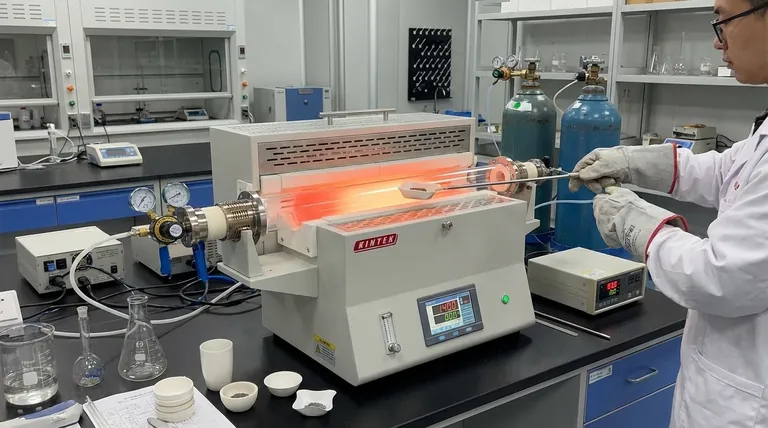
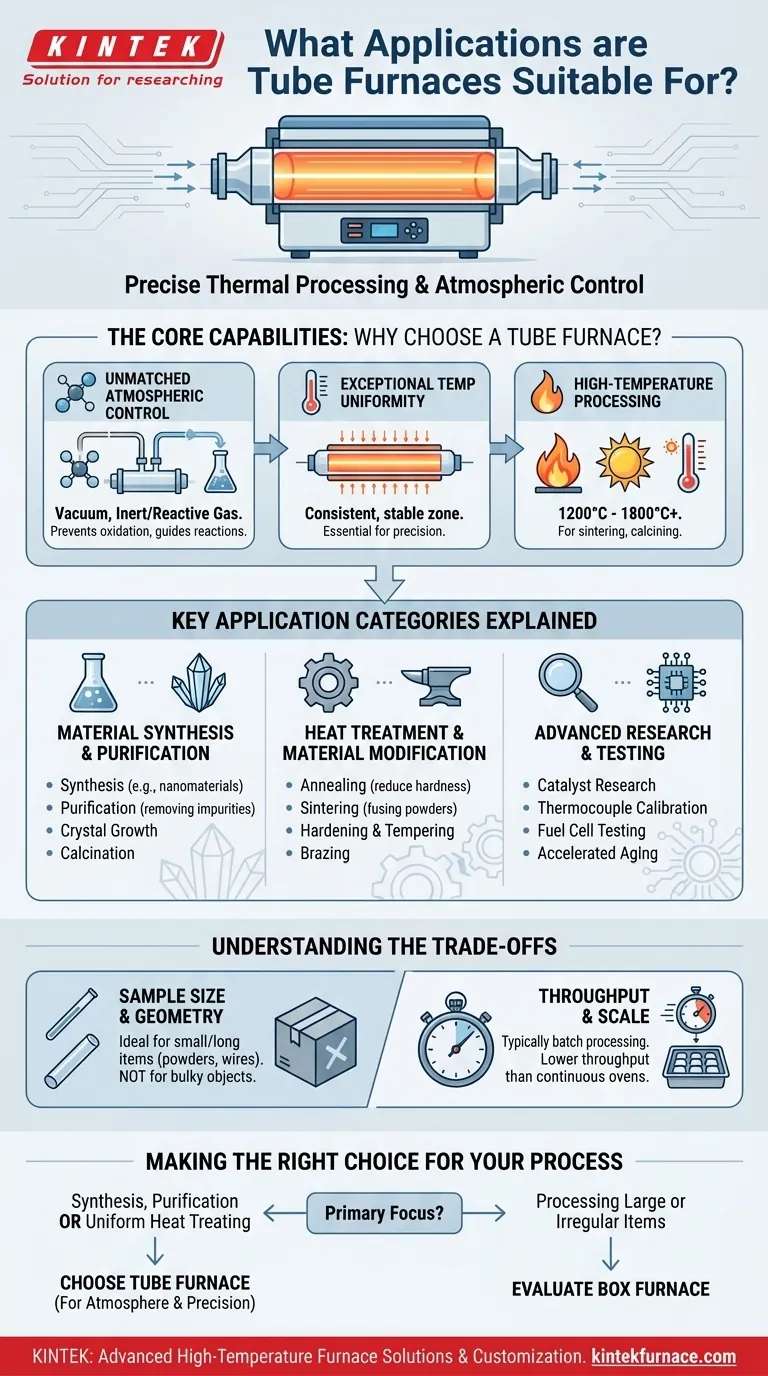
At their core, tube furnaces are highly versatile tools for precise thermal processing. They are indispensable in research and industry for a vast range of applications, including synthesizing new materials, purifying compounds, and altering the physical properties of samples through heat treatment. Their unique design makes them ideal for processes like annealing, sintering, and calcination, especially when a controlled atmosphere is required.
