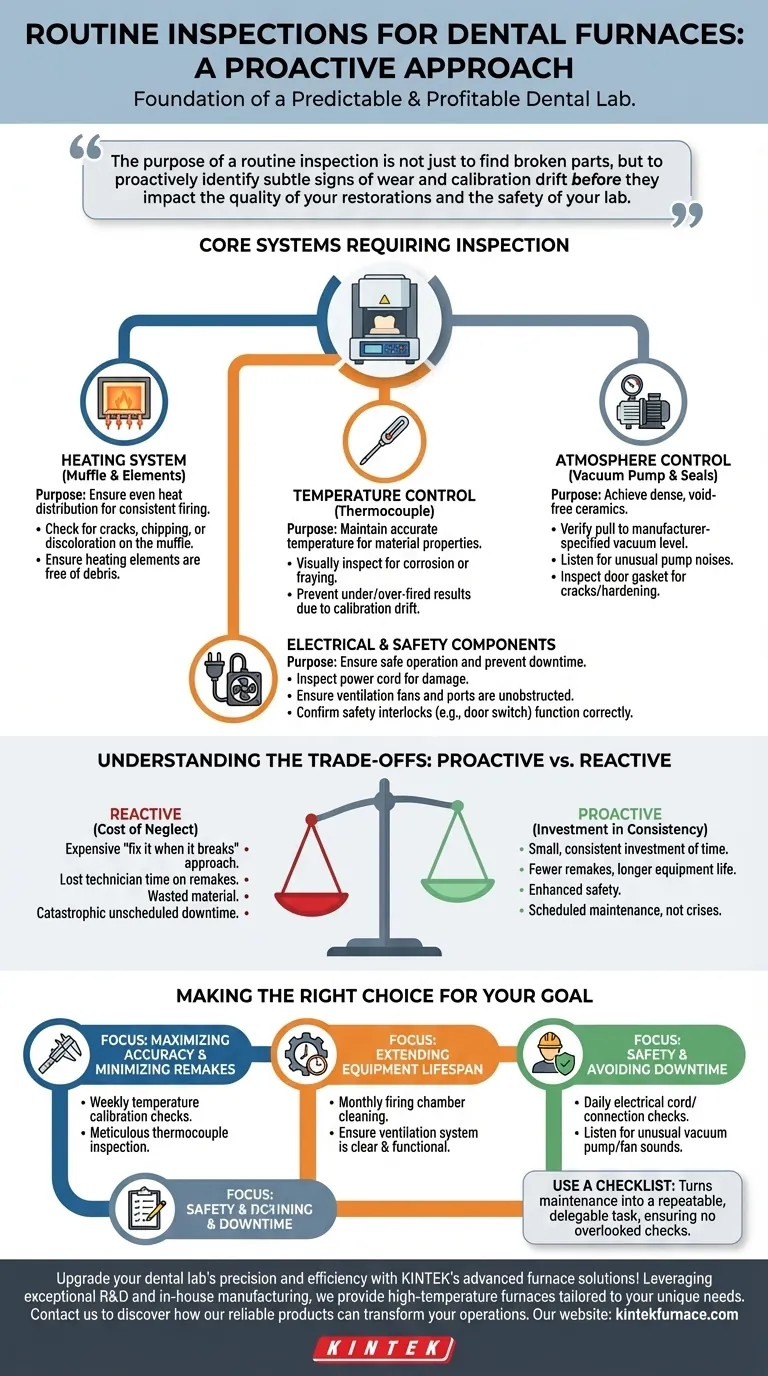
Routine inspections are the foundation of a predictable and profitable dental lab. A proper inspection focuses on three critical areas: the heating system (muffle and elements), the control systems (thermocouple and vacuum), and the overall electrical and safety integrity of the unit. This structured approach ensures consistent firing cycles, prevents costly remakes, and maintains a safe working environment.
The purpose of a routine inspection is not just to find broken parts, but to proactively identify subtle signs of wear and calibration drift before they impact the quality of your restorations and the safety of your lab.

