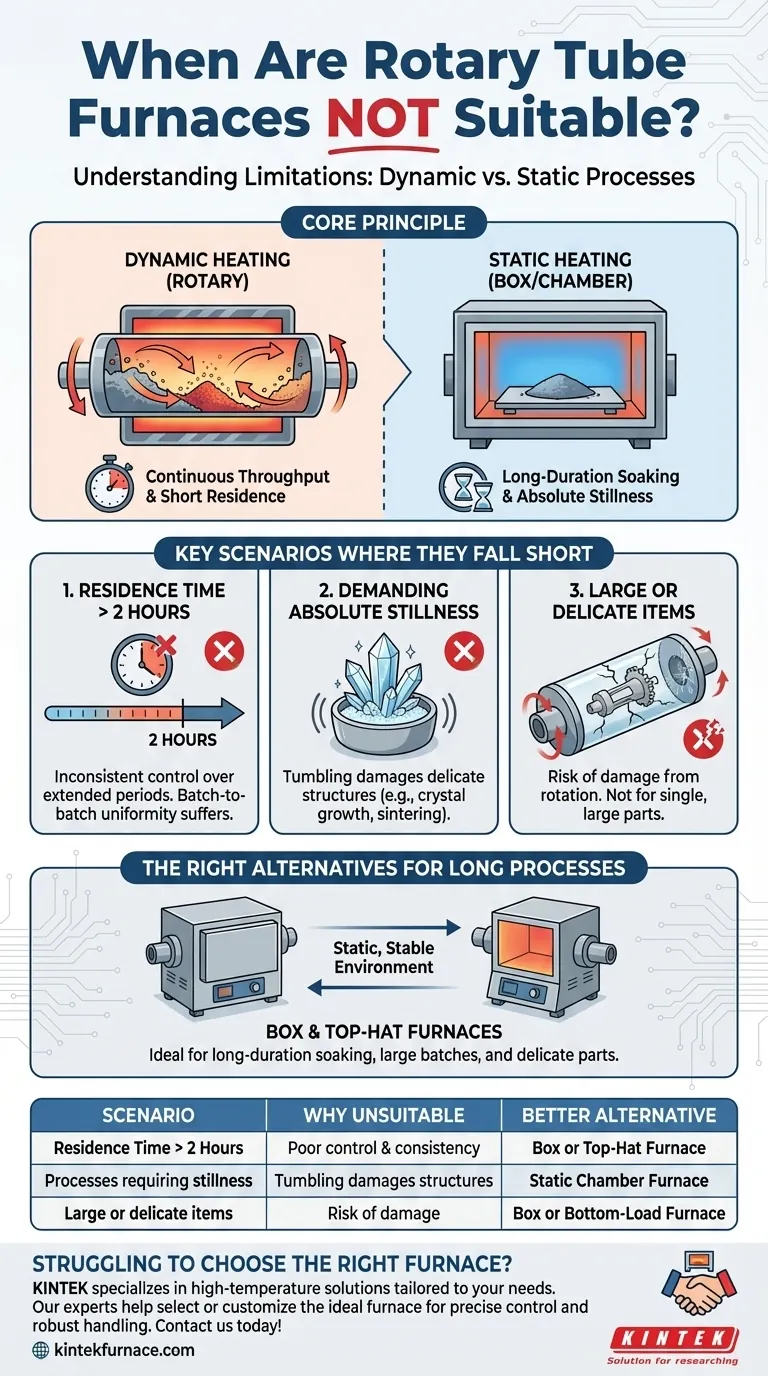
In short, a rotary tube furnace is fundamentally unsuitable for any process that requires a material residence time longer than two hours. Their design, which excels at continuous and uniform processing of powders, presents significant challenges in precisely controlling the material's environment over extended durations.
A rotary tube furnace is engineered for dynamic, continuous throughput. It is the wrong tool when your process requires a static, stable environment for a single batch over a very long period, a principle that dictates its primary limitations.
