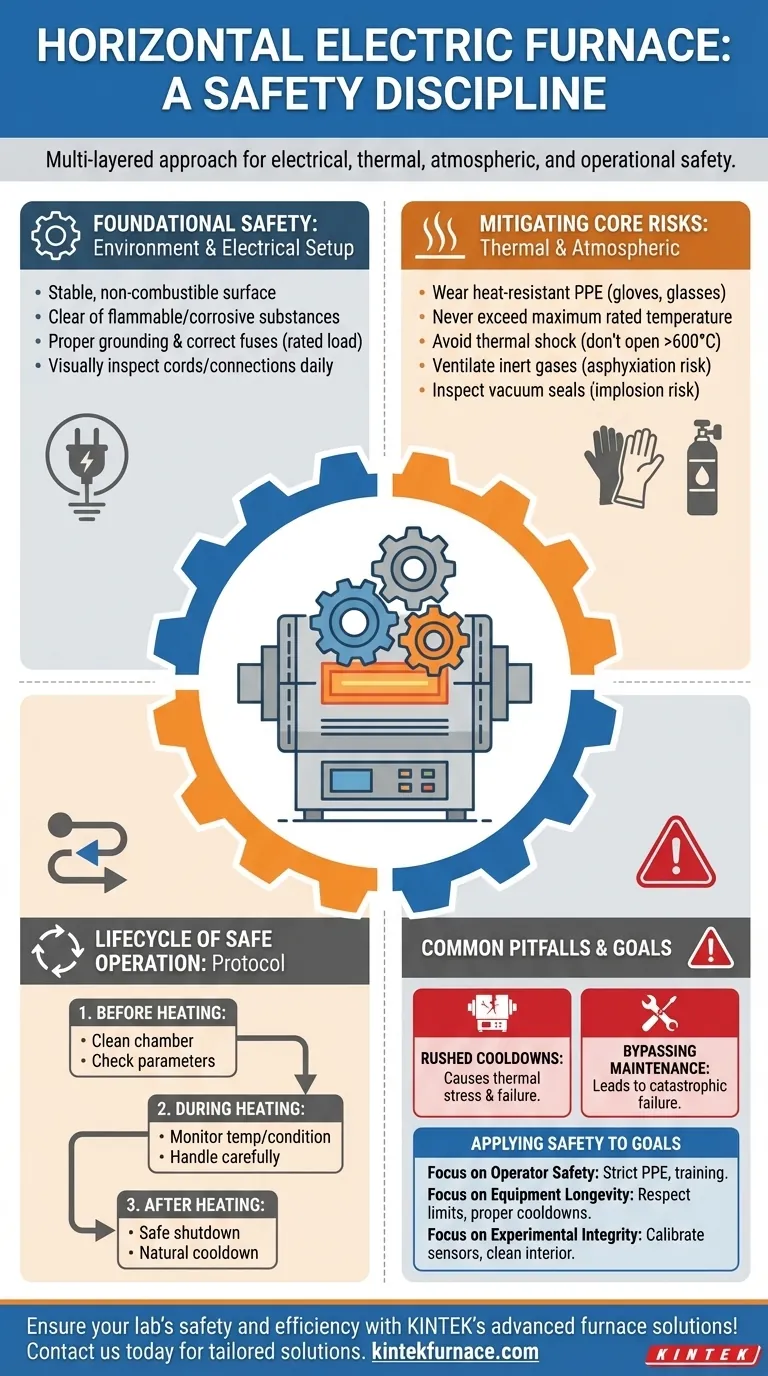
To operate a horizontal electric furnace safely, you must implement a multi-layered approach that addresses electrical integrity, thermal hazards, atmospheric conditions, and operator discipline. Key precautions include ensuring proper electrical grounding, using personal protective equipment (PPE) for heat, managing inert gas or vacuum atmospheres to prevent asphyxiation or implosion, and strictly adhering to operational protocols before, during, and after a heating cycle.
A horizontal electric furnace is a precise but unforgiving tool. True safety is not a checklist but a disciplined mindset, where every step—from setup to shutdown—is performed with a clear understanding of the potential electrical, thermal, and atmospheric risks involved.
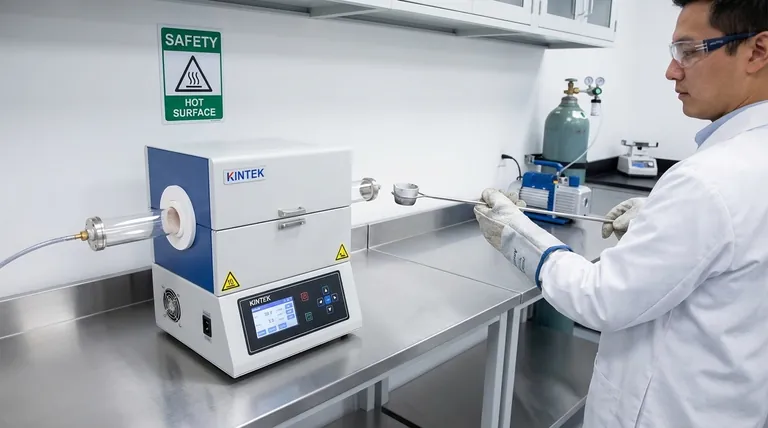

Foundational Safety: Environment and Electrical Setup
Before the furnace is even turned on, safety begins with its physical and electrical environment. These foundational steps prevent the most catastrophic failures.
