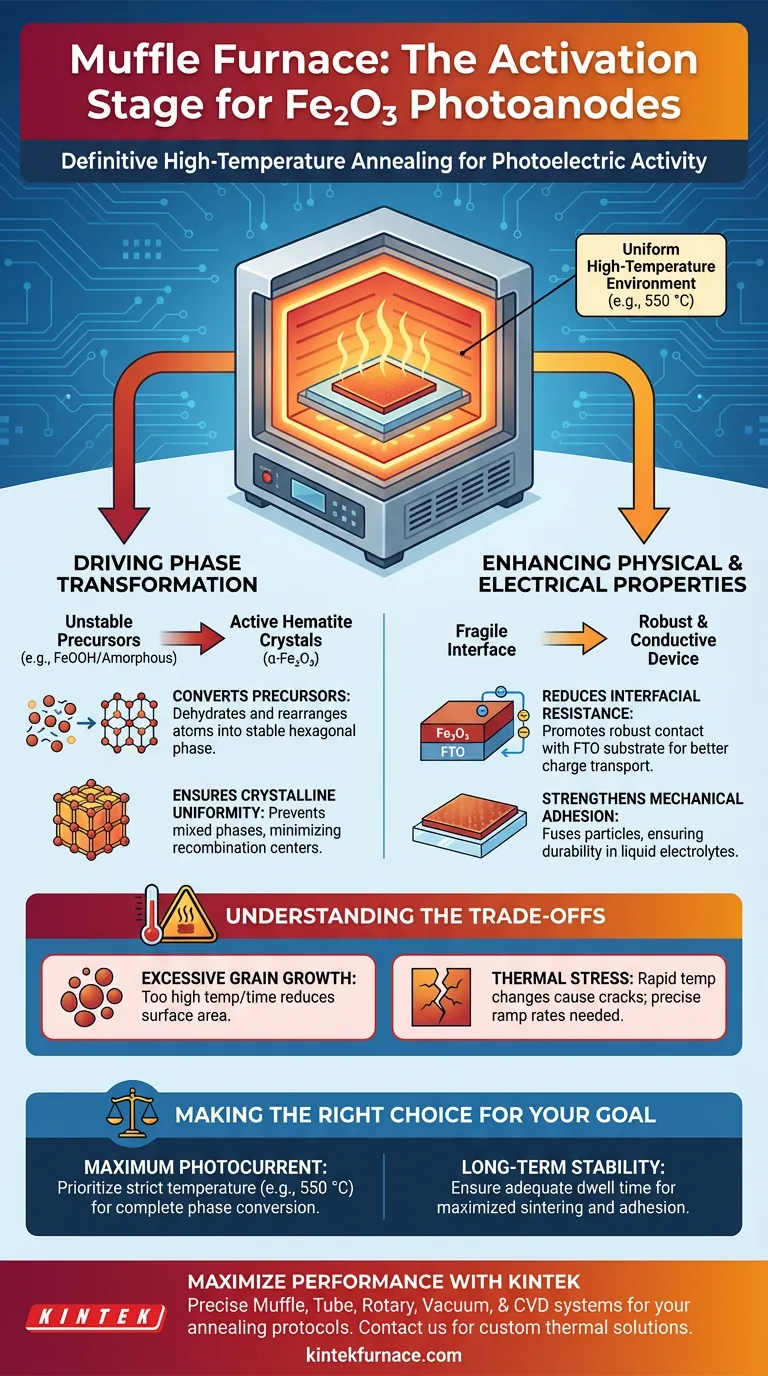
The muffle furnace acts as the definitive activation stage for Fe$_2$O$_3$ photoanodes. In the post-treatment of hydrothermally grown samples, it performs two critical functions: converting unstable precursors into photoelectrically active hematite crystals and physically fusing the material to the substrate. Without this precise high-temperature annealing, the photoanode would lack the necessary crystalline structure and electrical connectivity to function.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace provides a uniform high-temperature environment (typically 550 °C) essential for air annealing. This process drives the phase transformation of amorphous iron specifically into hexagonal phase hematite ($\alpha$-Fe$_2$O$_3$) while simultaneously minimizing interfacial resistance to ensure efficient charge transport.