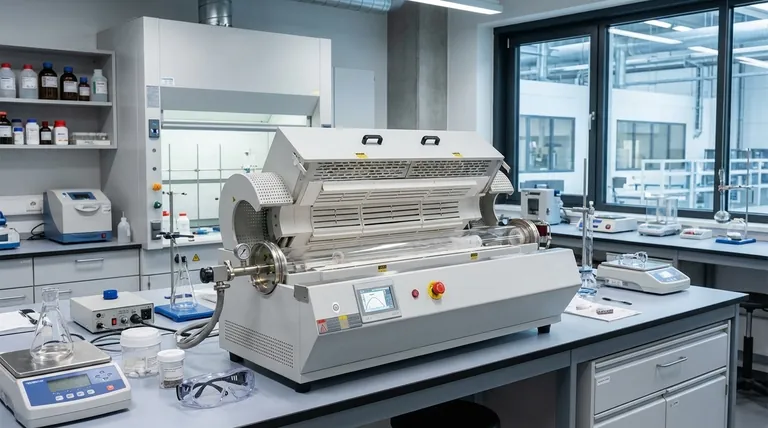

The Core Principle: Dynamic vs. Static Heating
To understand when a rotary tube furnace is the wrong choice, you must first grasp its core operational principle. It is a tool for dynamic material processing.
Engineered for Movement and Mixing
A rotary tube furnace continuously tumbles powders or granular materials as they pass through a heated tube. This rotation is its greatest strength, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat and atmosphere, which promotes exceptional uniformity.
Think of it like a highly sophisticated, heated cement mixer. It is designed to keep the material in motion.
Optimized for Throughput, Not Static Soaking
This design is ideal for continuous or semi-continuous production where a consistent flow of material needs to be processed quickly and uniformly. The goal is throughput—processing a quantity of material over time.
Key Scenarios Where Rotary Tube Furnaces Fall Short
The very design that makes these furnaces excellent for throughput creates specific limitations. They are unsuitable when the process requirements conflict with their dynamic nature.
Processes Requiring Extended Residence Times
The most significant limitation, as noted in process engineering guidelines, is a residence time exceeding two hours.
Controlling the precise condition and location of a material for longer than this becomes impractical in a moving tube. Batch-to-batch consistency suffers, and ensuring every particle has the exact same thermal history becomes a significant challenge.
Applications Demanding Absolute Stillness
Any process where the material must remain perfectly still is incompatible with a rotary furnace. Examples include the growth of single crystals, certain types of delicate sintering, or the bonding of layered materials.
The constant tumbling motion would destroy the desired structure, making a static furnace (like a box or chamber furnace) the only viable option.
Processing Large, Delicate, or Single-Piece Items
Rotary tube furnaces are designed for powders, granules, and small particulates. They are entirely unsuitable for processing a single large component or a delicate item that could be damaged by the tumbling action.
Loading and unloading a single, specific part into a rotating tube is impractical and risks damaging both the part and the furnace tube itself.
Understanding the Alternatives for Long Processes
When a rotary tube furnace is unsuitable due to long residence times, other furnace types provide the necessary static environment.
For Long, Static Batches: Box and Top-Hat Furnaces
A box (or chamber) furnace is the most common alternative. It provides a stable, static chamber where a batch of material can be placed and "soaked" at a specific temperature for many hours or even days.
Top-hat and bottom-load furnaces operate on a similar principle, allowing for easy loading of large or heavy loads that can then be heated in a static state for extended durations. These are the go-to solutions when residence time, not throughput, is the critical process variable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct thermal processing equipment is a critical decision. Base your choice on the fundamental requirements of your material and process goals.
- If your primary focus is continuous, uniform processing of powders or granules with short residence times: A rotary tube furnace is an excellent, highly efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is long-duration "soaking" (over two hours) for a single batch: A static box, top-hat, or bottom-load furnace is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is processing a single large part or a delicate assembly: You must use a static chamber furnace to avoid movement and potential damage.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's core design principle with your process objective is the key to achieving a successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Why Unsuitable | Better Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Residence time > 2 hours | Poor control and consistency in dynamic environment | Box or top-hat furnace |
| Processes requiring stillness | Tumbling damages structures (e.g., crystal growth) | Static chamber furnace |
| Large or delicate single items | Risk of damage from rotation | Box or bottom-load furnace |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you need precise control for long-duration processes or robust handling of delicate materials, our experts can help you select or customize the ideal furnace. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















