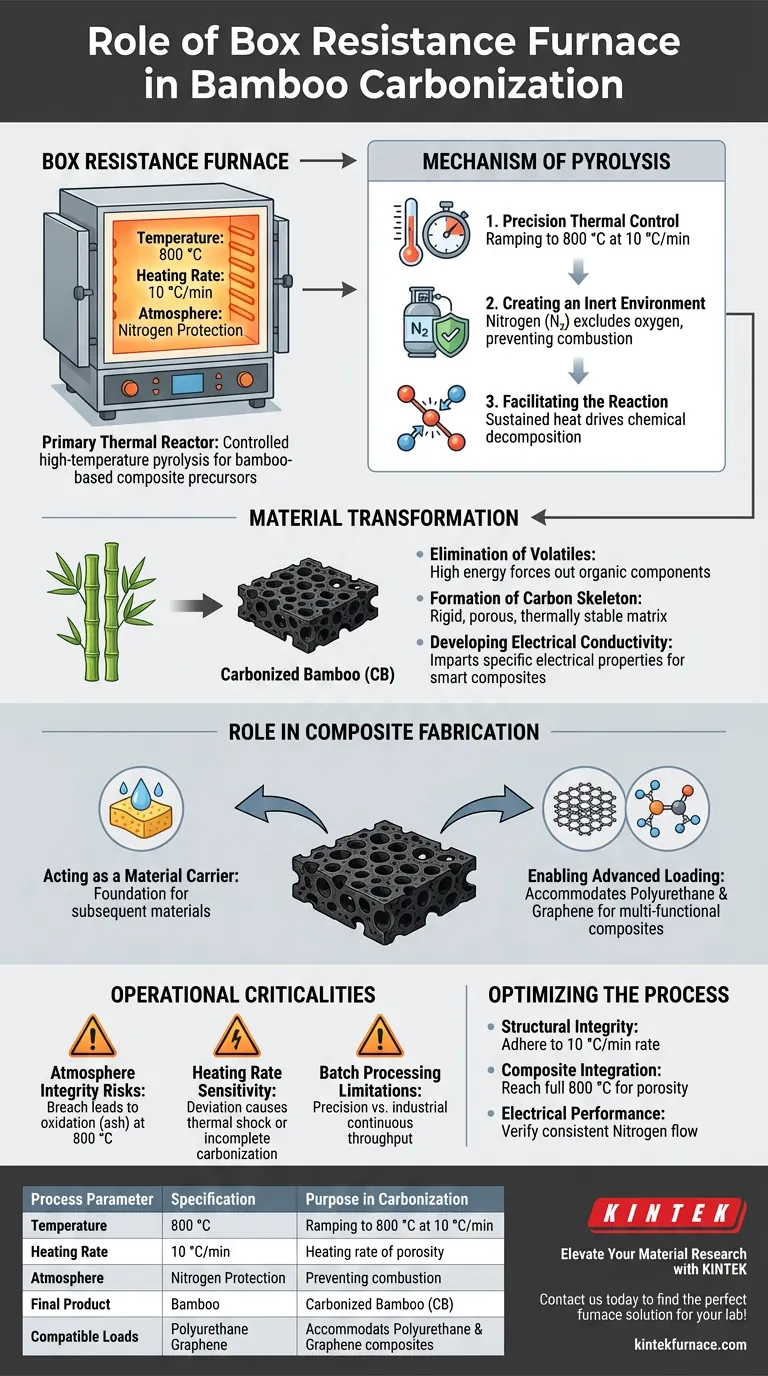
The box resistance furnace serves as the primary thermal reactor for transforming raw bamboo into a functional carbonized skeleton. It provides a strictly controlled, high-temperature environment—specifically heating to 800 °C under nitrogen protection—to facilitate the pyrolysis necessary for creating bamboo-based composite precursors.
The furnace’s precise thermal regulation and inert atmosphere enable the removal of volatile components without incinerating the material. This process yields a porous, conductive carbonized bamboo (CB) framework that acts as an essential carrier for advanced composite materials.

The Mechanism of Pyrolysis
Precision Thermal Control
The core function of the box resistance furnace is to execute a specific heating profile. For bamboo precursors, this involves ramping the temperature to 800 °C at a constant, controlled rate of 10 °C/min.
Creating an Inert Environment
To prevent the bamboo from turning into ash, the furnace operates under nitrogen protection. This excludes oxygen from the chamber, ensuring the material undergoes carbonization (thermal decomposition) rather than combustion.
