At its core, a muffle furnace ensures energy efficiency by excelling at two things: generating heat precisely where it's needed and keeping that heat from escaping. This is achieved through a combination of superior thermal insulation, a sealed chamber design, and intelligent temperature control systems that minimize wasted energy.
The energy efficiency of a muffle furnace is not a single feature, but the result of a deliberate engineering system. It focuses on maximizing heat retention and optimizing energy input, which directly translates to lower operational costs and greater process consistency.
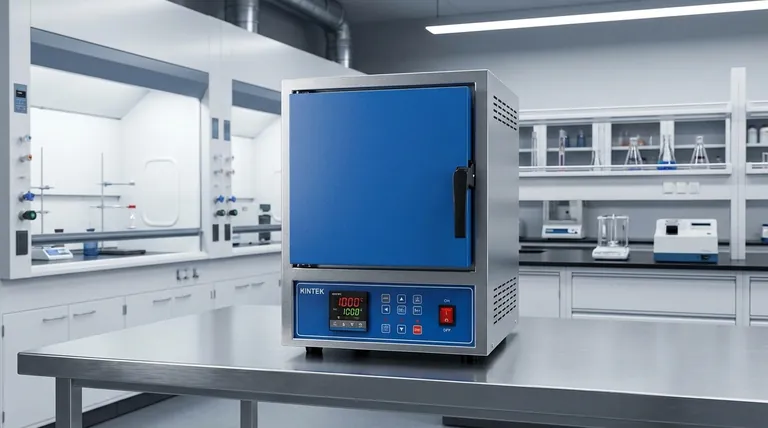

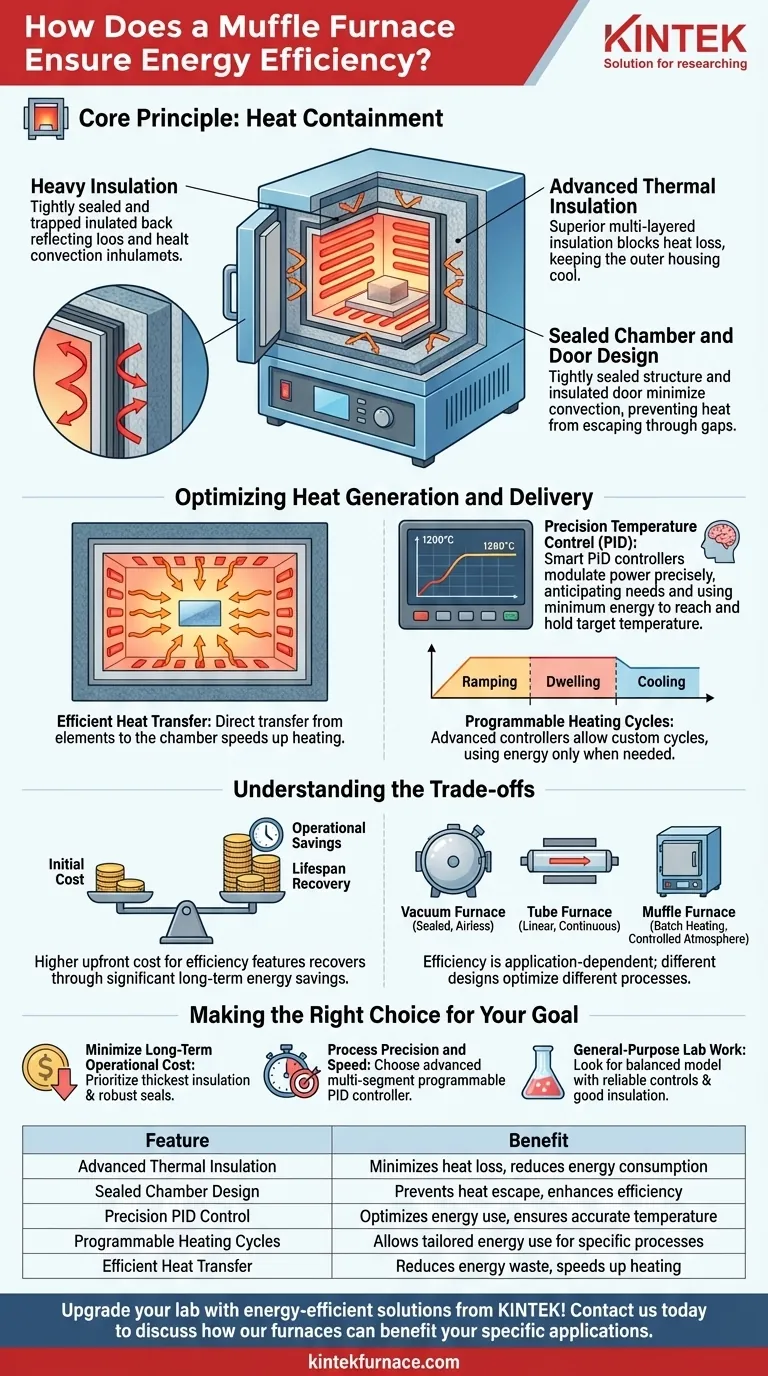
The Core Principle: Heat Containment
The most significant factor in a furnace's energy efficiency is its ability to contain the immense heat it generates. Any heat that leaks out is wasted energy that must be constantly replaced.
