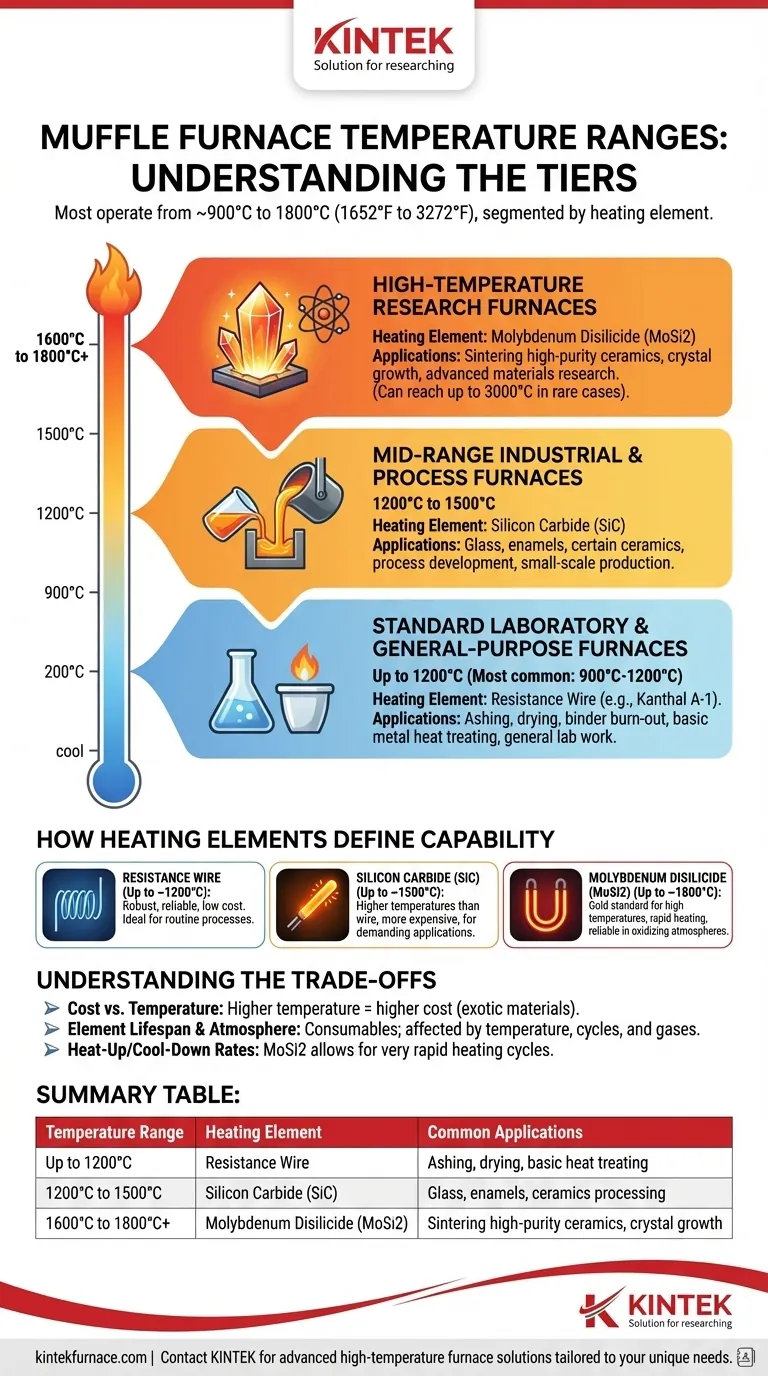
In short, most muffle furnaces operate within a broad temperature range of approximately 900°C to 1800°C (1652°F to 3272°F). The specific maximum temperature a furnace can achieve is not arbitrary; it is determined directly by the material used for its heating elements and its overall construction.
The critical takeaway is not the temperature range itself, but understanding that this range is segmented into distinct tiers. Each tier—standard, mid-range, and high-temperature—is defined by a different type of heating element, which dictates the furnace's capabilities, cost, and ideal applications.

