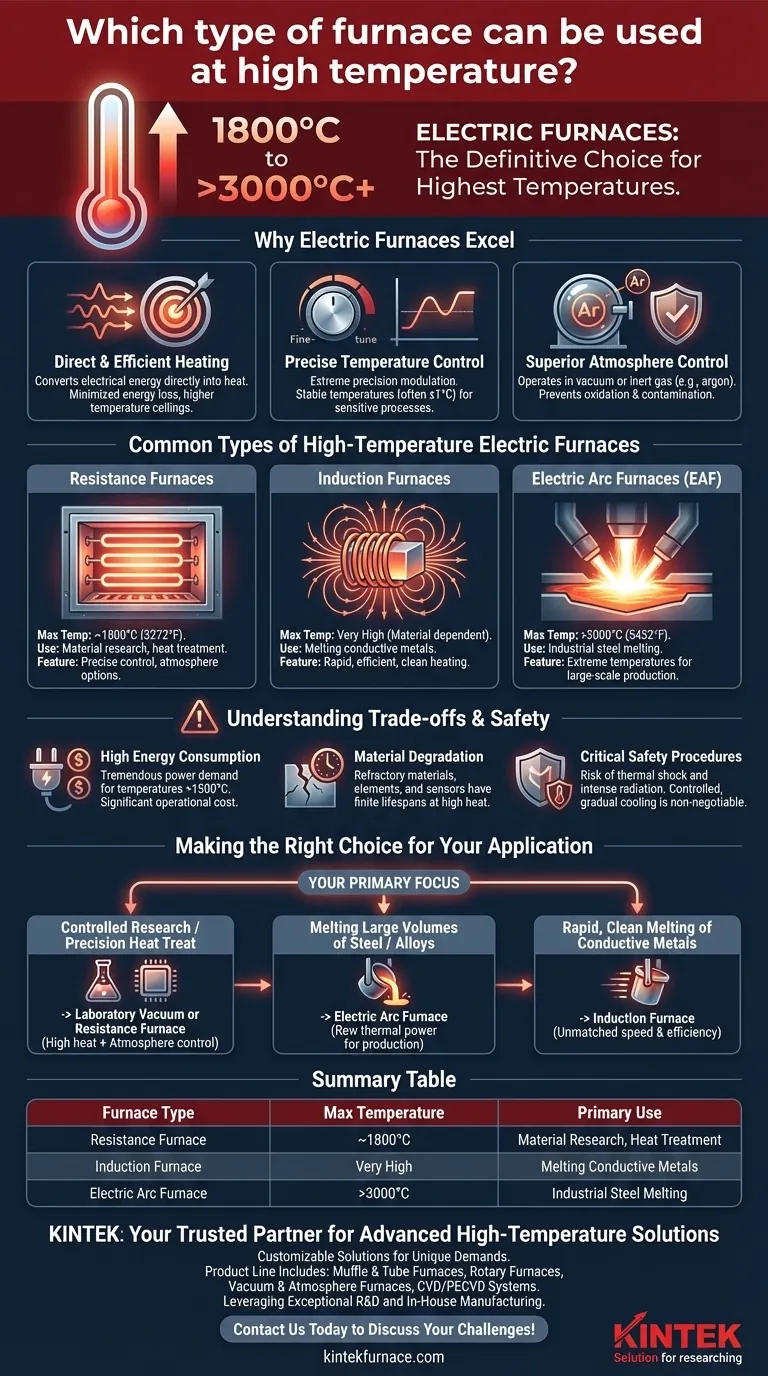
For achieving the highest possible temperatures, an electric furnace is the definitive choice. While combustion-based furnaces are common, they cannot match the extreme heat generated by electrical methods, which can range from 1800°C to over 3000°C depending on the specific design and application.
While the simple answer is "electric furnace," the critical decision lies in choosing the right type of electric furnace. Your choice will depend on your required temperature, the need for atmospheric control, and the material you are working with.
