining a high vacuum environment during AZ31 sintering? Prevent Oxidation and Porosity
- What is Vacuum Hot Pressing used for in ceramic and powder metal targets? Achieve Superior Density and Purity
- What is a vacuum press and what are its primary uses? Unlock High-Performance Material Processing
- What are the primary advantages of industrial SPS vs. vacuum hot-pressing for Ti-6Al-4V? Achieve Superior Microstructure



















