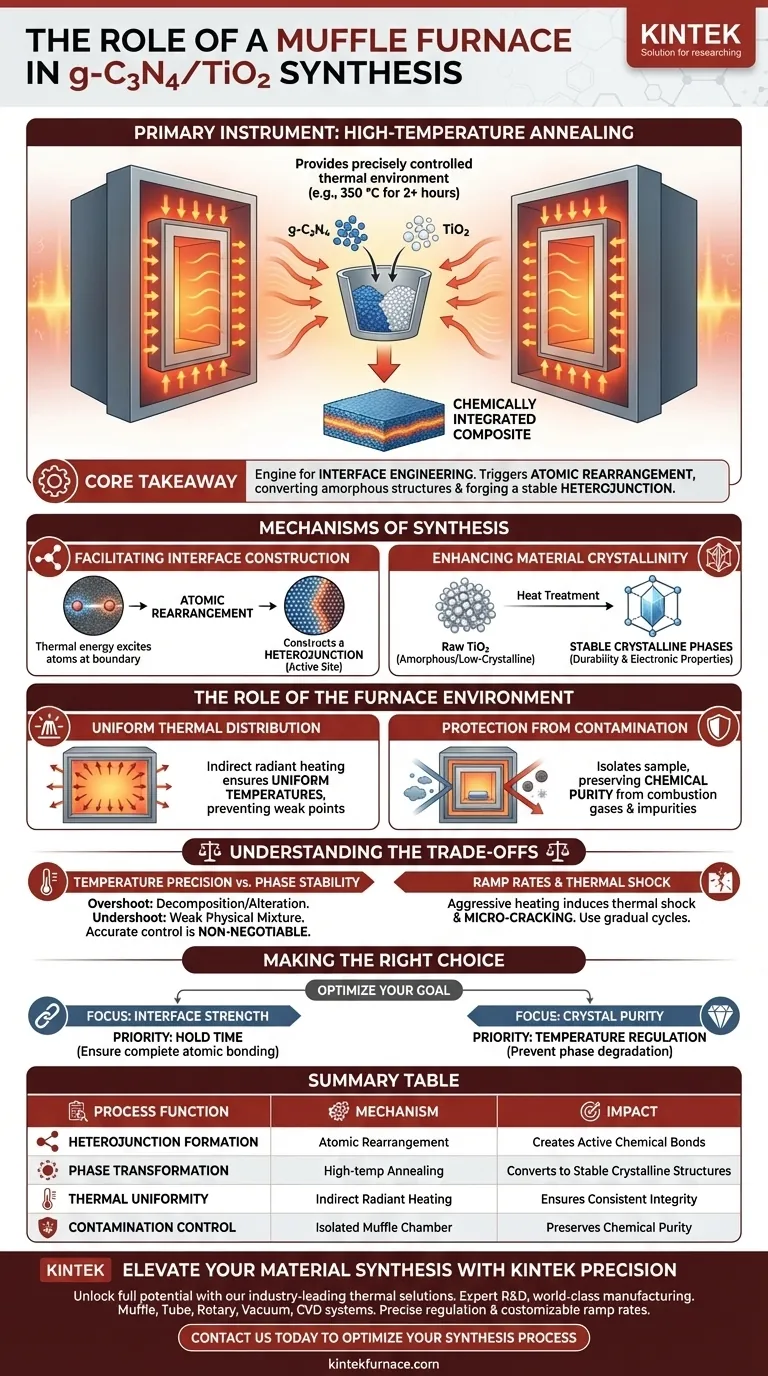
A muffle furnace serves as the primary instrument for high-temperature annealing during the synthesis of g-C3N4/TiO2 composites. It provides a precisely controlled thermal environment, typically maintaining temperatures around 350 °C for extended periods, to drive the chemical reactions necessary for combining Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4) and Titanium Dioxide (TiO2). Without this specific thermal processing, the materials would remain a physical mixture rather than a chemically integrated composite.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace is not merely a drying tool; it is an engine for interface engineering. It supplies the exact thermal energy required to trigger atomic rearrangement, converting amorphous structures into crystalline phases and forging a stable heterojunction between the two distinct materials.

Mechanisms of Synthesis
Facilitating Interface Construction
The primary function of the furnace is to facilitate atomic rearrangement at the microscopic level.
