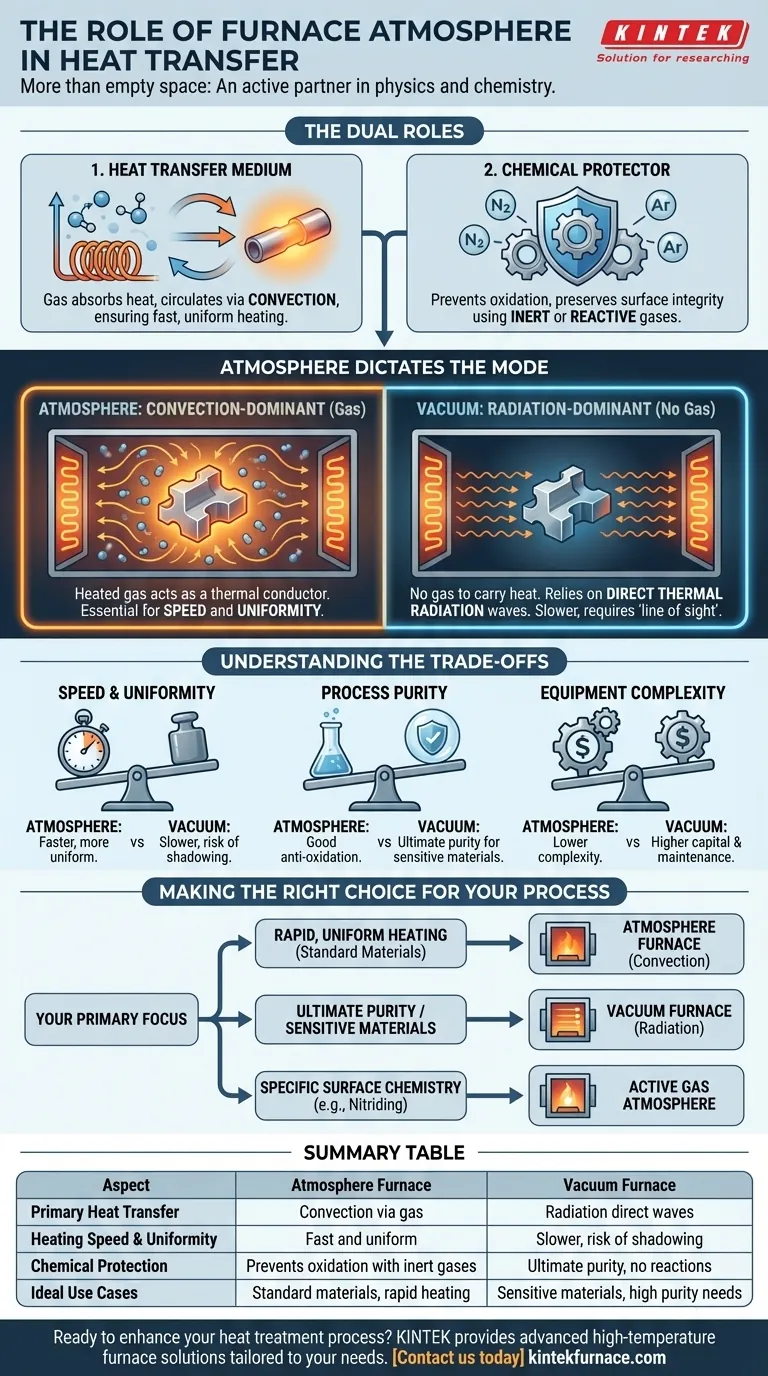
At its core, the furnace atmosphere is an active participant in the heating process, not merely the empty space inside the chamber. It primarily functions as a thermal conductor, carrying heat from the furnace walls and heating elements to the workpiece. This process, known as convection, is critical for accelerating heat transfer and ensuring the material is heated uniformly.
