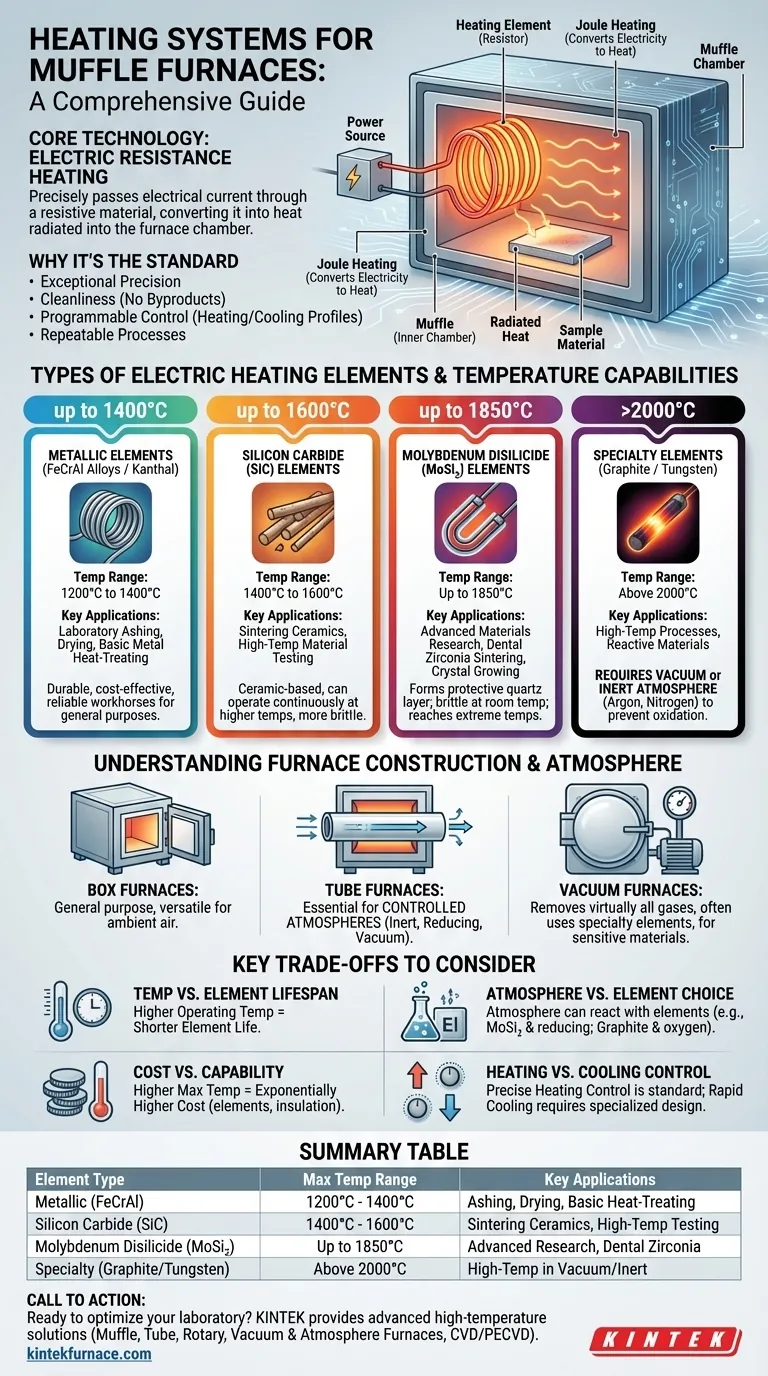
At its core, a modern muffle furnace operates using electric resistance heating. While different brands and furnace configurations exist, the fundamental system involves passing an electric current through a specialized heating element. The material of this element is what truly defines the furnace's capabilities, dictating its maximum temperature, lifespan, and suitability for different atmospheric conditions.
The critical distinction is not between furnace brands, but between the type of electric heating element used and the overall furnace construction. This combination determines the achievable temperature, the ability to control the atmosphere, and ultimately, whether the furnace is right for your specific task.

The Core Technology: Electric Resistance Heating
How It Works
Electric resistance heating is a straightforward and highly effective principle. An electrical current is passed through a material that is designed to resist the flow of electricity. This resistance converts electrical energy directly into heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
This heat is then radiated into the furnace's insulated chamber, providing the high temperatures needed for processes like ashing, sintering, or heat-treating materials. The muffle, or inner chamber, isolates the material being heated from direct contact with the heating elements, ensuring purity and preventing contamination.
