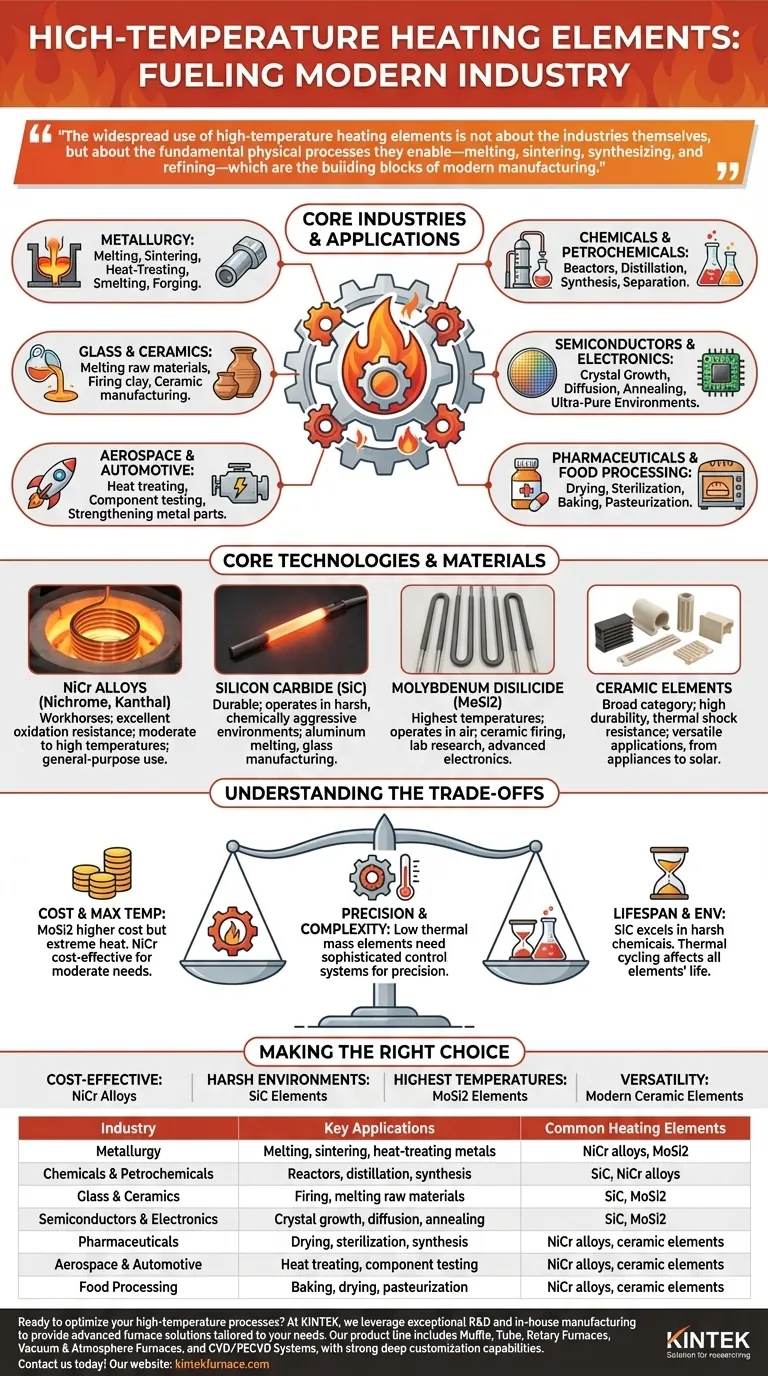
At their core, high-temperature heating elements are indispensable tools across a vast range of sectors, including chemical and petrochemical processing, metallurgy, glass and ceramics manufacturing, and the production of semiconductors and electronics. These components are fundamental to any industrial process that requires precise and intense heat, from melting metals and firing ceramics to synthesizing pharmaceuticals and processing microchips.
The widespread use of high-temperature heating elements is not about the industries themselves, but about the fundamental physical processes they enable—melting, sintering, synthesizing, and refining—which are the building blocks of modern manufacturing.

The Role of Heat in Modern Industry
High-temperature heating is a cornerstone of industrial capability. It allows for the transformation of raw materials into finished goods by altering their physical or chemical states. Different industries harness this capability for specific, critical applications.
Material Transformation and Synthesis
Many industries are built on their ability to create or reshape materials. This requires enormous energy delivered with precision.
- Metallurgy: Furnaces use elements to melt, smelt, and heat-treat metals, achieving specific alloys and structural properties through processes like sintering and forging.
