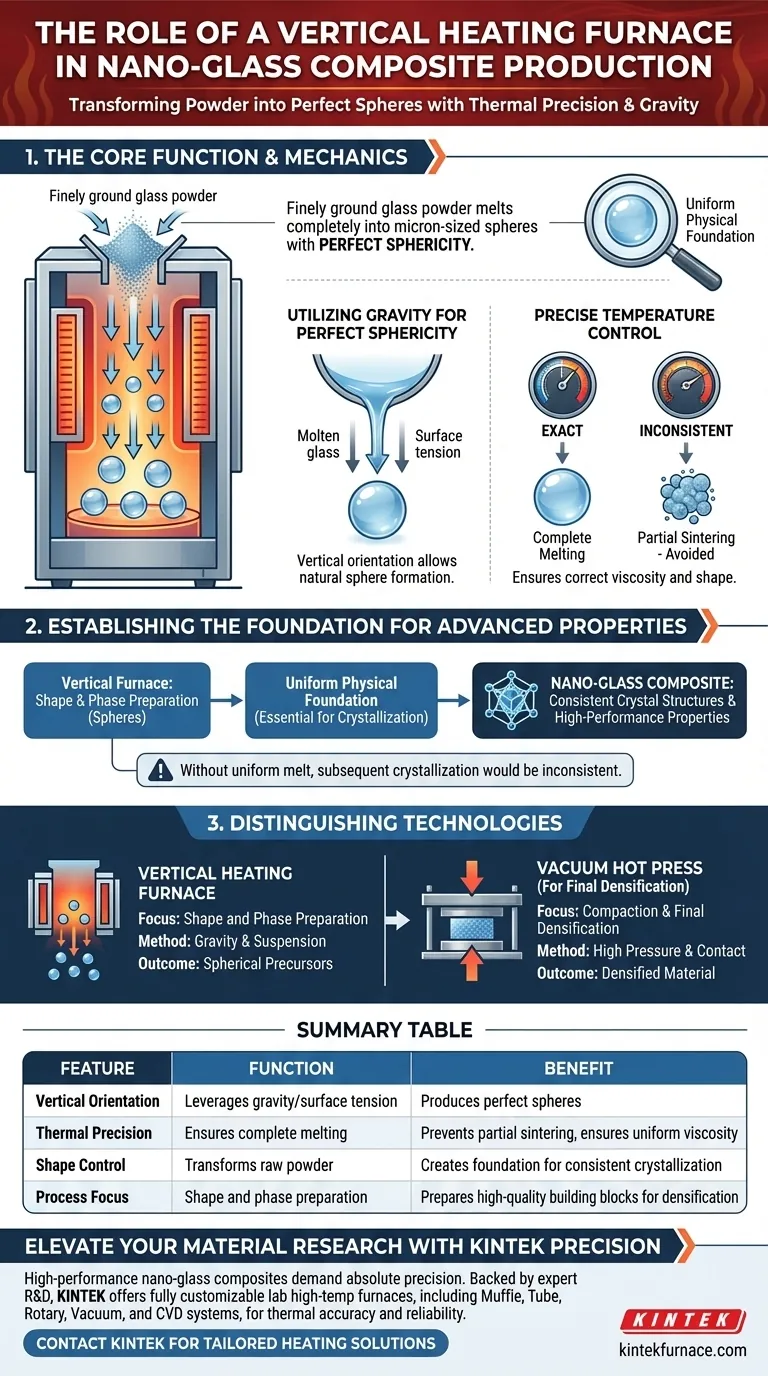
A vertical heating furnace serves as the critical mechanism for shaping and melting raw materials into precise geometries. Its primary function in the production of nano-glass composites is to transform finely ground glass powder into perfectly spherical micron-sized particles by leveraging thermal precision and gravity.
The Core Insight By utilizing a vertical orientation, this equipment allows molten glass to naturally form perfect spheres while falling or suspended. This creates a uniform physical foundation, which is strictly necessary for the success of subsequent crystallization and heat treatment processes.

The Mechanics of Formation
Utilizing Gravity for Perfect Sphericity
The unique value of a vertical heating furnace lies in its orientation.
