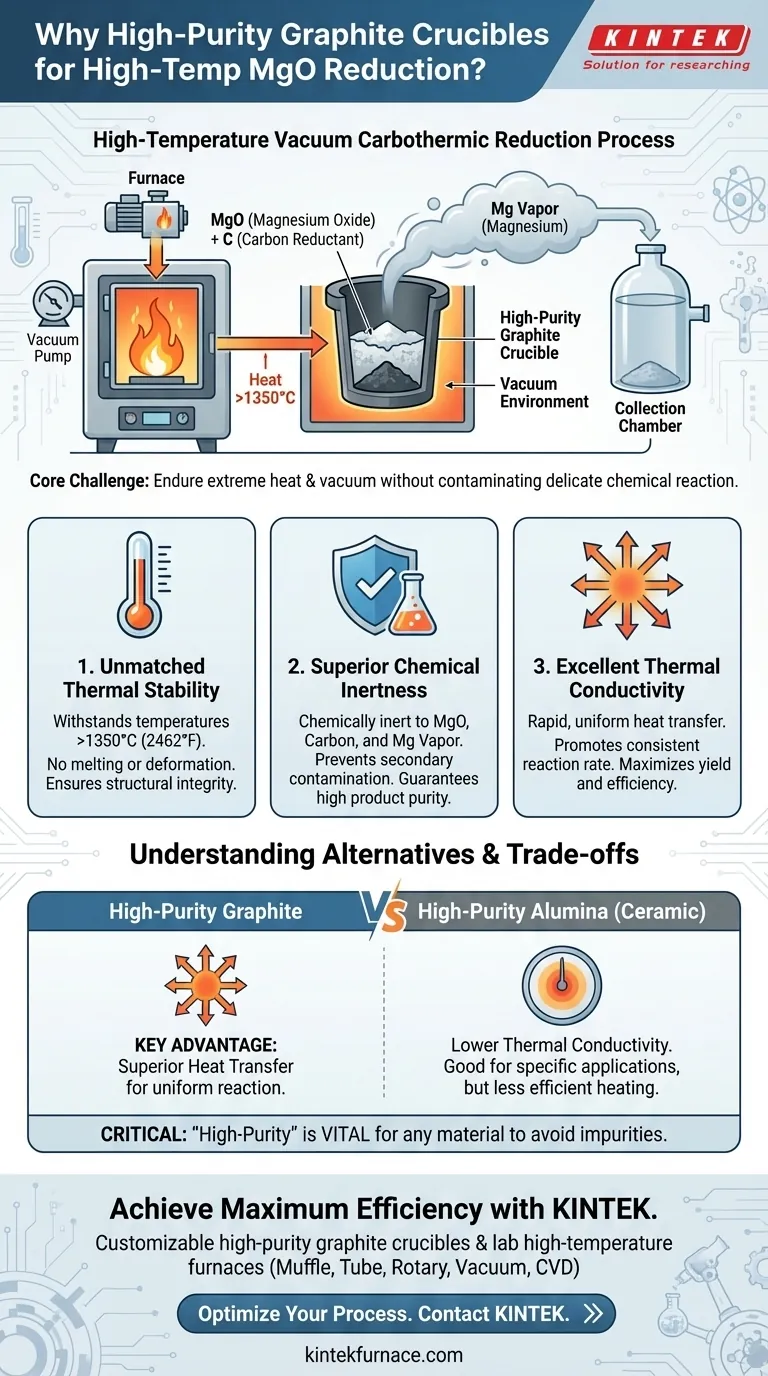
A high-purity graphite crucible is chosen for the carbothermic reduction of magnesium oxide because it possesses a unique combination of properties essential for success in a high-temperature vacuum environment. It offers exceptional heat resistance to prevent melting, superior chemical stability to avoid contaminating the pure magnesium product, and high thermal conductivity to ensure the reaction proceeds evenly and efficiently.
The core challenge is finding a material that can endure extreme heat and vacuum without interfering with a delicate chemical reaction. High-purity graphite is the standard solution because it acts as a passive, durable, and highly efficient vessel for heat transfer under these precise conditions.