Ensuring a Safe Workspace
The area around the furnace must be controlled. Place the unit on a stable, non-combustible surface, such as a dedicated cement platform.
Keep the immediate workspace clear of all flammable, explosive, or corrosive substances. A high-temperature environment can cause unforeseen reactions with nearby materials.
Verifying Electrical Integrity
Proper grounding is non-negotiable. This is the primary defense against electrical shock in the event of an internal fault.
Ensure the power supply uses the correct plugs, sockets, and fuses rated for the furnace's load. An undersized circuit creates a significant fire hazard.
Before each use, visually inspect power cords and connections for any signs of wear, fraying, or damage that could compromise electrical safety.
Mitigating Core Operational Risks
Once the environment is secure, the focus shifts to managing the primary hazards of operation: extreme heat and controlled atmospheres.
Thermal Hazards: Preventing Burns and Fires
Operators must always wear appropriate PPE, including heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses, when loading, unloading, or working near the furnace.
Never exceed the furnace's maximum rated temperature. Pushing the equipment beyond its design limits risks heating element failure and thermal runaway, a serious fire risk.
Do not open the furnace door at high temperatures (e.g., above 600°C). This can cause thermal shock to the furnace's refractory materials, leading to cracking, and poses an immediate and severe burn risk to the operator.
Atmospheric Hazards: Gas and Vacuum Safety
When using inert gases like nitrogen or argon, ensure the room is well-ventilated. A leak can displace oxygen and create a serious asphyxiation risk.
For vacuum operations, understand that a defect in the chamber or seals can lead to a violent implosion. Always inspect seals and viewports before pulling a vacuum.
The Lifecycle of a Safe Operation
A disciplined, step-by-step procedure is essential for repeatable and safe outcomes. Every heating cycle should follow a clear protocol.
Before Heating: Pre-operation Checks
Always check that the furnace chamber is clean and free of residues from previous runs, which could contaminate the experiment or create a fire hazard.
Carefully set your desired temperature and heating rate. Double-check that all parameters are within the safe operating limits for both the furnace and the material being processed.
During Heating: Active Monitoring
Constantly monitor the furnace's temperature display and overall condition during operation. If you notice any abnormalities, erratic temperature changes, or unusual noises, cut power immediately.
Handle samples and crucibles with care. Close the furnace door gently to avoid jarring the internal components or the sample.
After Heating: Safe Shutdown and Cooldown
Once the cycle is complete, turn off the main power supply. Never leave a furnace unattended while it is still hot.
Allow the furnace to cool naturally. You may slightly open the door after it has cooled significantly to aid the process, but rapid cooling is dangerous for the equipment.
Understanding Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Shortcuts are the primary cause of accidents and equipment damage. Understanding the trade-offs between speed and safety is critical for any operator.
The Danger of Rushed Cooldowns
Forcing a rapid cooldown by opening the door wide at high temperatures is a common mistake. This introduces extreme thermal stress on the heating elements and insulation, drastically shortening the furnace's lifespan and risking immediate equipment failure.
The Risk of Bypassing Maintenance
Skipping routine maintenance feels efficient until it leads to failure. An uncalibrated temperature controller can ruin an experiment, while a worn-out heating element can fail catastrophically. Regular cleaning, inspection, and calibration are essential investments in safety and reliability.
Applying This to Your Work
Your safety strategy should align with your primary goals, whether they are protecting personnel, preserving the equipment, or ensuring process accuracy.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Enforce strict adherence to PPE usage, procedural discipline, and comprehensive training on all potential hazards.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Prioritize respecting temperature limits, conducting proper cooldowns, and performing all scheduled maintenance without fail.
- If your primary focus is experimental integrity: Emphasize periodic temperature sensor calibration, maintaining a clean furnace interior, and ensuring atmosphere integrity for gas or vacuum work.
Ultimately, a safe operation is a controlled operation, which is the foundation for achieving reliable and accurate results.
Summary Table:
| Safety Aspect | Key Precautions |
|---|---|
| Electrical Setup | Ensure proper grounding, correct fuses, and inspect power cords for damage. |
| Thermal Hazards | Wear PPE, avoid exceeding max temperature, and prevent thermal shock by not opening door at high temps. |
| Atmospheric Risks | Ventilate for inert gases, inspect seals for vacuum to prevent asphyxiation or implosion. |
| Operational Lifecycle | Perform pre-checks, monitor during heating, and allow natural cooldown after shutdown. |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs, enhancing operator protection and process reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