Driving Phase Transformation
The primary chemical role of the muffle furnace is to alter the fundamental structure of the material.
Converting Precursors to Active Material
Hydrothermal growth often leaves the material in an amorphous or intermediate state (such as FeOOH). The muffle furnace supplies the thermal energy required to dehydrate these precursors and rearrange the atoms into the stable hexagonal phase hematite ($\alpha$-Fe$_2$O$_3$). This specific crystal phase is required for the material to exhibit photoactivity.
Ensuring Crystalline Uniformity
Consistency is vital for semiconductor performance. The furnace creates a uniform thermal field, ensuring that the crystallization process occurs evenly across the entire sample. This prevents the formation of mixed phases that could act as recombination centers and lower efficiency.
Enhancing Physical and Electrical Properties
Beyond chemical changes, the heat treatment significantly improves the physical interface of the device.
Reducing Interfacial Resistance
The furnace promotes the formation of a robust electrical contact between the photoactive Fe$_2$O$_3$ layer and the Fluorine-doped Tin Oxide (FTO) substrate. This high-temperature sintering reduces the barrier to electron flow, facilitating better charge extraction.
Strengthening Mechanical Adhesion
Unannealed films are often fragile and prone to delamination. The thermal treatment fuses the nanoparticles into a cohesive network and bonds them firmly to the conductive glass. This ensures the mechanical durability required for the device to operate in liquid electrolytes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While necessary, the use of a muffle furnace involves precise variables that can negatively impact the sample if mismanaged.
The Risk of Excessive Grain Growth
Temperature control is not just about reaching a target; it is about limits. If the temperature is too high or held for too long, nanoparticles may merge excessively, leading to reduced surface area and lower catalytic activity.
Thermal Stress and Structural Damage
Rapid temperature fluctuations can cause cracks in the film or the substrate. Precise ramp rates (e.g., 10 °C/min) are often employed to prevent thermal shock, ensuring the morphology of the nanostructures remains intact during the transition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific parameters of your muffle furnace treatment should be tuned based on your primary performance metric.
- If your primary focus is maximum photocurrent: Prioritize a strict temperature protocol (often around 550 °C) to ensure complete conversion to the $\alpha$-Fe$_2$O$_3$ phase without inducing excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability: Ensure adequate dwell time to maximize the sintering effect, reinforcing the adhesion between the hematite layer and the FTO substrate.
Mastering the annealing profile is as critical as the synthesis itself; it turns a raw chemical coating into a functional semiconductor device.
Summary Table:
| Process Function | Impact on Fe2O3 Photoanodes | Key Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Transformation | Converts FeOOH/amorphous iron to $\alpha$-Fe$_2$O$_3$ | Enables photoactivity and crystallinity |
| Thermal Sintering | Reduces interfacial resistance with FTO substrate | Enhances charge transport and extraction |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent crystal growth across sample | Minimizes recombination centers |
| Mechanical Fusion | Bonds nanoparticles firmly to conductive glass | Improves durability in liquid electrolytes |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is the difference between an amorphous coating and a high-performance semiconductor. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your specific annealing protocols.
Whether you are optimizing hematite phase transformation or scaling lab research, our advanced high-temperature furnaces provide the uniformity and ramp-rate precision your materials demand. Contact our specialists today to find your custom thermal solution.
Visual Guide
References
- S-Doped FeOOH Layers as Efficient Hole Transport Channels for the Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance of Fe2O3. DOI: 10.3390/nano15100767
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is a laboratory high-temperature muffle furnace utilized in g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Thermal Polycondensation
- What materials are used in the construction of the muffle furnace? Discover the Key Components for High-Temp Performance
- How does a muffle furnace ensure energy efficiency? Achieve Lower Costs and Better Performance
- What is the function of a laboratory muffle furnace in the post-treatment of HTC products? Engineering Carbon Excellence
- What are the key components of a muffle furnace as shown in its diagram? Discover Its Core Architecture
- What comprises the working chamber of a box type resistance furnace? Discover the Core Components for Efficient High-Temp Operations
- What are the limitations of a muffle furnace? Key Constraints for High-Temperature Applications
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the pyrolysis process for preparing softwood biochar? Expert Insights



















