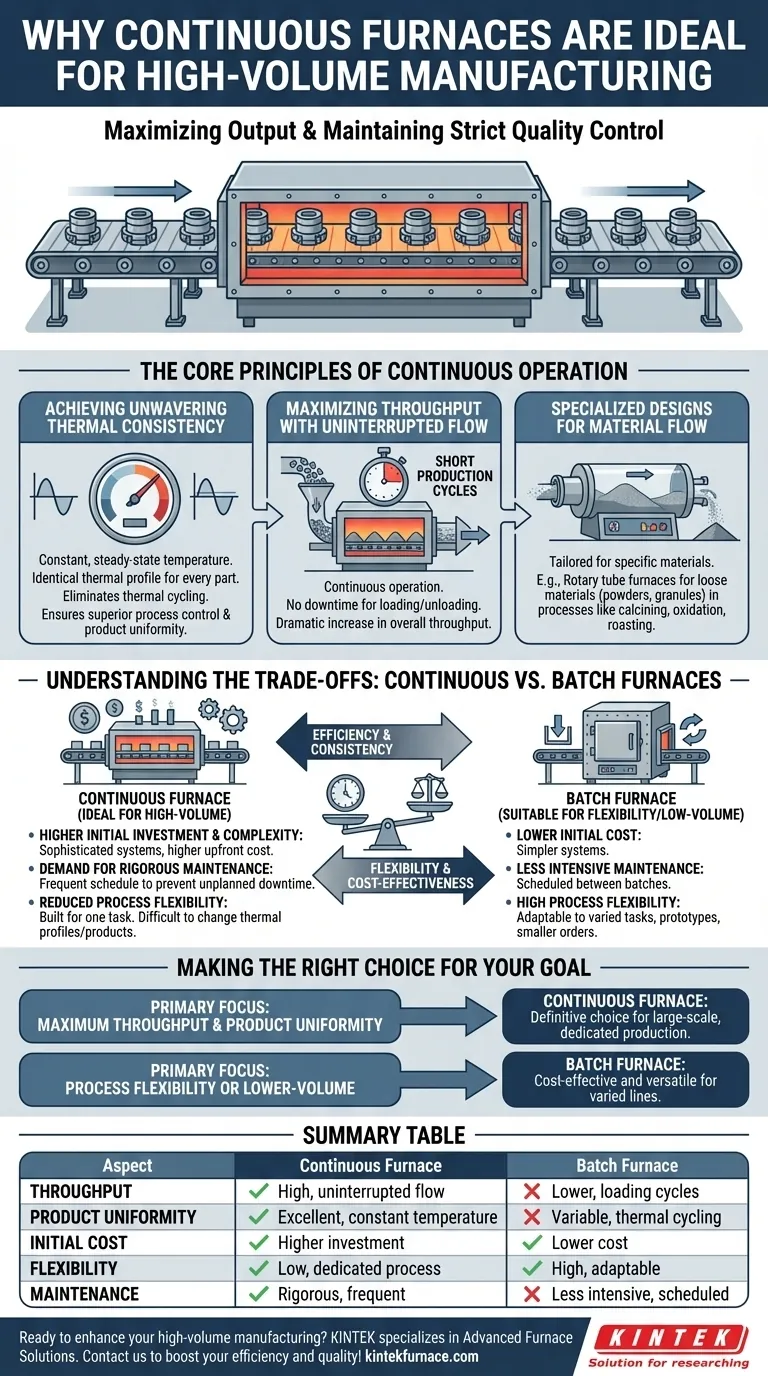
For any high-volume manufacturing operation, the goal is to maximize output while maintaining strict quality control. Continuous furnaces are ideal for this because they are engineered for uninterrupted material flow at a constant temperature, delivering both exceptional throughput and consistent, uniform processing that batch systems cannot match at scale.
The core advantage of a continuous furnace is not just its speed, but its ability to transform a thermal process into a predictable, assembly-line-like operation. This trades higher initial cost and lower flexibility for unparalleled efficiency and product consistency in large-scale production environments.
