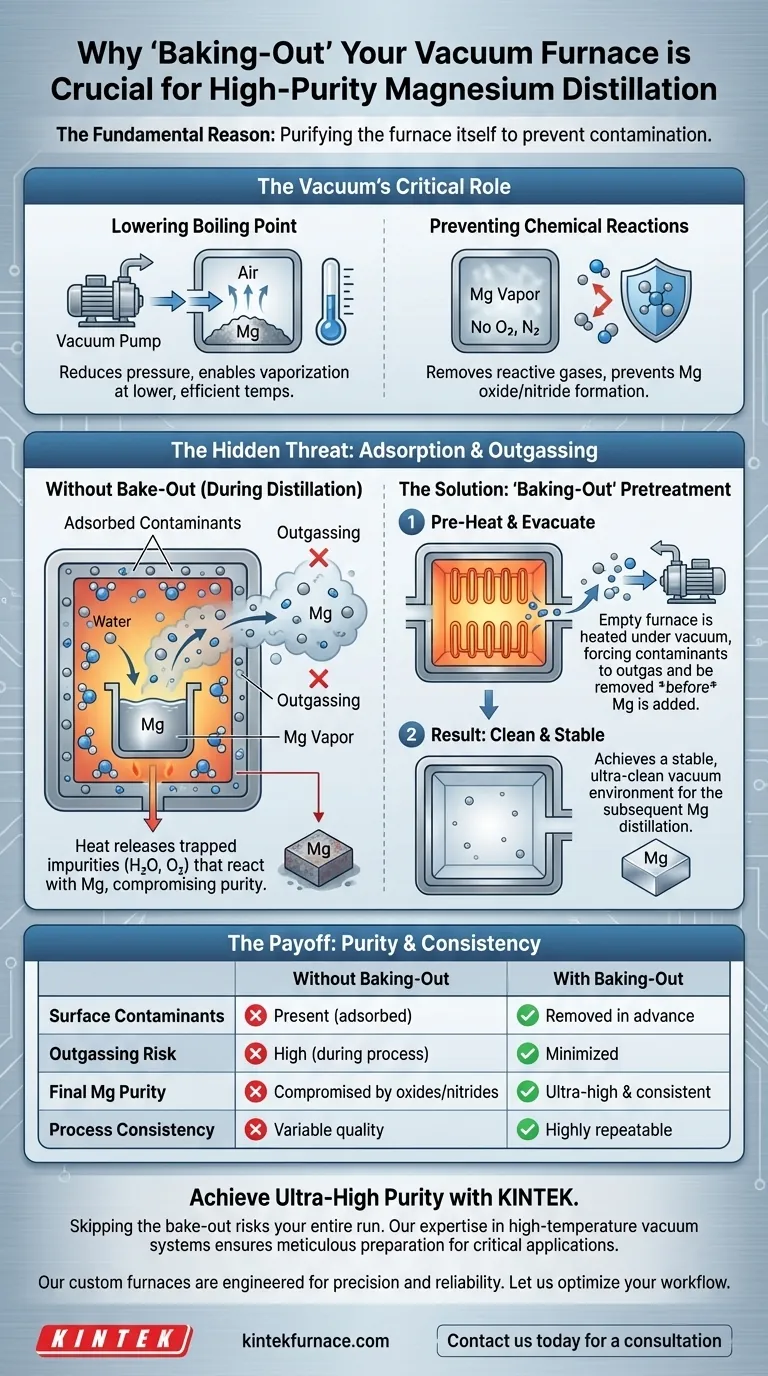
The fundamental reason for a 'baking-out' pretreatment is to purify the vacuum furnace itself before the magnesium distillation begins. This process involves heating the empty furnace chamber under vacuum to drive off adsorbed moisture, gases, and other volatile impurities from its internal surfaces, ensuring they do not later contaminate the magnesium vapor during the critical purification step.
Achieving ultra-high purity in any material is not just about purifying the material itself, but also about controlling its environment. Baking-out is the essential step that ensures the processing chamber—the furnace—is cleaner than the material you intend to produce.

