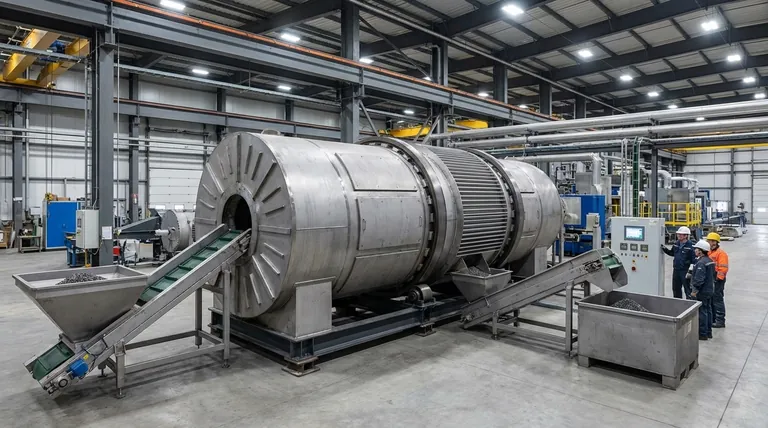
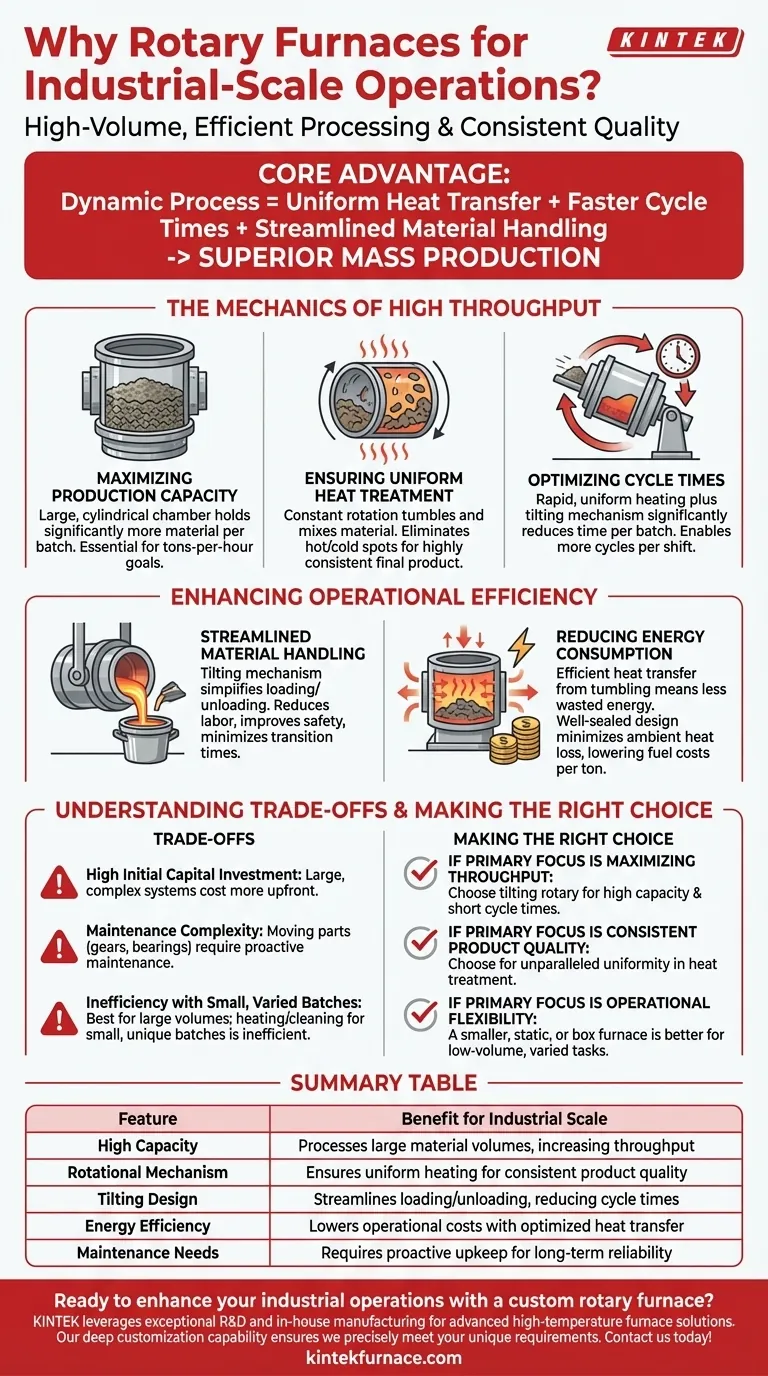
In essence, rotary furnaces are suitable for industrial-scale operations because their design is fundamentally built for high-volume, efficient processing. Their ability to handle large quantities of material, combined with a rotational mechanism that ensures uniform heating, directly translates to the high throughput and consistent quality required by industry.