The choice of furnace atmosphere dictates the primary mode of heat transfer. While a gaseous atmosphere enables rapid, uniform heating via convection, a vacuum eliminates this mechanism, making radiation the dominant method while offering unparalleled protection against chemical reactions.

The Dual Roles of the Furnace Atmosphere
A furnace's internal environment is engineered to perform two critical functions simultaneously: transferring thermal energy and controlling the material's chemical environment.
Role 1: The Heat Transfer Medium
In a furnace filled with a gas (like air, nitrogen, or argon), that gas becomes the primary vehicle for heat transfer. The heating elements heat the gas molecules, which then circulate throughout the chamber.
This movement, or convection, allows the hot gas to transfer its thermal energy to the cooler workpiece. This method is highly effective at reaching all surfaces of a part, promoting even and consistent temperature distribution.
Role 2: The Chemical Protector
Beyond physics, the atmosphere plays a crucial chemical role. Many high-temperature processes, such as bright annealing or sintering, would cause the material to oxidize or react undesirably if exposed to oxygen.
Using an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a specific reactive gas (for processes like carburizing) prevents these unwanted chemical changes, preserving the material's surface finish and integrity.
How the Atmosphere Dictates the Mode of Heat Transfer
The presence or absence of a gaseous atmosphere fundamentally changes how heat moves from its source to the workpiece.
Convection-Dominant Furnaces
Most industrial furnaces operate with a gaseous atmosphere. Heat is generated by electrical elements—such as resistance wires or silicon carbon rods—which heat the surrounding chamber and the gas within it.
This heated gas then becomes a "thermal conductor," actively carrying energy throughout the furnace. This convective flow is essential for speed and uniformity, especially for parts with complex geometries.
Radiation-Dominant Furnaces (Vacuum)
In a vacuum furnace, the atmosphere is removed. With virtually no gas molecules to carry heat, convection is eliminated.
In this environment, heat transfer occurs almost exclusively through thermal radiation—electromagnetic waves traveling from the hot heating elements directly to the workpiece. This is similar to how the sun heats the Earth through the vacuum of space. While effective, it relies on a clear "line of sight" between the heat source and the part.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
The decision to use an atmosphere or a vacuum involves significant trade-offs in performance, cost, and process capability.
Speed and Uniformity
Atmosphere-based furnaces generally provide faster and more uniform heating due to the pervasive nature of convection. A vacuum furnace can suffer from "shadowing," where parts of the workpiece not in the direct line of sight of the heating elements heat more slowly, creating a temperature gradient.
Process Purity
A vacuum provides the ultimate protection against contamination, as there are no gas molecules to react with the workpiece. This is critical for highly sensitive metals like titanium or refractory metals. Inert atmospheres are excellent for preventing oxidation but cannot match the purity of a high vacuum.
Equipment Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are inherently more complex and costly. They require robust, sealed chambers, sophisticated pumping systems to remove the air, and precise pressure controls, all of which increase capital and maintenance expenses compared to standard atmosphere furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the proper environment is critical for achieving your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is rapid, uniform heating of standard materials: An atmosphere-based furnace leveraging convection is the most efficient and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive materials or preventing any possibility of oxidation: A vacuum furnace is necessary, relying on radiation for heat transfer to ensure absolute purity.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific surface chemistry (e.g., nitriding): A specialized active gas atmosphere is required, serving as both a heat transfer medium and a chemical reactant.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment lies in understanding that the furnace atmosphere is a powerful tool to control both the physics and the chemistry of your process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Atmosphere Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Heat Transfer | Convection (via gas) | Radiation (direct waves) |
| Heating Speed & Uniformity | Fast and uniform | Slower, risk of shadowing |
| Chemical Protection | Prevents oxidation with inert gases | Ultimate purity, no reactions |
| Ideal Use Cases | Standard materials, rapid heating | Sensitive materials, high purity needs |
Ready to enhance your heat treatment process? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need rapid, uniform heating or absolute material purity, we have the expertise to help. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