Advanced Thermal Insulation
High-quality muffle furnaces use thick, multi-layered insulation within their walls. These materials are chosen for their low thermal conductivity, creating a barrier that keeps heat locked inside the main chamber.
This is why modern furnaces can reach extremely high temperatures while the outer housing remains relatively cool to the touch, drastically reducing energy consumption.
Sealed Chamber and Door Design
Heat doesn't just escape through walls; it escapes through gaps. Muffle furnaces feature a tightly sealed chamber and a heavily insulated door, often using high-density fiber materials.
This robust construction minimizes heat loss through convection, ensuring the energy input is used to heat the sample, not the surrounding room. The housing, typically made of durable stainless steel, further supports this sealed, compact structure.
Optimizing Heat Generation and Delivery
Beyond simply trapping heat, an efficient furnace must also generate and apply that heat intelligently.
Efficient Heat Transfer
The internal walls are designed not just to insulate, but to effectively transfer thermal energy from the heating elements into the furnace chamber. This rapid and direct transfer means less energy is wasted heating the structural components of the furnace itself.
This design is what allows for the high heating speeds and rapid temperature recovery that modern furnaces are known for.
Precision Temperature Control (PID)
Modern digital furnaces utilize a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller. Think of this as an exceptionally smart thermostat.
Instead of crudely turning the heater on and off and overshooting the target temperature, a PID controller anticipates the heating needs. It modulates power precisely to reach the set temperature quickly and hold it with an accuracy of +/- 1°C, using the absolute minimum energy required.
Programmable Heating Cycles
Advanced controllers allow for programmable segments for ramping, dwelling, and cooling. This allows a user to design a heating cycle that uses energy only when needed, avoiding prolonged periods of unnecessary high-temperature operation and further optimizing energy use for specific processes like thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) or quenching.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, it's important to understand the context of this performance.
Initial Cost vs. Operational Savings
The features that drive energy efficiency—thick multi-layer insulation, advanced PID controllers, and robust construction—often result in a higher initial purchase price.
However, this upfront investment is typically recovered over the furnace's lifespan through significant savings in energy costs, especially in settings where the furnace is used frequently.
Efficiency is Application-Dependent
The advertised "energy efficiency" is directly tied to its intended use. The rapid heating and cooling cycles are a major efficiency benefit for processes like quenching or quality control, where speed is critical.
For applications requiring long, stable soaks at a single temperature, the quality of the insulation and the stability of the PID controller become the most important efficiency factors.
Furnace Type Matters
While the principles of insulation and control are universal, they are applied differently. A vacuum furnace achieves efficiency in a sealed, airless environment, while a tube furnace is optimized for linear, continuous processes. A muffle furnace is specifically engineered for outstanding efficiency in batch heating applications within a controlled atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right furnace, align its features with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational cost: Prioritize models with the thickest, highest-quality multi-layer insulation and the most robust door seal design.
- If your primary focus is process precision and speed: Choose a furnace with an advanced, multi-segment programmable PID controller for exact temperature profiling.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work: Look for a balanced model that offers a compact design, reliable digital controls, and good-quality thermal insulation.
Understanding these design principles empowers you to see beyond marketing claims and choose a furnace based on sound technical reasoning.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Advanced Thermal Insulation | Minimizes heat loss, reduces energy consumption |
| Sealed Chamber Design | Prevents heat escape, enhances efficiency |
| Precision PID Control | Optimizes energy use, ensures accurate temperature |
| Programmable Heating Cycles | Allows tailored energy use for specific processes |
| Efficient Heat Transfer | Reduces energy waste, speeds up heating |
Upgrade your lab with energy-efficient solutions from KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you save on energy costs and enhance performance. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