The Critical Demands of the Process
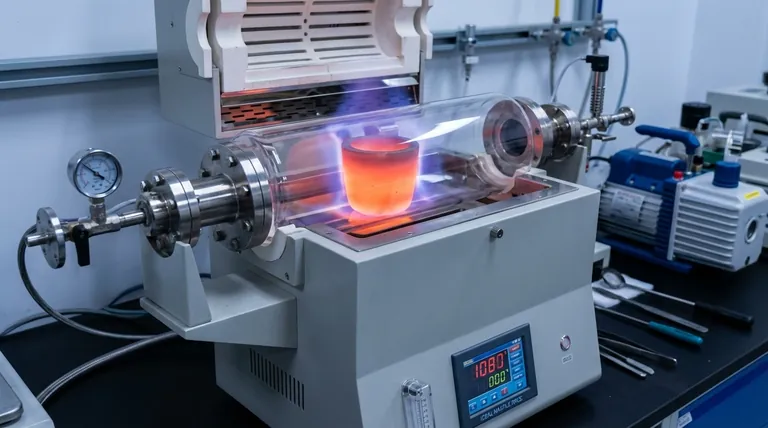
The vacuum carbothermic reduction of magnesium oxide is a demanding industrial process. To understand the choice of crucible, we must first appreciate the environment it operates in.
Extreme Temperature and Vacuum
The reaction requires temperatures exceeding 1350°C (2462°F) to proceed effectively. At this temperature, magnesium is produced as a vapor, which necessitates a vacuum environment to collect it and prevent it from reacting with air.
The Need for Absolute Purity
The goal is to produce high-purity magnesium. The reaction vessel itself must not react with the magnesium oxide, the carbon reductant, or the final magnesium vapor. Any side-reaction would introduce impurities into the final product and degrade the crucible.
Why Graphite Excels Under Pressure
High-purity graphite is not merely a suitable material; it is uniquely optimized for this task due to three fundamental properties.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Graphite has an extremely high melting point (around 3600°C), ensuring it maintains its structural integrity and does not soften or deform at the reaction temperature. This physical stability is non-negotiable for safety and process reliability.
Superior Chemical Inertness
In this specific environment, graphite is chemically inert. It does not react with the molten reactants or the resulting magnesium vapor. This prevents secondary contamination, guaranteeing the purity of the final magnesium product.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity
This is a critical performance factor. Graphite's high thermal conductivity allows heat from the furnace to transfer uniformly and rapidly throughout the furnace charge. This homogeneous heating promotes a consistent reaction rate, maximizing the yield and preventing unreacted cold spots.
Understanding the Alternatives and Trade-offs
While graphite is the typical choice, other refractory materials can be used, highlighting the specific advantages graphite brings.
The Case for Alumina Crucibles
High-purity ceramics like alumina (corundum) also offer exceptional high-temperature resistance and chemical inertness. They can withstand the thermal and chemical demands of the process without breaking down or reacting with the magnesium.
Graphite's Key Advantage: Heat Transfer
The primary distinction is thermal conductivity. Graphite conducts heat far more efficiently than ceramics like alumina. This superior heat transfer makes graphite the preferred choice for processes where uniform and rapid heating are critical to driving a complete and efficient reaction.
The Importance of "High-Purity"
For any material considered—be it graphite or alumina—the "high-purity" designation is vital. Lower-grade materials contain binders or impurities that can vaporize or react at high temperatures, contaminating the product and compromising the vacuum.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your choice of material should be dictated by the specific priorities of your reaction environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum reaction efficiency and yield: Graphite is the superior choice due to its high thermal conductivity, which ensures the most uniform heat distribution.
- If your primary focus is mitigating a specific carbon-related side reaction: A high-purity ceramic crucible, like alumina, could be a viable alternative, provided its lower thermal conductivity is acceptable.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: The proven track record and combination of thermal, chemical, and conductive properties make high-purity graphite the lowest-risk option for this specific application.
Ultimately, the selection of a high-purity graphite crucible is a deliberate engineering decision based on its optimal performance in an unforgiving process environment.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for MgO Reduction |
|---|---|
| High Thermal Stability | Withstands temperatures >1350°C without melting or deforming. |
| Superior Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of pure magnesium product. |
| Excellent Thermal Conductivity | Ensures uniform heating for a complete, efficient reaction. |
| High Purity | Avoids introducing impurities that can compromise the vacuum and final product. |
Achieve Maximum Efficiency in Your High-Temperature Processes
Choosing the right reaction vessel is critical for the success and purity of your materials. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-purity graphite crucibles and a full range of lab high-temperature furnaces (including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems), all customizable for your unique needs.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the significance of porcelain furnaces in academic and scientific research? Unlock Innovation with Precise High-Temperature Control



















