Laboratory furnaces are essential because they provide the highly controlled, high-temperature environments that are fundamental to modern science and manufacturing. Unlike a simple oven, these instruments allow for the precise manipulation of materials at a molecular level, enabling processes from strengthening a metal alloy to synthesizing a novel compound for medical research.
The true value of a laboratory furnace lies not just in its ability to generate heat, but in its power to create a precisely controlled thermal and atmospheric environment. This control is the key that unlocks material transformations and scientific discoveries that would otherwise be impossible.

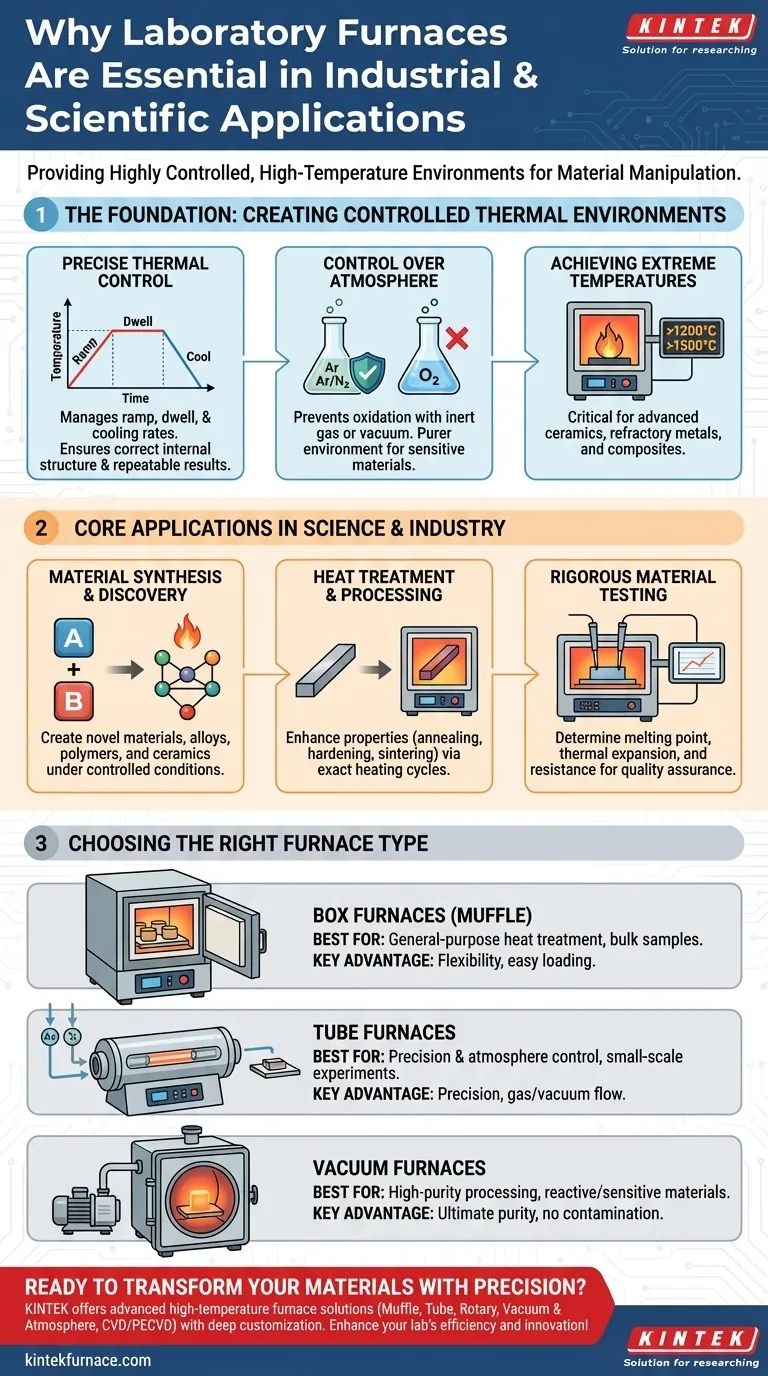
The Foundation: Creating Controlled Thermal Environments
At their core, laboratory furnaces solve a fundamental problem: most advanced materials do not achieve their desired properties at room temperature. They must be transformed through carefully managed thermal processes.
