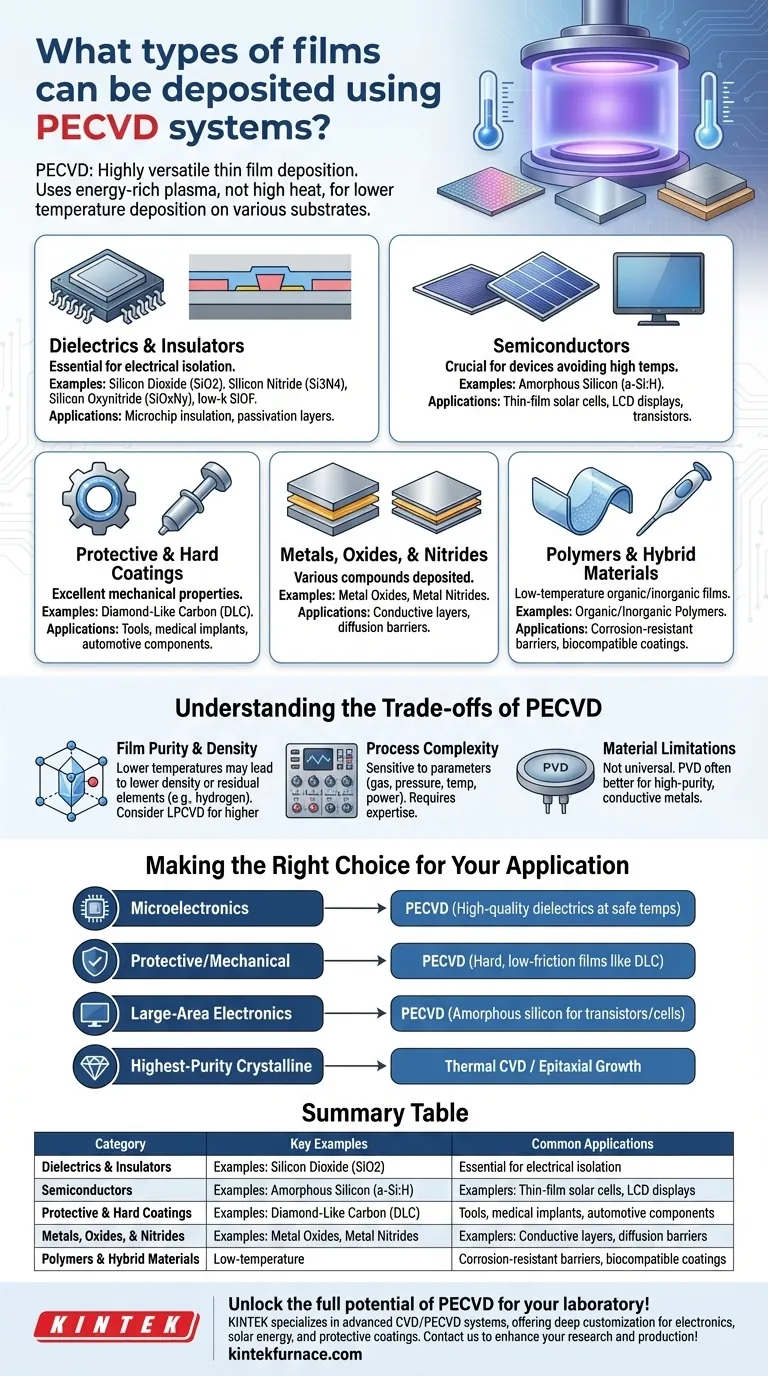
In short, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a highly versatile technology capable of depositing a vast range of thin films. These include critical materials for the electronics industry like dielectrics (silicon dioxide, silicon nitride) and semiconductors (amorphous silicon), as well as advanced materials like hard protective coatings (Diamond-Like Carbon), polymers, and various metal oxides and nitrides.
The core strength of PECVD is its use of an energy-rich plasma rather than high heat to drive chemical reactions. This fundamental difference allows for film deposition at much lower temperatures, enabling a wider variety of materials to be deposited on a broader range of substrates than is possible with traditional thermal methods.