Understanding the Tiers of Muffle Furnace Performance
A muffle furnace's temperature rating is the primary indicator of its intended use. These uses can be broken down into three main categories based on their operating temperature.
Standard Laboratory & General-Purpose Furnaces (Up to 1200°C)
This is the most common and widely used category of muffle furnace. They are the workhorses of general laboratories for applications like ashing, drying, binder burn-out, and basic metal heat treating.
These furnaces typically rely on metallic wire heating elements and represent the most cost-effective option for a huge range of routine thermal processes. The most frequently used range for these models is between 900°C and 1200°C.
Mid-Range Industrial & Process Furnaces (1200°C to 1500°C)
When processes require temperatures that exceed the limits of standard metallic elements, furnaces equipped with Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are used.
These models bridge the gap between standard lab work and high-performance material science. They are common in process development and small-scale production involving materials like glass, enamels, and certain ceramics.
High-Temperature Research Furnaces (1600°C to 1800°C+)
The highest tier of performance is reserved for furnaces using Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements. These are specialized instruments designed for advanced materials research and processing.
Applications include sintering high-purity technical ceramics like zirconia, firing dental ceramics, and growing crystals. While extremely rare, highly specialized models for niche industrial or research applications can potentially exceed this range, reaching up to 3000°C.
How Heating Elements Define Furnace Capability
The material of the heating element is the single most important factor determining a furnace's maximum temperature, lifespan, and cost. Understanding these materials is key to understanding furnace performance.
Resistance Wire Elements (Up to ~1200°C)
Standard furnaces almost universally use an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy (like Kanthal A-1). These wire elements are robust, reliable in air, and relatively inexpensive, making them ideal for the most common temperature range.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements (Up to ~1500°C)
Silicon Carbide is a ceramic material that can operate at significantly higher temperatures than metallic wire. Furnaces using SiC rods are more expensive but provide the performance needed for more demanding applications.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Elements (Up to ~1800°C)
Known as "moly-D" elements, these are the gold standard for reaching very high temperatures. They can heat up extremely quickly and operate reliably up to 1800°C in an oxidizing atmosphere, where they form a protective layer of silica glass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance needs with practical constraints. Higher temperatures invariably come with higher costs and different operating considerations.
Cost vs. Temperature
There is a direct and significant correlation between maximum temperature and cost. The exotic materials required for SiC and MoSi2 elements make high-temperature furnaces substantially more expensive to purchase and maintain than standard models.
Element Lifespan and Atmosphere
Heating elements are consumables. Their lifespan is affected by operating temperature, the speed of heating/cooling cycles, and the chemical atmosphere inside the furnace. Elements like MoSi2 perform best in air but can be damaged by certain reactive gases.
Heat-Up and Cool-Down Rates
While a typical furnace may take around an hour to reach its maximum temperature, this varies greatly with size, insulation quality, and the power of the elements. High-performance MoSi2 elements are known for their ability to support very rapid heating cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, focus on the maximum temperature your process truly requires, not just the highest temperature available.
- If your primary focus is general lab work (ashing, drying, basic heat treating): A standard 1100°C or 1200°C furnace with resistance wire elements is your most cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is process development or small-scale production (glass, enamels): A mid-range furnace with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements provides the necessary performance for temperatures up to 1500°C.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research (sintering zirconia, growing crystals): You require a high-temperature furnace with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements capable of reaching 1700°C or 1800°C.
Ultimately, selecting a muffle furnace is about precisely matching the heating element technology to your required process temperature and budget.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Heating Element | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Resistance Wire (e.g., Kanthal A-1) | Ashing, drying, basic metal heat treating |
| 1200°C to 1500°C | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Glass, enamels, ceramics processing |
| 1600°C to 1800°C+ | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Sintering high-purity ceramics, crystal growth |
Struggling to select the right muffle furnace for your temperature requirements? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our diverse product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise alignment with your experimental goals, whether for general lab work, industrial processes, or cutting-edge research. Don't compromise on performance—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