Precision Beyond a Simple Oven
A standard oven provides generalized heat. A laboratory furnace provides programmable, precise thermal control.
This includes managing the rate of temperature increase (ramp), the duration at a specific temperature (dwell), and the rate of cooling. This precision ensures that a material's internal structure—such as its crystal lattice—is formed correctly, leading to repeatable and reliable results.
Control Over the Atmosphere
Many materials react negatively with air, especially at high temperatures. Oxygen can cause unwanted oxidation, which compromises the integrity of metals, ceramics, and other sensitive compounds.
Laboratory furnaces solve this by enabling atmosphere control. By introducing an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, or by creating a vacuum, they establish a pure environment where thermal processes can occur without contamination.
Achieving Extreme Temperatures
These furnaces are engineered to safely and reliably reach temperatures far beyond the capability of conventional equipment, often exceeding 1200°C, 1500°C, or even higher.
This capability is critical for working with advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and composites that require extreme heat for synthesis, sintering, or testing.
Core Applications in Science and Industry
The precise control offered by laboratory furnaces makes them indispensable across a wide range of fields, from foundational research to industrial quality control.
For Material Synthesis and Discovery
In research and development, furnaces are used to create entirely new materials. Scientists can experiment with different elements and compounds, heating them under controlled conditions to synthesize novel alloys, advanced polymers, and specialized ceramics with unique properties.
For Heat Treatment and Processing
In manufacturing, furnaces are workhorses for enhancing material properties. Processes like annealing (softening metal), hardening (strengthening it), and sintering (fusing powder into a solid mass) all rely on exact heating and cooling cycles to achieve the desired strength, durability, and performance.
For Rigorous Material Testing
Furnaces are crucial for quality assurance and safety testing. They are used to determine a material's melting point, thermal expansion, and resistance to heat-related degradation. This data is vital for engineering applications, from aerospace components to biomedical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Choosing the Right Furnace Type
The term "laboratory furnace" encompasses several designs, each optimized for different tasks. The choice depends entirely on the specific requirements of the application.
Box Furnaces: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A box furnace (or muffle furnace) features a front-opening chamber, making it easy to load and unload samples of various shapes and sizes. They are highly flexible and reliable for general-purpose heat treatment, annealing, and material processing.
Tube Furnaces: For Precision and Atmosphere Control
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical chamber, which is ideal for processing smaller samples or for applications requiring a tightly controlled atmosphere. Their shape makes it easy to create a continuous flow of gas over a sample or to establish a high-quality vacuum.
Vacuum Furnaces: For Ultimate Purity
When preventing any and all atmospheric contamination is the top priority, a vacuum furnace is essential. By removing virtually all air and other gases, these furnaces provide the purest possible environment for processing highly reactive metals or manufacturing sensitive electronic and semiconductor components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace is a critical decision that directly impacts the outcome of your work. Your primary objective should guide your choice.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment or processing bulk samples: A box furnace offers the best combination of capacity, flexibility, and reliability.
- If your primary focus is small-scale experimentation requiring strict atmospheric control: A tube furnace is the ideal tool for precise thermal processing of samples under a specific gas or vacuum.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing of reactive or sensitive materials: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for eliminating atmospheric contamination and ensuring material integrity.
Ultimately, a laboratory furnace is more than just a source of heat; it is an instrument of transformation that enables innovation across science and industry.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Box Furnace | Tube Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | General-purpose heat treatment, bulk samples | Small-scale experiments, atmosphere control | High-purity processing, reactive materials |
| Key Advantage | Flexibility, easy loading | Precision, gas/vacuum flow | Ultimate purity, no contamination |
| Common Uses | Annealing, material processing | Synthesis, controlled experiments | Semiconductor, reactive metal processing |
Ready to transform your materials with precision? KINTEK offers advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?



















