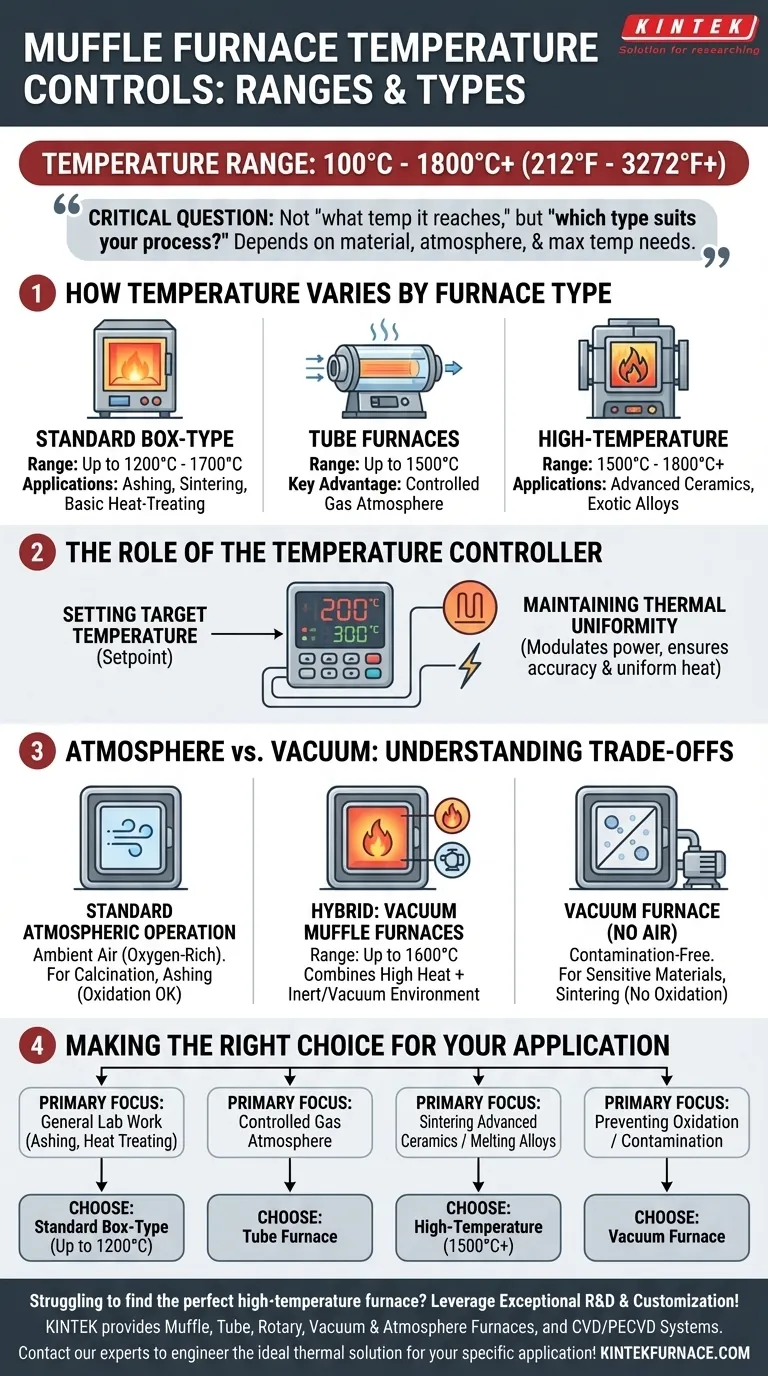
The temperature a muffle furnace controls is not a single value but a wide range, typically from 100°C up to 1800°C (212°F to 3272°F), with some specialized models exceeding this. The precise temperature capability is determined entirely by the furnace's specific type and construction, as different models are engineered for different thermal processes.
The critical question is not "what temperature can a muffle furnace reach," but rather "which type of muffle furnace provides the precise thermal environment my specific process requires?" The answer depends entirely on your material, your desired atmosphere, and your maximum temperature needs.