The Core Systems Requiring Inspection
A dental furnace is a precision instrument. Its performance depends on several interconnected systems working in harmony. Your inspection protocol should systematically check each one.
The Heating System: Muffle and Elements
The muffle and heating elements are the heart of the furnace, responsible for generating and evenly distributing heat.
Degradation here directly leads to inconsistent firing, resulting in weak or poorly shaded restorations. Look for cracks, chipping, or discoloration on the muffle, and check that heating elements are free of debris.
The Temperature Control System: The Thermocouple
The thermocouple is the furnace's thermometer. Its accuracy is non-negotiable for achieving the correct material properties in your restorations.
A degraded or contaminated thermocouple can drift, reporting an incorrect temperature. This is a primary cause of under-fired, porous ceramics or over-fired, glassy results. Visually inspect it for signs of corrosion or fraying.
The Atmosphere Control: Vacuum Pump and Seals
For porcelain furnaces, creating a strong vacuum is essential for removing gases and achieving dense, void-free ceramics.
Check that the furnace pulls to the manufacturer-specified vacuum level. Listen for unusual noises from the pump, which can indicate wear, and inspect the door gasket for cracks or hardening that could cause leaks.
Electrical and Safety Components
These components ensure the furnace operates reliably and safely, protecting both the equipment and the operator.
Your check should include inspecting the power cord for damage, ensuring ventilation fans and ports are unobstructed, and confirming that all safety interlocks (like the door switch) function correctly.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Proactive vs. Reactive Maintenance
Choosing how to maintain your equipment is a strategic decision with clear consequences for your lab's bottom line.
The Cost of Neglect
A reactive "fix it when it breaks" approach is deceptively expensive. The true cost isn't just the repair bill, but the lost technician time on remakes, the wasted material, and the catastrophic impact of unscheduled downtime on your production schedule.
The Investment in Consistency
Proactive maintenance is a small, consistent investment of time. The payoff is predictability. You gain fewer remakes, longer equipment life, enhanced safety, and the ability to schedule major repairs on your own terms, not in a moment of crisis.
When to Use a Checklist
Using a formal checklist for monthly or quarterly inspections is critical. It turns the process into a repeatable, delegable task and ensures that subtle but important checks are never overlooked.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Implement a protocol that aligns with your lab's specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing accuracy and minimizing remakes: Prioritize weekly temperature calibration checks and meticulous inspection of the thermocouple.
- If your primary focus is extending equipment lifespan: Concentrate on monthly cleaning of the firing chamber and ensuring the ventilation system is clear and functional.
- If your primary focus is safety and avoiding downtime: Perform daily checks of all electrical cords and connections, and listen for any unusual sounds from the vacuum pump or fans.
By transforming maintenance from a reaction into a routine, you take control over your lab's quality, efficiency, and long-term success.
Summary Table:
| Inspection Area | Key Components | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Heating System | Muffle, Heating Elements | Ensure even heat distribution for consistent firing |
| Temperature Control | Thermocouple | Maintain accurate temperature for material properties |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum Pump, Seals | Achieve dense, void-free ceramics |
| Electrical & Safety | Power Cord, Fans, Interlocks | Ensure safe operation and prevent downtime |
Upgrade your dental lab's precision and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your equipment meets exact experimental requirements, reducing remakes and enhancing safety. Don't let maintenance issues slow you down—contact us today to discover how our reliable products can transform your operations and drive long-term success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does an efficient cooling system benefit dental furnace operations? Boost Productivity and Quality in Your Lab
- What is the main purpose of a sintering furnace in dentistry? Transform Zirconia into Strong Dental Restorations
- How does a vacuum porcelain furnace ensure the bonding quality? Achieve Superior Metal-Ceramic Restorations
- How does precise temperature control in a porcelain furnace benefit sintering? Achieve Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the use of porcelain in dentistry? Achieve Lifelike, Durable Dental Restorations



