Why It's the Standard
This method is the industry standard for muffle furnaces due to its exceptional precision and cleanliness. Unlike combustion-based heating, there are no byproducts that can contaminate the sample. It allows for fully programmable control over heating rates, hold times, and cooling profiles, which is essential for repeatable scientific and manufacturing processes.
Types of Electric Heating Elements
The "heating system" is truly defined by the material used for the heating element. Each material has a distinct temperature range and set of properties.
Metallic Elements (FeCrAl Alloys)
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum alloys, often known by the brand name Kanthal, are the workhorses of general-purpose furnaces. They are durable, relatively inexpensive, and perform reliably.
These elements are ideal for applications running up to approximately 1200°C to 1400°C, making them perfect for most laboratory ashing, drying, and basic metal heat-treating tasks.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements
For processes requiring higher temperatures, Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are a common choice. These ceramic-based elements are more brittle than their metallic counterparts but can operate continuously at higher temperatures.
SiC elements are typically used for applications in the 1400°C to 1600°C range, such as sintering technical ceramics or high-temperature material testing.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) Elements
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements represent the next step up in temperature capability. When heated, they form a protective layer of quartz glass (silica) on their surface, allowing them to withstand extreme conditions.
These elements enable furnaces to reach temperatures up to 1850°C. They are brittle at room temperature and are used for advanced materials research, dental zirconia sintering, and growing crystals.
Specialty Elements (Graphite or Tungsten)
For the most extreme temperature requirements, furnaces may use elements made of graphite or refractory metals like tungsten. These materials can achieve temperatures well above 2000°C.
However, these elements will rapidly oxidize and burn up if heated in the presence of oxygen. They absolutely require the furnace to operate under a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen).
Understanding Furnace Construction
The physical design of the furnace is just as important as its heating element, as it determines how heat is applied and what atmospheres can be used.
Box Furnaces
This is the most common design, featuring a front-loading door and a rectangular chamber. It is a versatile, general-purpose furnace suitable for a wide range of applications where heating in ambient air is acceptable.
Tube Furnaces
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical tube (often made of ceramic or quartz) that passes through the heated chamber. This design is essential for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere. Gases can be flowed through the tube to create a specific environment (e.g., inert or reducing), or it can be evacuated to create a vacuum.
Vacuum Furnaces
These are highly specialized systems designed to remove virtually all air and other gases from the chamber during heating. This is critical for preventing oxidation or reactions when working with highly reactive or sensitive materials at high temperatures. They almost always use specialty elements like graphite or tungsten.
Key Trade-offs to Consider
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance, longevity, and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making a sound investment.
Temperature vs. Element Lifespan
A heating element's lifespan is inversely related to its operating temperature. Consistently running a furnace at its absolute maximum rated temperature will significantly shorten the life of the heating elements, leading to more frequent and costly replacements.
Atmosphere vs. Element Choice
The atmosphere inside the furnace can react with the heating elements. For example, some reducing atmospheres can damage MoSi₂ elements, while graphite elements are entirely dependent on a vacuum or inert atmosphere to avoid being consumed.
Cost vs. Capability
The cost of a muffle furnace increases exponentially with its maximum temperature capability. A furnace rated for 1800°C is significantly more expensive than one rated for 1200°C due to the cost of the MoSi₂ elements and the higher-grade insulation required.
Heating vs. Cooling Control
Standard muffle furnaces offer precise control over the heating rate. However, cooling is typically a passive or fan-assisted process and is much less controlled. Achieving specific, rapid cooling rates requires specialized and more expensive furnace designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is general laboratory work (below 1200°C): A standard box furnace with durable and cost-effective metallic (FeCrAl) elements is your most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is sintering ceramics or materials testing (up to 1700°C): You will need a furnace equipped with Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or working with reactive materials: A tube or vacuum furnace is non-negotiable, with the element choice (e.g., graphite) dictated by your temperature and atmospheric needs.
By matching the heating element and furnace construction to your specific application, you ensure efficient, reliable, and cost-effective results.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Max Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic (FeCrAl) | 1200°C - 1400°C | Laboratory ashing, drying, basic heat-treating |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1400°C - 1600°C | Sintering ceramics, high-temperature testing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to 1850°C | Advanced materials research, dental zirconia sintering |
| Specialty (Graphite/Tungsten) | Above 2000°C | High-temperature processes in vacuum/inert atmospheres |
Ready to optimize your laboratory with the perfect high-temperature furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