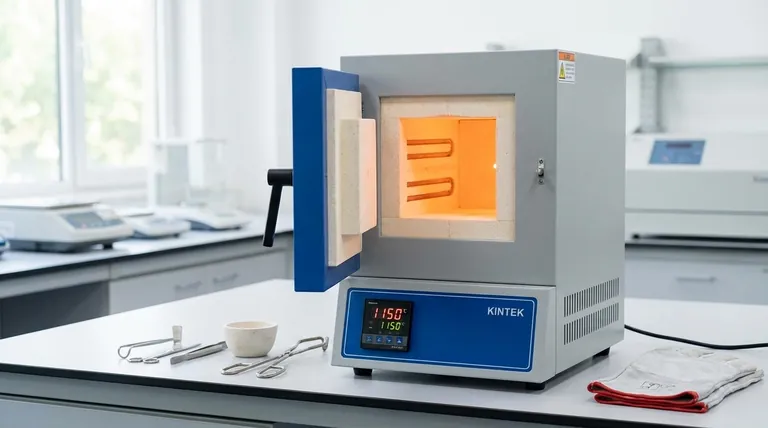

How Temperature Varies by Furnace Type
The term "muffle furnace" describes a category of equipment. The operational temperature is the primary factor that distinguishes different models designed for specific applications.
Standard Box-Type Furnaces
These are the most common muffle furnaces found in general laboratory and industrial settings.
Most box-type models operate at temperatures up to 1200°C (2192°F), though some can reach 1700°C (3100°F). This range makes them ideal for common applications like ashing, sintering, and basic heat-treating of metals.
Tube Furnaces
Tube furnaces use a cylindrical chamber, which is ideal for processing samples in a tightly controlled atmosphere.
Their temperature range often extends up to 1500°C (2732°F). The key advantage is the ability to flow inert or reactive gases over a sample, which is not possible in a standard box furnace.
High-Temperature Furnaces
As the name implies, these units are built for processes that demand extreme heat.
These furnaces are specifically designed to operate consistently above 1500°C, with many models reaching 1700°C to 1800°C or higher. They are essential for working with advanced ceramics and specialized alloys.
The Role of the Temperature Controller
A furnace's maximum temperature is only one part of the equation. The ability to precisely control that temperature is what makes it a useful scientific instrument.
Setting the Target Temperature
All modern muffle furnaces are equipped with a digital temperature controller. The operator sets a specific temperature, or "setpoint," that the process requires.
Maintaining Thermal Uniformity
Once powered on, the controller continuously monitors the internal temperature via a thermocouple. It then modulates power to the heating elements to maintain the setpoint with high accuracy and ensure uniform heat throughout the chamber.
Operation is confirmed when the controller's display shows the temperature gradually rising and stabilizing at the desired level.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
A critical limitation of a standard muffle furnace is its operating atmosphere. This is the most common point of failure when selecting equipment.
Standard Atmospheric Operation
A conventional muffle furnace operates in ambient air. The heating elements heat the "muffle," or insulated chamber, which then radiates heat onto the sample. This environment is, by definition, oxygen-rich.
This is perfectly acceptable for processes like calcination or ashing, where oxidation is intended or irrelevant.
When a Vacuum is Necessary
For heat-treating sensitive materials or sintering powders that must not oxidize, a standard muffle furnace is unsuitable. The presence of air will contaminate or destroy the sample.
In these cases, a vacuum furnace is required. These systems are designed to pump out all air and gases before the heating cycle begins, creating a contamination-free environment.
The Hybrid: Vacuum Muffle Furnaces
Specialized vacuum muffle furnaces do exist. These models combine the heating principles of a muffle furnace with the atmospheric control of a vacuum system.
They typically operate at temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F) and are used for processes like hardening, brazing, or sintering where both high heat and an inert environment are non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific process goals. Consider the following guidelines.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing or basic heat treating: A standard box-type muffle furnace operating up to 1200°C is typically sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is processing materials in a controlled gas atmosphere: A tube furnace is the ideal choice due to its ability to contain a specific gas flow.
- If your primary focus is sintering advanced ceramics or melting exotic alloys: You will need a specialized high-temperature furnace capable of reliably reaching 1500°C or more.
- If your primary focus is preventing any oxidation or material contamination: A vacuum furnace is the only suitable choice, as a standard muffle furnace cannot provide this environment.
By understanding these distinctions, you can confidently select a furnace that provides the precise thermal control your work demands.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Box-Type | Up to 1200°C - 1700°C | Ashing, sintering, basic heat-treating |
| Tube Furnace | Up to 1500°C | Processing in controlled gas atmospheres |
| High-Temperature | 1500°C to 1800°C+ | Advanced ceramics, exotic alloys |
| Vacuum Muffle | Up to 1600°C | Processes requiring inert/contamination-free environment |
Struggling to find the perfect high-temperature furnace for your unique requirements? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can engineer the ideal thermal solution for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production



















