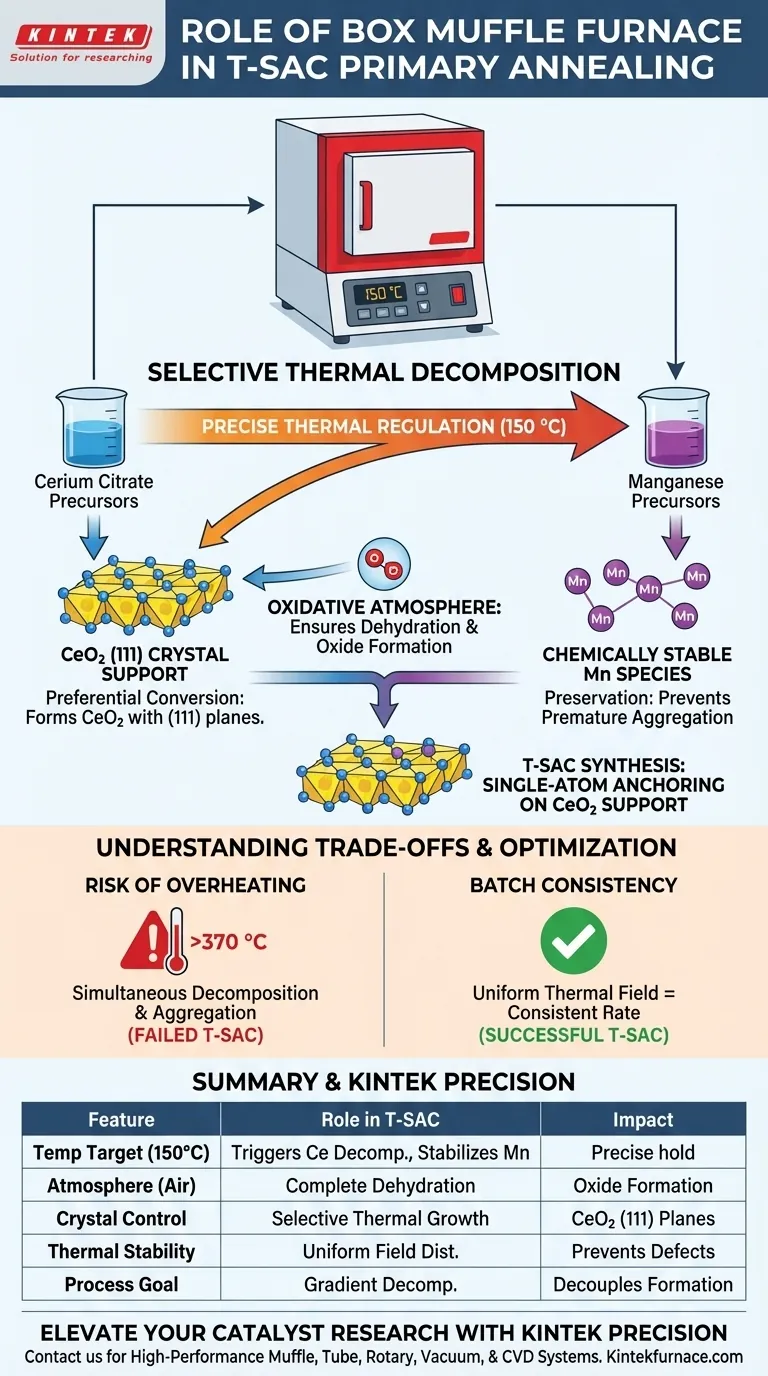
The box muffle furnace functions as a precision tool for selective thermal decomposition during the primary annealing of topological single-atom catalysts (T-SACs). Specifically, it maintains a strictly controlled environment at 150 °C to trigger the gradient decomposition of cerium citrate. This process converts cerium precursors into a specific support structure while deliberately preventing the premature reaction of manganese components.
By maintaining a low-temperature thermal environment, the furnace decouples the reaction timelines of different precursors, allowing the support structure to crystallize without destroying the conditions necessary for single-atom anchoring.

The Mechanism of Gradient Decomposition
Precise Thermal Regulation
The primary role of the box muffle furnace in this context is temperature specificity rather than high-heat calcination. While many annealing processes operate above 300 °C, this specific T-SAC synthesis requires a steady hold at exactly 150 °C. This relatively low temperature is calibrated to affect only the most volatile components of the precursor mix.
