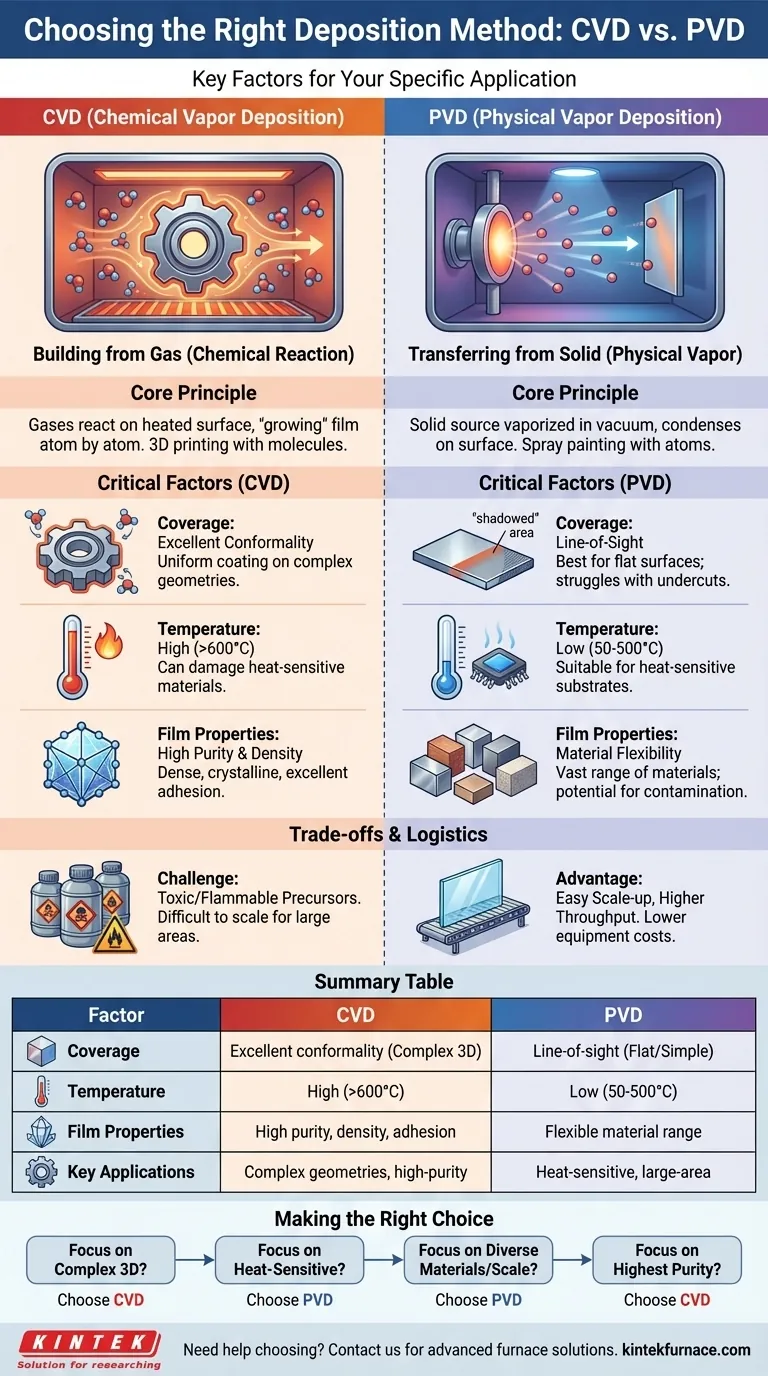
To select the right deposition method, you must evaluate your specific application against a few critical factors. The most important considerations include the geometry of the part you are coating, the material's tolerance for heat, and the desired final properties of the film, such as its uniformity and purity. Methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), for example, are known for excellent uniformity but operate at very high temperatures, which may not be suitable for all materials.
The choice between deposition methods is not about finding the "best" process, but about understanding a fundamental trade-off. Your decision will hinge on whether your application demands the uniform, conformal coating of a chemical process (CVD) or the versatile, low-temperature, line-of-sight deposition of a physical process (PVD).