The core advantage of a rotary furnace isn't merely its size, but the dynamic process it enables. The constant rotation is the key that unlocks uniform heat transfer, faster cycle times, and streamlined material handling, making it a superior choice for mass production environments.

The Mechanics of High Throughput
The industrial suitability of a rotary furnace stems from several interconnected design principles that work together to maximize output.
Maximizing Production Capacity
A defining feature of rotary furnaces is their large, cylindrical chamber. This allows them to hold and process significantly more material in a single batch than most static furnace types.
For operations where output is measured in tons per hour, this high capacity is a non-negotiable starting point for achieving production goals.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Treatment
The furnace's rotation is its most critical feature for quality at scale. As the drum turns, the material inside is constantly tumbled and mixed.
This action ensures that every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source, eliminating hot spots and unprocessed cold spots. The result is a highly consistent and predictable final product, which is crucial for meeting industrial quality standards.
Optimizing Cycle Times
Industrial productivity depends on how quickly you can complete a full process cycle—from loading to heating to unloading. Tilting rotary furnaces excel here.
The combination of rapid, uniform heating and the ability to quickly tilt the furnace for loading and pouring significantly reduces the time required for each batch. This allows for more cycles per shift, directly increasing overall plant throughput.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Beyond sheer speed, rotary furnaces bring practical efficiencies that reduce operational costs and complexity, key concerns in any industrial setting.
Streamlined Material Handling
Tilting rotary furnaces dramatically simplify the logistics of loading raw materials and unloading finished products.
The tilting mechanism allows for easy charging of scrap or other solids and provides controlled pouring of molten metal or discharge of treated material. This reduces labor requirements, improves safety, and minimizes transition time between batches.
Reducing Energy Consumption
Energy is a primary operational cost in thermal processing. The efficient heat transfer from the tumbling action means less energy is wasted bringing the material up to temperature.
A well-sealed rotary furnace also minimizes ambient heat loss. This efficiency means lower fuel or electricity consumption per ton of processed material, delivering significant cost savings at an industrial scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary furnaces are not a universal solution. Acknowledging their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
High Initial Capital Investment
These are large, mechanically complex systems. The upfront cost for purchasing and installing a rotary furnace is substantially higher than for simpler, static batch furnaces.
Maintenance Complexity
The rotational and tilting mechanisms involve gears, bearings, motors, and robust seals that require a dedicated and proactive maintenance schedule. While reliable, the maintenance is more involved than on a furnace with no moving parts.
Inefficiency with Small, Varied Batches
The strength of a rotary furnace is processing large volumes of the same material. It is not well-suited for high-mix, low-volume work, as the time and energy spent heating and cleaning the large chamber for a small, unique batch is highly inefficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
To determine if a rotary furnace is the correct tool, you must align its capabilities with your primary production goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: The combination of high capacity and short cycle times makes a tilting rotary furnace an exceptional choice for large-scale processing.
- If your primary focus is consistent product quality: The rotational mixing action provides unparalleled uniformity in heat treatment, which is critical for meeting stringent industrial specifications at scale.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility for small jobs: The scale and design of a rotary furnace are likely inappropriate; a smaller, static, or box furnace would offer better efficiency for varied, low-volume tasks.
Ultimately, a rotary furnace excels when the core operational driver is efficient, high-volume, and uniform material processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Industrial Scale |
|---|---|
| High Capacity | Processes large material volumes, increasing throughput |
| Rotational Mechanism | Ensures uniform heating for consistent product quality |
| Tilting Design | Streamlines loading/unloading, reducing cycle times |
| Energy Efficiency | Lowers operational costs with optimized heat transfer |
| Maintenance Needs | Requires proactive upkeep for long-term reliability |
Ready to enhance your industrial operations with a custom rotary furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can boost your efficiency and throughput!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency



