Preferential Conversion of the Support
At this specific temperature, the furnace facilitates the decomposition of cerium citrate into cerium dioxide (CeO2). Crucially, this thermal treatment promotes the formation of CeO2 with (111) crystal planes. This crystallographic orientation provides the topological foundation required for the final catalyst structure.
Preservation of Active Species
Simultaneously, the furnace environment ensures the manganese precursors remain chemically stable. If the temperature were allowed to spike, the manganese would decompose prematurely, likely aggregating into clusters rather than single atoms. By strictly limiting the heat, the furnace creates a "time lag" between the formation of the support and the activation of the metal atoms.
The Role of Atmospheric Control
Oxidative Environment
Standard industrial and laboratory muffle furnaces are designed to provide a stable oxidative (air) environment. In the context of T-SACs, this oxygen-rich atmosphere assists in the clean dehydration of the dried powders. It ensures that the conversion of cerium salts to oxides is complete and uniform across the batch.
Batch Consistency
The box muffle furnace offers excellent thermal field stability, minimizing temperature gradients within the chamber. This ensures that the gradient decomposition occurs at the exact same rate throughout the powder sample. Uniformity is vital for preventing structural defects that could inhibit the directional anchoring of single atoms later in the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Overheating
A common pitfall is applying standard calcination protocols to T-SAC synthesis. Supplementary data indicates that many oxides (like tin or iron-based systems) require temperatures between 370 °C and 525 °C for phase transformation. However, applying these standard high temperatures to T-SAC precursors would cause simultaneous decomposition, destroying the gradient effect and ruining the single-atom dispersion.
Throughput vs. Precision
While industrial muffle furnaces are prized for high-volume processing, the T-SAC process prioritizes precision over speed. The low-temperature (150 °C) anneal is a slower, more delicate phase transformation compared to rapid high-heat sintering. Operators must accept longer processing times to achieve the specific (111) crystal plane orientation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the synthesis of topological single-atom catalysts, you must align your thermal treatment with the specific chemical needs of your precursors.
- If your primary focus is T-SAC Synthesis: Maintain the furnace strictly at 150 °C to separate the decomposition phases of the support (Ce) and the active metal (Mn).
- If your primary focus is General Oxide Support (e.g., SnO2): Utilize higher temperature ranges (370 °C - 525 °C) to ensure complete phase transformation and crystallinity.
- If your primary focus is Scale-Up: Ensure your furnace has verified thermal field stability to prevent hot spots that could trigger premature Mn decomposition in parts of the batch.
Success in this process depends not on maximizing heat, but on utilizing the furnace to achieve selective chemical evolution through precise thermal restraint.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in T-SAC Synthesis | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Target | Precise hold at 150 °C | Triggers cerium citrate decomposition while stabilizing Mn |
| Atmosphere | Oxidative (Air) | Ensures complete dehydration and oxide formation |
| Crystal Control | Selective Thermal Growth | Favors formation of specific CeO2 (111) crystal planes |
| Thermal Stability | Uniform Field Distribution | Prevents premature metal aggregation and structural defects |
| Process Goal | Gradient Decomposition | Decouples support formation from single-atom anchoring |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
Precise thermal regulation is the difference between a failed batch and a high-performance Topological Single-Atom Catalyst (T-SAC). At KINTEK, we understand that advanced materials require more than just heat—they require exact control.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are targeting specific crystal planes at 150 °C or performing high-temp sintering, our furnaces are fully customizable for your lab's unique needs.
Ready to optimize your synthesis process? Contact us today to find the perfect thermal solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Weibin Chen, Ruqiang Zou. Designer topological-single-atom catalysts with site-specific selectivity. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55838-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What features might advanced muffle furnace models include? Enhance Precision, Safety, and Efficiency
- How does a Muffle Furnace facilitate the formation of Ru-2 cluster catalysts? Precision for Ruthenium Calcination
- Why is a laboratory high-temperature muffle furnace used for BaTiO3? Achieve Optimal Tetragonal Crystalline Phases
- What safety features are incorporated in muffle furnaces? Ensure Operator Protection and Equipment Safety
- What are the temperature capabilities of a muffle furnace? Find Your Perfect High-Temp Solution
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in nitrogen-doped carbon precursor synthesis? Key Roles in Thermal Condensation
- What is a box furnace and what are its common uses? Discover Versatile High-Temperature Solutions
- How does a muffle furnace ensure the quality of high-temperature solid-state synthesis? Achieve Superior Phase Purity



