When the precursor materials are held at a sustained temperature (e.g., 350 °C for 2 hours), thermal energy excites the atoms at the boundary where g-C3N4 and TiO2 meet.
This energy drives the formation of chemical bonds, successfully constructing a heterojunction. This junction is the critical active site that defines the performance of the composite material.
Enhancing Material Crystallinity
Beyond bonding the two materials, the heat treatment dramatically improves the structural quality of the TiO2 component.
Raw TiO2 precursors often exist in amorphous or low-crystalline states which lack stability and efficiency.
The muffle furnace converts these unstable components into stable crystalline phases. This phase transformation is essential for the material's long-term durability and electronic properties.
The Role of the Furnace Environment
Uniform Thermal Distribution
A muffle furnace utilizes indirect heating, where elements radiate heat from outside the inner chamber (the muffle).
This ensures the sample is exposed to uniform temperatures from all sides, rather than direct contact with a heat source.
Uniformity is vital for synthesis; uneven heating would lead to inconsistent crystallinity and weak points in the composite structure.
Protection from Contamination
The design of the muffle chamber isolates the sample from direct exposure to combustion gases or heating element contaminants.
This creates a clean, controlled environment that protects the chemical purity of the g-C3N4/TiO2 composite.
This isolation ensures that the final product's properties are a result of the intended chemical synthesis, not external impurities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Precision vs. Phase Stability
While high heat is necessary, accurate temperature control is non-negotiable.
If the furnace temperature overshoots, you risk decomposing the g-C3N4 component or altering the TiO2 phase beyond the desired crystalline structure.
Conversely, underheating will fail to initiate the atomic rearrangement, leaving you with a weak physical mixture rather than a bonded composite.
Ramp Rates and Thermal Shock
Modern muffle furnaces allow for programmable ramp-up rates, but aggressive heating can be detrimental.
Heating the sample too quickly can induce thermal shock, potentially causing micro-cracking within the composite material.
It is critical to utilize the furnace's programmable controller to set gradual heating and cooling cycles to maintain structural integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your synthesis process, you must align the furnace parameters with your specific material objectives.
- If your primary focus is Interface Strength: Prioritize the hold time (e.g., the full 2 hours) to ensure sufficient thermal energy is delivered for complete atomic bonding at the heterojunction.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Purity: Focus on precise temperature regulation, ensuring the furnace does not fluctuate from the target annealing temperature (e.g., 350 °C) to prevent phase degradation.
Success in synthesis depends not just on the materials you use, but on the precision of the thermal environment you create.
Summary Table:
| Process Function | Mechanism | Impact on g-C3N4/TiO2 Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Heterojunction Formation | Atomic rearrangement at 350°C | Creates active chemical bonds between components |
| Phase Transformation | High-temp annealing | Converts amorphous precursors into stable crystalline structures |
| Thermal Uniformity | Indirect radiant heating | Ensures consistent crystallinity and structural integrity |
| Contamination Control | Isolated muffle chamber | Preserves chemical purity by blocking combustion gases |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your g-C3N4/TiO2 research with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the rigorous demands of lab-scale and industrial high-temperature processing.
Whether you need precise temperature regulation for interface engineering or customizable ramp rates to prevent thermal shock, our furnaces are engineered for your unique material needs. Contact us today to optimize your synthesis process and see why leading researchers trust KINTEK for their high-temp laboratory equipment.
Visual Guide
References
- Matevž Roškarič, Albin Pintar. Effect of TiO2 Morphology on the Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of g-C3N4/TiO2 Nanocomposites Under Visible-Light Illumination. DOI: 10.3390/molecules30030460
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How was a muffle furnace used in environmental sample analysis? Purify Samples for Accurate Pollution Detection
- What are the primary heat transfer mechanisms in a box furnace? Master Radiation and Convection for Optimal Heating
- What is the role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in treating Mn3O4 nanowires? Optimize Phase Stability
- What temperature ranges are used for different muffle furnace applications? Optimize Your Heat Processes with KINTEK
- What are some common uses of muffle furnaces in material testing? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Accurate Results
- What is the significance of thermal radiation in muffle furnace sintering? Master Heat Transfer for Precision
- How is a Muffle furnace used in environmental treatment? Essential for Waste Analysis and Small-Scale Incineration
- How does the muffle furnace ensure uniform heating? Achieve Precise, Even Heat for Your Lab



