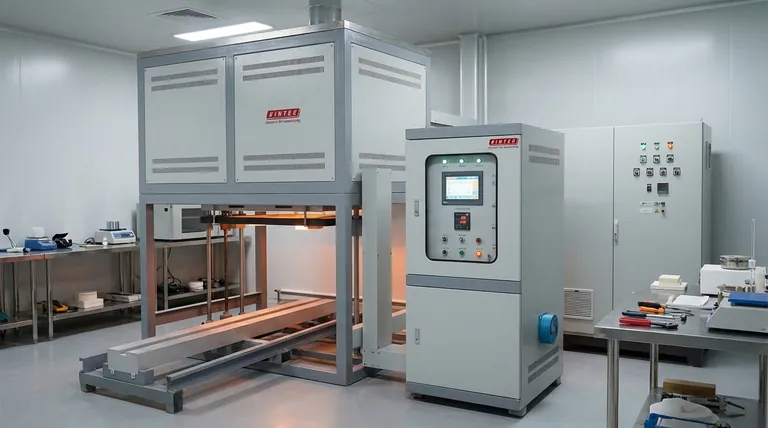

Why Electric Furnaces Excel at High Temperatures
Electric furnaces are not limited by the thermodynamics of fuel combustion. Instead, they convert electrical energy directly into heat, allowing for greater control and higher temperature ceilings.
Direct and Efficient Heating
Electric heating methods—such as resistance, induction, or arc—are incredibly direct. The heat is generated precisely where it is needed, minimizing energy loss to the surrounding environment and enabling the system to reach temperatures impossible for fossil fuel flames.
Precise Temperature Control
Electrical power can be modulated with extreme precision. This allows laboratory and industrial furnaces to maintain a stable temperature, often within a single degree of the setpoint, which is critical for sensitive material processing and research.
Superior Atmosphere Control
Unlike combustion furnaces that produce exhaust gases like CO2 and water vapor, electric furnaces can operate with a controlled atmosphere. They can create a near-perfect vacuum or be filled with an inert gas (like argon), preventing oxidation and contamination of materials at extreme temperatures.
Common Types of High-Temperature Electric Furnaces
The term "electric furnace" covers several distinct technologies, each suited for different temperature ranges and tasks.
Resistance Furnaces
These are common in laboratories and for heat-treating applications. They use heating elements made from materials like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide that glow hot when electricity passes through them. They reliably operate at temperatures up to approximately 1800°C (3272°F).
Induction Furnaces
An induction furnace uses powerful electromagnets to induce an electric current directly within the material being heated (which must be electrically conductive). This process is extremely fast and efficient, used for melting metals and for high-purity material synthesis.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
This is the technology used to achieve the highest temperatures. An EAF creates a massive electric arc—essentially a continuous lightning bolt—between graphite electrodes and the target material. The immense energy of the arc can reach temperatures above 3000°C (5432°F) and is primarily used for melting scrap steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety
Operating at extreme temperatures introduces significant challenges and requires strict protocols.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures above 1500°C demands a tremendous amount of electrical power. The operational costs, particularly for large arc or induction furnaces, are a primary consideration.
Material Degradation
The furnace itself must be constructed from advanced refractory materials to withstand the internal heat. Heating elements, thermocouples, and insulation all have finite lifespans and degrade more quickly at higher operational temperatures.
Critical Safety Procedures
High-temperature furnaces are inherently dangerous. Thermal shock can shatter components if the furnace is cooled or heated too quickly. Opening a furnace door at high temperatures (e.g., above 600°C) can cause catastrophic damage and expose operators to intense thermal radiation. A controlled, gradual cooling cycle is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, you must look beyond the maximum temperature and consider the process requirements.
- If your primary focus is controlled material research or precision heat treatment: A laboratory vacuum or resistance furnace offers the vital combination of high heat and atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is melting large volumes of steel or other high-melting-point alloys: An electric arc furnace provides the raw thermal power needed for industrial-scale production.
- If your primary focus is rapid, clean melting of conductive metals: An induction furnace offers unmatched speed and efficiency for foundry and metallurgical applications.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's heating technology and environmental controls to your specific material and process is the key to successful high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Max Temperature | Primary Use | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance Furnace | Up to ~1800°C | Material research, heat treatment | Precise temperature control, atmosphere control |
| Induction Furnace | Very High (Material dependent) | Melting conductive metals | Rapid, efficient, clean heating |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | >3000°C | Industrial steel melting | Extreme temperatures for large-scale production |
Ready to Find Your Perfect High-Temperature Solution?
KINTEK is your trusted partner for advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. We understand that every application has unique demands for temperature, atmosphere, and precision.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with a comprehensive product line, including:
- Muffle & Tube Furnaces for controlled atmosphere applications
- Rotary Furnaces for continuous processing
- Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces for contamination-free environments
- CVD/PECVD Systems for advanced material synthesis
Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements, whether you need precise temperature stability or extreme heat for industrial melting.
Contact us today to discuss your high-temperature challenges and let our experts help you select or customize the ideal furnace for your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