The Core Categories of PECVD Films
PECVD's versatility allows for the creation of films with widely different properties, which can be grouped into several key categories. Each serves a distinct industrial or research purpose.
Dielectrics and Insulators
This is the most common application for PECVD. These films are essential for electrically isolating conductive layers in microchips and other electronic devices.
Key examples include silicon dioxide (SiO2), used for insulation between metal layers, and silicon nitride (Si3N4), used as a passivation layer to protect devices from moisture and contaminants. Variations like silicon oxynitride (SiOxNy) and low-k dielectrics such as SiOF are also common.
Semiconductors
PECVD is crucial for depositing semiconductor materials, especially when high temperatures must be avoided.
The most prominent example is amorphous silicon (a-Si:H), which is fundamental to the manufacturing of thin-film solar cells and the transistors used in large-area displays (like LCD screens). In-situ doping during the deposition process is also possible.
Protective and Hard Coatings
PECVD can create films with excellent mechanical properties, making them ideal for protective applications.
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a standout material in this category. It provides an extremely hard, low-friction, and wear-resistant surface for tools, medical implants, and automotive components.
Metals, Oxides, and Nitrides
While other methods are often preferred for pure metals, PECVD is effective at depositing a variety of metal compounds.
This includes various metal oxides and metal nitrides, which have applications ranging from conductive transparent layers to diffusion barriers in integrated circuits.
Polymers and Hybrid Materials
The low-temperature nature of PECVD also allows for the deposition of organic and inorganic polymer films.
These specialized materials are used in niche applications such as creating highly corrosion-resistant barriers for food packaging or biocompatible coatings for medical implants.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PECVD
While incredibly flexible, PECVD is not the optimal choice for every situation. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Film Purity and Density
Because PECVD operates at lower temperatures, the resulting films can sometimes have lower density or incorporate residual elements from the precursor gases (like hydrogen).
For applications demanding the highest purity or crystalline quality, a higher-temperature process like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) may be a better choice, assuming the substrate can tolerate the heat.
Process Complexity
The quality and properties of a PECVD film are extremely sensitive to a wide range of process parameters, including gas composition, pressure, temperature, and plasma power.
Developing a new deposition "recipe" requires significant expertise and process control. It is not a "plug-and-play" technology; it is a highly tunable and therefore complex process.
Material Limitations
While versatile, PECVD is not the universal solution. For depositing high-purity, highly conductive metal films, physical vapor deposition (PVD) techniques like sputtering or evaporation are often more efficient and effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right deposition technology depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is modern microelectronics: PECVD is the industry standard for depositing high-quality dielectric insulators (SiO2, Si3N4) at temperatures that will not damage previously fabricated components.
- If your primary focus is protective or mechanical coatings: PECVD is an excellent choice for creating hard, durable, and low-friction films like Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) on a wide variety of substrates.
- If your primary focus is large-area electronics or solar cells: PECVD is the essential technology for depositing the amorphous silicon films that form the backbone of thin-film transistors and photovoltaic cells.
- If your primary focus is the highest-purity crystalline films: You should evaluate higher-temperature thermal CVD methods or epitaxial growth techniques, as the chemistry of PECVD can introduce impurities.
Ultimately, PECVD's strength lies in its low-temperature versatility, making it an indispensable tool for fabricating a vast range of functional thin films across many industries.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Examples | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectrics and Insulators | Silicon Dioxide (SiO2), Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) | Microchip insulation, passivation layers |
| Semiconductors | Amorphous Silicon (a-Si:H) | Thin-film solar cells, LCD displays |
| Protective and Hard Coatings | Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Tools, medical implants, automotive parts |
| Metals, Oxides, and Nitrides | Metal Oxides, Metal Nitrides | Conductive layers, diffusion barriers |
| Polymers and Hybrid Materials | Organic/Inorganic Polymers | Corrosion-resistant barriers, biocompatible coatings |
Unlock the full potential of PECVD for your laboratory! KINTEK specializes in advanced CVD/PECVD systems, offering deep customization to meet your unique thin-film deposition needs. Whether you're in electronics, solar energy, or protective coatings, our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures reliable, high-performance solutions. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