A tube furnace is the definitive choice when your process demands a combination of high-temperature uniformity and precise atmospheric control. While other furnaces can get hot, the tube furnace excels at managing the gaseous environment around the sample, whether it's a vacuum, an inert gas, or a reactive gas.

The Core Capabilities: Why Choose a Tube Furnace?
Understanding the fundamental strengths of a tube furnace reveals why it's so widely used across chemistry, materials science, and engineering. Its suitability stems from a few key design principles.
Unmatched Atmospheric Control
The defining feature of a tube furnace is the process tube, typically made of ceramic, quartz, or metal. This enclosed chamber is easy to seal.
This allows you to either pull a vacuum or introduce a continuous flow of a specific gas. This control is critical for preventing unwanted oxidation or enabling specific chemical reactions.
Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
The heating elements in a tube furnace are positioned cylindrically around the process tube. This arrangement creates a highly consistent and stable temperature zone along the central length of thetube.
This thermal uniformity is essential for processes like annealing or crystal growth, where even minor temperature fluctuations can compromise the final result.
High-Temperature Processing
Tube furnaces are engineered to reach very high temperatures, often exceeding 1200°C and sometimes reaching up to 1800°C or higher, depending on the model and heating elements.
This capability is necessary for energy-intensive processes like sintering metal powders, calcining ceramic materials, or conducting pyrolysis.
Key Application Categories Explained
The capabilities of a tube furnace translate into three broad categories of use, from fundamental research to industrial production.
Material Synthesis and Purification
This is a primary application in chemistry and materials science. The controlled environment is perfect for creating or cleaning materials.
Common uses include:
- Synthesis: Creating inorganic compounds, nanomaterials (like graphene), and polymer composites.
- Purification: Removing volatile impurities from a sample at high heat, often under a vacuum or an inert gas flow.
- Crystal Growth: Growing single, high-purity crystals from a melt or vapor phase, which demands stable, uniform temperatures.
- Calcination: Decomposing materials and removing volatile substances, such as converting minerals into their oxide forms.
Heat Treatment and Material Modification
These processes use heat to alter the microstructure and physical properties (like hardness or ductility) of a material without melting it.
Common uses include:
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling a material (like metal or glass) to reduce hardness and increase ductility.
- Sintering: Fusing particles of a powder together below its melting point to create a solid object. This is widely used in ceramics and powder metallurgy.
- Hardening & Tempering: A two-step process to increase the hardness and toughness of metals.
- Brazing: Joining two pieces of metal using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature, often done under a vacuum to ensure a clean bond.
Advanced Research and Testing
The precision of a tube furnace makes it an essential tool for repeatable experiments and quality control testing.
Common uses include:
- Catalyst Research: Testing the effectiveness and lifespan of catalysts by passing reactive gases over them at specific temperatures.
- Thermocouple Calibration: Verifying the accuracy of temperature sensors against a known, stable heat source.
- Fuel Cell Testing: Simulating the high-temperature operating conditions of components like solid oxide fuel cells.
- Accelerated Aging: Exposing samples to high temperatures to simulate the effects of long-term use and test material durability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, a tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating applications. Its primary limitation is a direct consequence of its core design.
Sample Size and Geometry
The diameter of the process tube inherently restricts the size and shape of the sample you can process.
Tube furnaces are ideal for powders, wafers, small components, wires, or thin strips that fit easily inside the tube. They are poorly suited for large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects. For those, a box or chamber furnace is a more practical choice.
Throughput and Scale
Most laboratory tube furnaces are designed for batch processing, where one sample or a small group of samples is processed at a time.
While some industrial models are designed for continuous feeding of wires or strips, they generally offer lower throughput than larger, specialized industrial ovens.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace is about matching its capabilities to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or purification: A tube furnace is the ideal tool due to its superior atmospheric control, which is critical for preventing contamination and guiding reactions.
- If your primary focus is heat treating for uniform properties: The exceptional temperature uniformity of a tube furnace makes it the superior choice for processes like annealing or sintering, ensuring consistent results.
- If your primary focus is processing large or irregularly shaped items: You should evaluate a box or chamber furnace, as the restrictive geometry of a tube furnace will be a significant bottleneck.
By aligning your need for atmospheric control and thermal precision with the furnace's design, you ensure a successful and repeatable outcome for your process.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Material Synthesis & Purification | Synthesis of nanomaterials, purification, crystal growth, calcination |
| Heat Treatment & Material Modification | Annealing, sintering, hardening, tempering, brazing |
| Advanced Research & Testing | Catalyst research, thermocouple calibration, fuel cell testing, accelerated aging |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're in materials science, chemistry, or engineering, we can help you achieve superior thermal processing results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment



