As the finely ground glass powder enters the heating zone, it melts into a liquid state.
Because the material is falling or suspended within the vertical chamber, surface tension and gravity work together to shape the molten liquid into micron-sized glass spheres with perfect sphericity.
Precise Temperature Control
Achieving a consistent sphere requires exact thermal regulation.
The furnace provides highly specific temperature control to ensure the glass powder melts completely rather than partially sintering.
This guarantees that every particle achieves the correct viscosity and shape before it cools.
The Role in the Broader Process
Establishing a Physical Foundation
The vertical furnace is not responsible for the final composite properties, but rather for preparing the raw material.
By ensuring perfect sphericity and complete melting, it establishes a solid physical foundation.
This uniformity is a prerequisite for the next stage of production: controlled heat treatment and crystallization.
Preparing for Crystallization
Nano-glass composites rely on specific crystalline structures to achieve their advanced properties.
The spheres produced in the vertical furnace serve as the ideal precursors for this transformation.
Without the uniform melt provided by this specific furnace type, subsequent crystallization would likely be inconsistent, leading to structural flaws in the final material.
Distinguishing Process Technologies
Vertical Heating vs. Vacuum Hot Pressing
It is important not to confuse the vertical heating furnace with a vacuum hot press furnace, as they serve different stages of production.
While the vertical furnace uses gravity and suspension to create spherical precursors, a vacuum hot press (often used later or for different materials) utilizes high pressure (e.g., 30 MPa) and physical contact to densify materials.
The vertical furnace focuses on shape and phase preparation, whereas other equipment focuses on compaction and final densification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your production line, you must align the equipment with your specific processing stage.
- If your primary focus is Particle Geometry: Rely on the vertical heating furnace to produce perfectly spherical micron-sized glass beads through gravity-assisted melting.
- If your primary focus is Material Homogeneity: Use the vertical furnace’s precise temperature controls to ensure complete melting of powder prior to crystallization.
- If your primary focus is Final Densification: Recognize that the vertical furnace is a preparatory tool; you will need high-pressure equipment (like a vacuum hot press) for the final consolidation of composites.
The vertical heating furnace is the indispensable tool for converting raw powder into the uniform, spherical building blocks required for high-performance nano-glass.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Nano-Glass Production | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Orientation | Leverages gravity and surface tension | Produces perfect micron-sized spheres |
| Thermal Precision | Ensures complete melting of glass powder | Prevents partial sintering and ensures uniform viscosity |
| Shape Control | Transforms raw powder into spherical precursors | Creates the foundation for consistent crystallization |
| Process Focus | Shape and phase preparation | Prepares high-quality building blocks for final densification |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
High-performance nano-glass composites demand absolute precision from the very first melt. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all of which are fully customizable to meet your unique processing needs.
Whether you are focusing on particle geometry or final material densification, our equipment provides the thermal accuracy and reliability required for groundbreaking results. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and see how our tailored heating solutions can optimize your production line.
Visual Guide
References
- Zhigang Gao, Guoping Dong. Robust low threshold full-color upconversion lasing in rare-earth activated nanocrystal-in-glass microcavity. DOI: 10.1038/s41377-024-01671-3
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a constant temperature and humidity curing chamber essential for geopolymerization? Ensure Structural Strength
- Why is it necessary to use an annealing furnace at 350°C for three hours? Ensuring Glass Stability and Clarity
- How does the introduction of SiO2 as an additive improve the sintering process of solid electrolytes? Boost Densification
- How do stirring equipment and temperature-controlled heating stages influence magnetic nanoparticle quality?
- What advantages does a vacuum drying oven offer for Fe-N-BC catalysts? Protect Integrity and Improve Uniformity
- What is the function of a furnace in CuAlMn alloy treatment? Achieve Perfect Microstructural Homogenization
- What is the purpose of using a thermal evaporation coating system? Enhancing I-V Testing Accuracy for Nanocomposites
- What factors influence the time and temperature of the annealing process? Optimize Your Heat Treatment for Better Results



















