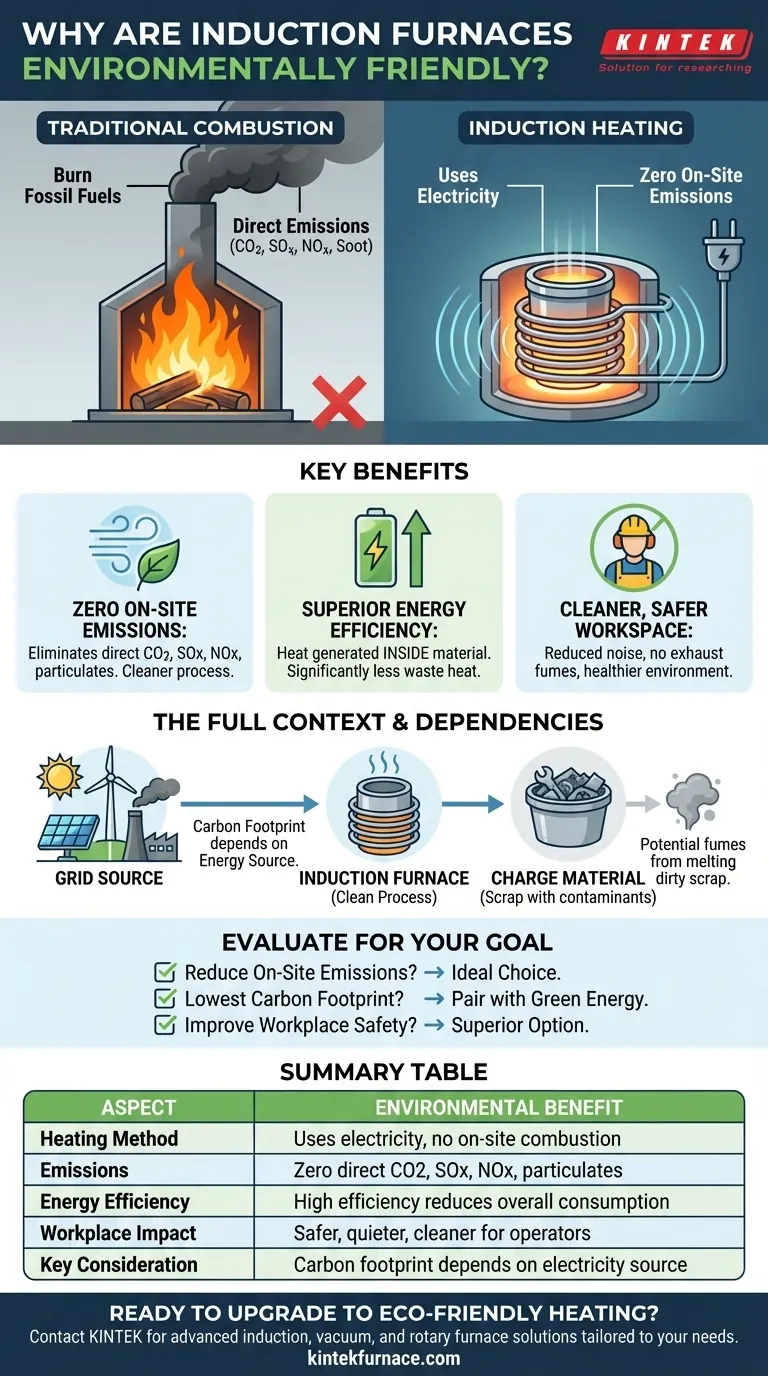
At their core, induction furnaces are considered environmentally friendly because they use electricity, not combustion, to generate heat. This fundamental difference means they do not burn fossil fuels on-site, which eliminates the direct release of greenhouse gases and other harmful pollutants associated with traditional fuel-fired smelting methods. This results in a cleaner process with a significantly smaller direct carbon footprint.