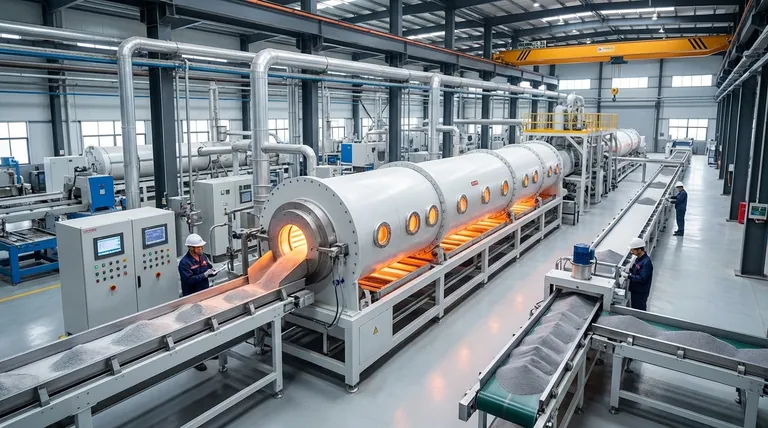

The Core Principles of Continuous Operation
To understand why continuous furnaces dominate high-volume applications, you must look at their fundamental design principles, which prioritize flow and stability over the stop-and-start nature of other systems.
Achieving Unwavering Thermal Consistency
A continuous furnace operates at a constant, steady-state temperature within its various heating zones. Materials move through these zones, ensuring every single part is exposed to the exact same thermal profile.
This eliminates the thermal cycling—heating up and cooling down—inherent in batch furnaces. By removing this variable, you achieve superior process control and product uniformity, which is critical for maintaining quality across millions of units.
Maximizing Throughput with Uninterrupted Flow
The defining feature is continuous operation. Material is constantly fed into one end of the furnace and emerges processed from the other, creating a seamless and predictable production line.
This design results in very short production cycles for individual parts and eliminates the significant downtime associated with loading, heating, cooling, and unloading an entire batch. The result is a dramatic increase in overall throughput.
Specialized Designs for Material Flow
Continuous furnaces are not a one-size-fits-all solution; they are often designed for specific material types and processes.
For example, rotary tube furnaces are built for the continuous processing of loose materials like powders or granules. They are ideal for applications such as calcining, oxidation, and roasting that depend on an uninterrupted flow of material for efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Continuous vs. Batch Furnaces
While ideal for high volume, the continuous model introduces specific constraints and costs that make it unsuitable for all manufacturing scenarios. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to making an informed investment.
Higher Initial Investment and Complexity
Continuous furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to install than their batch counterparts. The sophisticated conveyor or transport systems and advanced control mechanisms required for steady-state operation contribute to a much higher upfront capital cost.
The Demand for Rigorous Maintenance
Because a continuous furnace is designed for non-stop operation, any unplanned downtime can halt the entire production line, leading to major losses.
This necessitates a frequent and rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure optimal performance and prevent failures. These ongoing maintenance costs are a critical part of the total cost of ownership.
Reduced Process Flexibility
The greatest strength of a continuous furnace—its dedication to a single, optimized process—is also its primary weakness. These systems are highly inflexible.
It is difficult and time-consuming to change the thermal profile or switch to a different product. They are built for one task, done millions of times, making them a poor fit for high-mix, low-volume production environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between a continuous and a batch furnace is a strategic one that hinges on your specific production needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput and product uniformity: A continuous furnace is the definitive choice for large-scale, dedicated production where consistency is paramount.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility or lower-volume production: A batch furnace provides a more cost-effective and versatile solution for handling varied product lines, prototypes, or smaller orders.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental trade-off between dedicated scale and operational flexibility is what empowers you to align your capital investment with your long-term production strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Continuous Furnace | Batch Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | High, with uninterrupted flow | Lower, due to loading/unloading cycles |
| Product Uniformity | Excellent, constant temperature zones | Variable, thermal cycling effects |
| Initial Cost | Higher investment | Lower cost |
| Flexibility | Low, dedicated to one process | High, adaptable to varied tasks |
| Maintenance | Rigorous, frequent to prevent downtime | Less intensive, scheduled between batches |
Ready to enhance your high-volume manufacturing with reliable thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in advanced furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces and more, backed by deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can boost your efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits



