The Two Pillars of Deposition: CVD and PVD
To make an informed choice, you must first understand the core difference between the two primary families of deposition: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Building from Gas
CVD involves introducing precursor gases into a chamber containing a heated substrate. A chemical reaction occurs on the surface of the substrate, causing a solid film to "grow" atom by atom.
Think of it as 3D printing with molecules. Because the gas surrounds the entire part, CVD creates exceptionally uniform and conformal coatings, meaning it can evenly coat highly complex, three-dimensional shapes.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Transferring from a Solid
PVD works by turning a solid source material (a "target") into a vapor, which then travels through a vacuum and condenses onto the substrate as a thin film. This is typically done through methods like sputtering or thermal evaporation.
This process is more like spray painting with atoms. It is a line-of-sight process, meaning it excels at coating surfaces that directly face the source material but struggles to coat undercuts or complex internal geometries.
Critical Decision Factors for Your Application
Your specific project requirements will push you toward one method over the other. Analyze your needs against these four factors.
Factor 1: Coverage and Conformality
CVD's primary advantage is its ability to produce highly conformal films. The precursor gases can penetrate small crevices and complex geometries, ensuring a uniform coating everywhere.
PVD, being a line-of-sight technique, is excellent for coating flat or gently curved surfaces. However, it will produce thinner coatings (or no coating at all) on areas that are "shadowed" from the source.
Factor 2: Deposition Temperature
CVD processes almost always require high temperatures (often >600°C) to drive the necessary chemical reactions on the substrate's surface. This can damage or warp temperature-sensitive materials like plastics, polymers, or certain electronic components.
PVD is a "cold" process by comparison, typically operating at much lower temperatures (50-500°C). This makes it the default choice for coating finished goods or heat-sensitive substrates.
Factor 3: Film Properties and Purity
CVD can produce films that are extremely pure, dense, and crystalline, often with excellent adhesion. The quality is a direct result of the controlled chemical reaction on the surface.
PVD films can be very high quality but are more susceptible to contamination from the vacuum environment. However, PVD offers incredible flexibility in depositing a vast range of metals, alloys, and ceramics that are difficult or impossible to create with CVD's chemical constraints.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Logistics
Beyond the core technical differences, practical limitations and logistical challenges play a crucial role in your final decision.
The Challenge of CVD Precursors
CVD relies on volatile precursor gases, many of which can be highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive. Handling, storing, and disposing of these chemicals presents significant safety, environmental, and cost challenges.
The Line-of-Sight Limitation of PVD
The primary drawback of PVD is its inability to uniformly coat complex 3D parts. This requires either complex part rotation systems within the chamber or accepting non-uniform coverage.
Scale, Throughput, and Cost
PVD is often easier to scale for coating very large, flat surfaces, such as architectural glass or solar panels. CVD can be challenging to scale for large areas while maintaining perfect uniformity. For many standard applications, PVD can offer higher throughput and lower equipment costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, your application's highest priority dictates the correct deposition method.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D structures or internal surfaces: Choose CVD for its unmatched conformality, which ensures a perfectly uniform film thickness everywhere.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers or finished electronics: Choose PVD for its fundamentally low-temperature process that prevents damage to the underlying part.
- If your primary focus is depositing a wide variety of materials, including unique alloys, onto flat surfaces: PVD offers superior material flexibility and is generally easier to scale for large-area applications.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and density on a thermally robust substrate: CVD is often the superior choice for creating near-perfect crystalline films.
By evaluating these fundamental principles, you can confidently select the deposition method that aligns with your technical goals and practical constraints.
Summary Table:
| Factor | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Excellent conformality for complex 3D shapes | Line-of-sight; best for flat or simple surfaces |
| Temperature | High (>600°C), may damage sensitive materials | Low (50-500°C), suitable for heat-sensitive substrates |
| Film Properties | High purity, density, and adhesion | Flexible material range, potential for contamination |
| Key Applications | Complex geometries, high-purity films | Temperature-sensitive substrates, large-area coatings |
Struggling to choose the right deposition method for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, helping you achieve optimal coating results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