- Glass & Ceramics: Manufacturing relies on heating elements to melt raw materials into molten glass and to fire clay and other compounds into durable ceramic parts, from tableware to advanced technical components.
- Chemicals & Petrochemicals: Reactors and distillation columns are heated to facilitate chemical reactions, separate compounds, and produce everything from plastics to fertilizers.
Precision Manufacturing and Processing
In high-technology fields, heat is not a blunt instrument but a tool for microscopic refinement.
- Semiconductors & Electronics: High-temperature tube furnaces create the ultra-pure environments needed for growing crystals, diffusing dopants into silicon wafers, and annealing components.
- Aerospace & Automotive: Heat treating is critical for strengthening metal parts, and ceramic elements are used in testing and manufacturing components that must withstand extreme operational temperatures.
Refinement and Production
Heat is also essential for purification, drying, and sterilization processes that ensure product quality and safety.
- Pharmaceuticals: Precise heating is used for drying powders, sterilizing equipment, and enabling specific chemical syntheses in drug manufacturing.
- Food Processing: Industrial ovens and dryers rely on consistent heating for baking, drying, and pasteurization, ensuring product safety and longevity.
A Look at the Core Technologies
The ability to generate and control intense heat comes from specialized materials designed to withstand extreme conditions without degrading. The choice of material dictates the element's performance, lifespan, and application.
Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) Alloys
Often known by trade names like Nichrome or Kanthal, these are the workhorses of industrial heating. They offer excellent resistance to oxidation and are reliable for a wide range of furnace and oven applications at moderate to high temperatures.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
SiC elements are valued for their durability and ability to operate in harsh, chemically aggressive environments. They are frequently used in aluminum melting, glass manufacturing, and semiconductor processing where reliability is paramount.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2)
When the highest temperatures are required, MoSi2 elements are the standard. They can operate in air at temperatures far exceeding those of NiCr or SiC, making them essential for ceramic firing, laboratory research, and processing advanced electronic components.
Ceramic Elements
This broad category includes various materials that offer high durability, excellent thermal shock resistance, and versatility. They are used in everything from home appliances to complex industrial systems like solar thermal collectors, where they improve efficiency and reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element is a technical decision that involves balancing performance with operational realities. No single solution is perfect for every application.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
The primary trade-off is often cost. Materials capable of reaching the highest temperatures, like molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), are significantly more expensive than common nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloys. Over-specifying an element for an application that doesn't require extreme heat results in unnecessary capital expense.
Lifespan vs. Operating Environment
An element's longevity is directly tied to its operating conditions. Silicon carbide (SiC) elements excel in harsh chemical environments, while other materials might degrade quickly. Frequent thermal cycling (rapid heating and cooling) can also induce stress and shorten the life of any element.
Precision vs. System Complexity
Achieving precise temperature control requires more than just a good heating element. It demands a sophisticated control system with accurate sensors and power controllers. While elements with low thermal mass heat and cool rapidly for tight control, they necessitate a responsive system to prevent temperature overshoots.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal heating element is the one that meets the specific thermal and environmental demands of your application without exceeding your budget or operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose heating: NiCr alloys provide the best balance of performance and value for most standard furnaces and ovens.
- If your primary focus is durability in a harsh chemical atmosphere: SiC elements are engineered to withstand corrosive environments and offer exceptional service life.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures for advanced materials: MoSi2 elements are the definitive choice for applications like ceramic sintering and laboratory research.
- If your primary focus is versatility and reliable performance across various applications: Modern ceramic elements offer a robust solution for everything from metal forging to renewable energy systems.
Ultimately, understanding these core technologies empowers you to select the right tool for the job, turning heat into a productive and predictable industrial asset.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Common Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Melting, sintering, heat-treating metals | NiCr alloys, MoSi2 |
| Chemicals & Petrochemicals | Reactors, distillation, synthesis | SiC, NiCr alloys |
| Glass & Ceramics | Firing, melting raw materials | SiC, MoSi2 |
| Semiconductors & Electronics | Crystal growth, diffusion, annealing | SiC, MoSi2 |
| Pharmaceuticals | Drying, sterilization, synthesis | NiCr alloys, ceramic elements |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Heat treating, component testing | NiCr alloys, ceramic elements |
| Food Processing | Baking, drying, pasteurization | NiCr alloys, ceramic elements |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in metallurgy, chemicals, electronics, or other industries, we can enhance your efficiency and precision. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