Facilitating the Reaction
By maintaining the target temperature for a specific duration, the furnace drives the chemical changes required for pyrolysis. This sustained heat energy breaks down complex organic structures within the bamboo.
Material Transformation and Properties
Elimination of Volatiles
The high thermal energy forces volatile organic components to exit the bamboo structure. This effectively "cleans" the material, leaving behind only the thermally stable carbon matrix.
Formation of the Carbon Skeleton
The result of this treatment is Carbonized Bamboo (CB). Unlike the raw material, this CB acts as a rigid skeleton with a distinct, highly porous architecture.
Developing Electrical Conductivity
Beyond structural changes, the furnace treatment alters the electrical properties of the material. The carbonization process imparts specific electrical conductivity to the bamboo, a critical feature for its use in electronic or smart composites.
Role in Composite Fabrication
acting as a Material Carrier
The porous structure created by the furnace is not the end product but a foundation. This skeleton serves as a carrier or host matrix for subsequent materials.
Enabling Advanced Loading
Because the furnace creates a stable, open framework, the carbonized bamboo can be effectively loaded with other substances. Specifically, it accommodates polyurethane and graphene, allowing for the creation of multi-functional composite materials.
Operational Criticalities and Constraints
Atmosphere Integrity Risks
The success of the process relies entirely on the integrity of the nitrogen seal. Any breach in the furnace's protective atmosphere at 800 °C will lead to oxidation, destroying the bamboo skeleton and reducing the yield to ash.
Heating Rate Sensitivity
The specific rate of 10 °C/min is not arbitrary. Deviating from this ramp rate can cause thermal shock or incomplete carbonization, potentially leading to structural cracks or inconsistent porosity in the final precursor.
Batch Processing Limitations
Unlike continuous feed systems, a box resistance furnace is typically a batch-processing tool. This offers high precision for research and specific batches but may present throughput limitations compared to industrial continuous kilns.
Optimizing the Process for Your Goals
To derive the maximum value from a box resistance furnace in bamboo carbonization, align your parameters with your specific material requirements.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Strictly adhere to the 10 °C/min heating rate to prevent thermal stress fractures in the bamboo skeleton.
- If your primary focus is composite integration: Ensure the furnace reaches the full 800 °C to maximize the removal of volatiles and open up the porous structure for polyurethane and graphene loading.
- If your primary focus is electrical performance: Verify the nitrogen flow consistency throughout the dwell time to ensure pure carbonization and uniform conductivity.
The box resistance furnace is the defining tool that converts organic bamboo from a raw plant material into a sophisticated, conductive engineering substrate.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Specification | Purpose in Carbonization |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 800 °C | Facilitates complete pyrolysis and removal of volatiles |
| Heating Rate | 10 °C/min | Prevents thermal shock and ensures structural integrity |
| Atmosphere | Nitrogen Protection | Prevents combustion/oxidation of the bamboo skeleton |
| Final Product | Carbonized Bamboo (CB) | Creates a conductive, porous carrier for composites |
| Compatible Loads | Polyurethane & Graphene | Enables development of multi-functional materials |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Unlock the full potential of your bamboo-based composites with precision thermal processing. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your unique carbonization requirements.
Whether you need strict atmosphere control or precise heating profiles for advanced lab applications, our high-temperature furnaces provide the reliability your research demands. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Jin Wang, Jian Zhang. Synthesis, Electrical Conductivity, and Wave-Absorption Performances of Bamboo-Based Composites Co-Doped with Graphene Oxide and Polyaniline. DOI: 10.3390/polym17010078
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does an industrial-grade atmospheric furnace play in fire simulation tests? Master ASTM Safety Standards
- What is an atmosphere box furnace and what are its primary uses? Essential for Controlled Heat Processing
- What role does the furnace atmosphere play in heat transfer? Optimize Your Process with KINTEK
- What is the purpose of inerting in heat treatment furnaces? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Safety
- What are the considerations for air atmosphere and cooling in Inconel 625 heat treatment? Optimize 3D Part Stability
- What factors should be considered when selecting a controlled atmosphere furnace? Ensure Process Success with Expert Guidance
- Why is stress relief annealing essential for SLM titanium scaffolds? Ensure Durability and Fatigue Resistance
- What is the pressure range of an atmosphere box furnace under normal conditions? Learn How It Shields Your Materials



