The environmental advantage of an induction furnace is not in what it adds, but in what it removes: the act of burning fuel. Its eco-friendliness comes from an inherently clean heating mechanism that eliminates direct emissions, maximizes energy efficiency, and creates a safer workplace.

The Core Principle: Heating Without Fire
The primary environmental benefit of induction heating is that it fundamentally changes how heat is created. It replaces the chemical process of combustion with a physical one.
Eliminating Direct Combustion
Traditional furnaces burn coal, gas, or oil to generate heat, which is then transferred to the metal. Induction furnaces work differently, using a powerful alternating magnetic field.
This magnetic field induces strong electrical currents directly within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates precise and rapid heat. There is no flame, no burning fuel, and no combustion.
Zero On-Site Emissions
Because there is no combustion, an induction furnace does not produce the typical byproducts of burning fossil fuels.
This means zero direct emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), soot, or other particulates from the heating process itself. This drastically improves local air quality and helps organizations meet stringent environmental regulations.
Beyond Emissions: The Wider Impact
The benefits extend beyond simply cleaning up the smokestack. The efficiency and nature of the process have secondary environmental and safety advantages.
Superior Energy Efficiency
In induction heating, the heat is generated inside the material being melted. This is a highly efficient energy transfer, with significantly less waste heat escaping into the surrounding environment compared to a traditional furnace.
Greater efficiency means less overall energy is consumed per ton of metal melted. This reduces the load on the electrical grid and, by extension, the upstream environmental impact of power generation.
A Cleaner, Safer Workspace
The "environment" also includes the immediate area where people work. By eliminating open flames and the deafening roar of fuel burners, induction furnaces operate with much lower noise levels.
The absence of combustion also means no exhaust gases or smoke are released into the workplace, creating a healthier and safer environment for operators.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Full Context
To make a fully informed decision, it's critical to look at the entire system, not just the furnace itself. No technology is without its dependencies.
The Grid is the Source
The most important consideration is the source of the electricity. An induction furnace is only as "green" as the grid that powers it.
If the electricity comes from a coal-fired power plant, the carbon emissions have simply been moved upstream, not eliminated. The furnace's true carbon footprint is directly tied to the carbon intensity of its energy source.
Comparison to Other Technologies
Induction is not the only technology that avoids combustion. Vacuum furnaces, for example, also use electricity in an oxygen-free environment and produce no direct emissions.
Other technologies, like modern rotary furnaces, may still use fuel but incorporate advanced emissions control systems to capture pollutants after they are created. The key distinction is that induction technology avoids creating these emissions at the source.
Contaminants from the Charge Material
The furnace itself is clean, but the material being melted may not be. Melting scrap metal that contains plastics, oils, or other coatings can still release fumes and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when heated. These emissions originate from the charge material, not the furnace's heating process.
How to Evaluate Induction Furnaces for Your Goal
Choosing the right heating technology requires aligning its characteristics with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is reducing direct, on-site emissions: Induction furnaces are an ideal choice, as they eliminate local combustion and its associated pollutants entirely.
- If your primary focus is achieving the lowest possible carbon footprint: You must pair an induction furnace with a certifiably green electricity source, such as solar, wind, or nuclear power.
- If your primary focus is improving workplace health and safety: The absence of flames, loud combustion noise, and toxic exhaust fumes makes induction technology a superior option.
By understanding both the inherent advantages and the systemic dependencies of induction heating, you can make a truly informed and sustainable decision for your operations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Uses electricity, no on-site combustion |
| Emissions | Zero direct CO2, SOx, NOx, and particulates |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency reduces overall energy consumption |
| Workplace Impact | Safer, quieter, and cleaner for operators |
| Key Consideration | Carbon footprint depends on electricity source |
Ready to upgrade to eco-friendly heating? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including induction, vacuum, and rotary furnaces, tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your experimental and production goals. Contact us today to discuss how our sustainable technologies can enhance your operations and reduce your environmental impact!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