The Critical Role of Vacuum in Magnesium Purification
To understand why cleaning the furnace is so vital, we must first appreciate why a vacuum is used for magnesium distillation at all. The vacuum environment serves two primary purposes.
Lowering the Boiling Point
A deep vacuum, typically below 10⁻² mmHg, significantly reduces the pressure exerted on the magnesium. This lowers its boiling point, allowing the metal to vaporize (sublimate) at much lower and more energy-efficient temperatures than would be required at atmospheric pressure.
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
The vacuum removes reactive atmospheric gases, most notably oxygen and nitrogen. Hot magnesium vapor is highly reactive and would readily form magnesium oxide or magnesium nitride if these gases were present, destroying the purity of the final product.
The Hidden Contamination Source: The Furnace Itself
While a vacuum pump removes gases from the open chamber, it cannot easily remove molecules that are physically stuck to the internal surfaces of the furnace and crucible. This phenomenon is the central problem that baking-out solves.
Understanding Adsorption and Outgassing
Even in a vacuum, a thin layer of water molecules, residual gases, and other volatile compounds clings to all internal surfaces through a process called adsorption.
When the furnace is heated during the actual distillation run, this thermal energy gives the adsorbed molecules enough energy to escape back into the chamber. This process is known as outgassing.
The Impact of Outgassing on Purity
If outgassing occurs while the hot magnesium vapor is present, these newly released contaminants—especially water vapor and residual oxygen—will mix with and react with it. This directly compromises the purity of the distilled magnesium, undermining the entire purpose of the process.
How 'Baking-Out' Creates a Clean Environment
Baking-out is a preemptive strike against outgassing. It purifies the processing environment before the valuable material is ever introduced.
The Process: Pre-Heating and Evacuation
The procedure involves heating the sealed, empty furnace to a high temperature while the vacuum pumps are running. This forces the adsorbed contaminants to outgas from the internal surfaces.
The Goal: Removing Contaminants in Advance
Because the magnesium is not yet in the furnace, these released impurities are simply and safely removed from the system by the vacuum pumps.
The Result: A Stable, Ultra-High Vacuum
After cooling, the internal surfaces are exceptionally clean. This dramatically lowers the ultimate background pressure the system can achieve and ensures that minimal outgassing will occur during the actual magnesium distillation, creating a stable and pure environment for the process.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While essential for high-purity applications, baking-out is not without its costs. However, skipping it often carries a much higher price.
The Cost of a Bake-Out
The primary trade-off is the investment in time and energy. A thorough bake-out cycle can add several hours to the overall process time and consumes significant electrical energy.
The Cost of Skipping a Bake-Out
Failing to perform this step introduces a major variable into the process. The result is a high risk of producing lower-purity magnesium, inconsistent batch-to-batch quality, and potentially wasting an entire run of raw material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to incorporate a bake-out step is directly tied to the desired quality of the final product. It is a key differentiator between standard and high-purity metallurgical operations.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: A thorough bake-out is a non-negotiable step to minimize environmental contamination and achieve the highest possible grade of magnesium.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: Baking-out eliminates a critical source of variability, ensuring that each distillation run starts with an identically clean environment, leading to more predictable and reliable results.
Ultimately, meticulous preparation of the processing environment is the foundation upon which high-purity material production is built.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Without Baking-Out | With Baking-Out |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Contaminants | Present (adsorbed moisture/gases) | Removed in advance |
| Outgassing During Distillation | High risk of contamination | Minimized |
| Final Magnesium Purity | Compromised by oxides/nitrides | Ultra-high and consistent |
| Process Consistency | Variable batch quality | Highly repeatable |
Achieve ultra-high purity and batch consistency in your magnesium purification process.
Skipping the bake-out step risks contaminating your entire run with surface-level moisture and gases. At KINTEK, our expertise in high-temperature vacuum systems ensures your furnace environment is meticulously prepared for critical applications.
Our custom Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces are engineered for precision and reliability, backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. Let us help you optimize your purification workflow.
Contact us today for a consultation to discuss your specific high-purity metal processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















