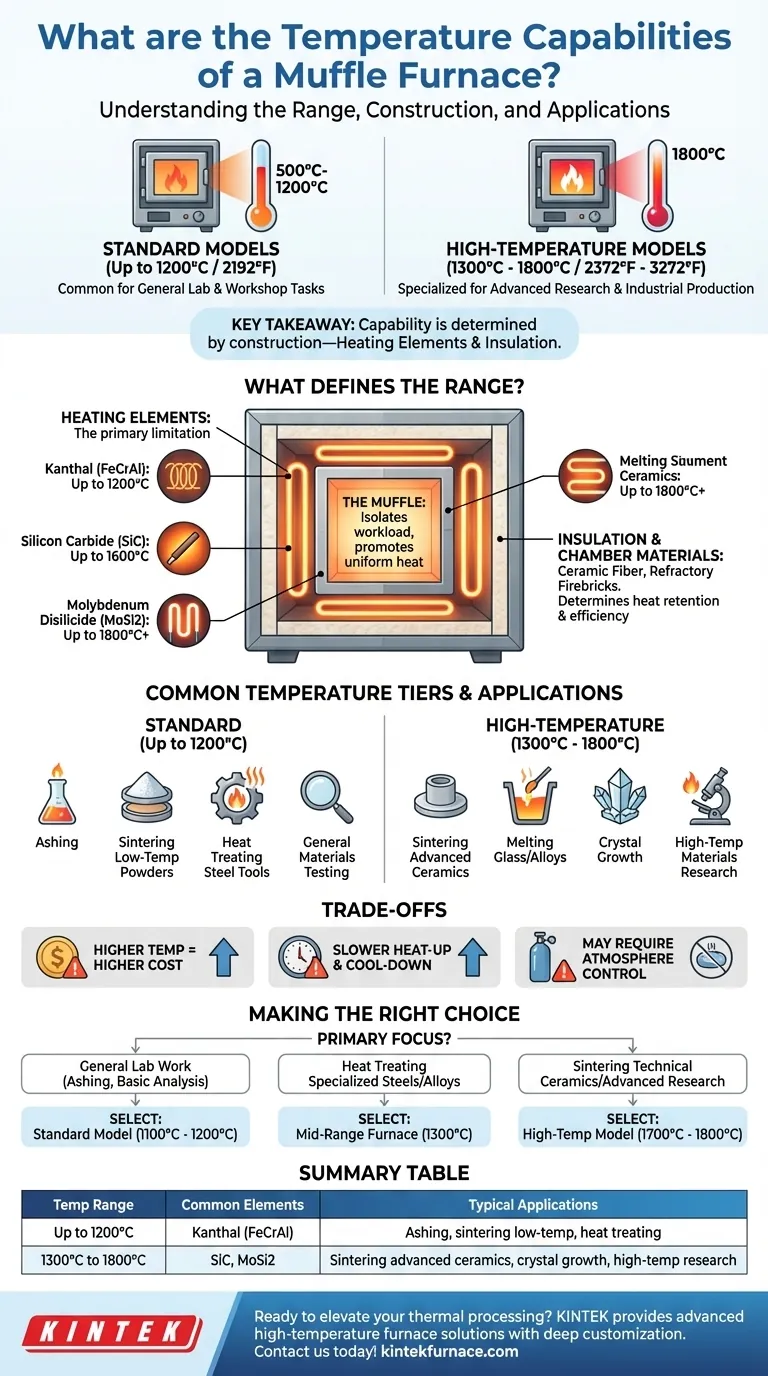
In short, a muffle furnace is designed for high-temperature applications, with most standard models operating between 500°C and 1200°C (932°F to 2192°F). However, specialized models built with advanced materials can reliably reach temperatures as high as 1800°C (3272°F) for more demanding industrial and research processes.
The key takeaway is not a single maximum temperature, but understanding that a muffle furnace's capability is determined by its specific construction. The choice of heating elements and insulation materials directly dictates its operational range and suitability for your application.
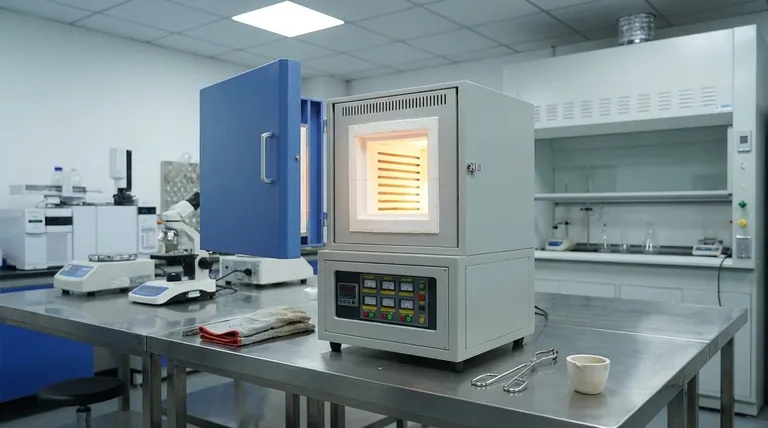

What Defines a Muffle Furnace's Temperature Range?
A muffle furnace isn't simply an oven; it's a piece of precision equipment. Its temperature capabilities are a direct result of its engineering and the materials used in its construction.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The defining feature of this furnace is the muffle itself—an inner chamber that isolates the workload from the heating elements.
This separation prevents contamination from combustion byproducts (in fuel-fired furnaces) or direct radiation damage from electric elements. It also promotes uniform heat distribution, which is critical for consistent results.
The Impact of Heating Elements
The maximum achievable temperature is fundamentally limited by the heating elements. Different materials have different operational ceilings.
- Kanthal (FeCrAl) elements are common in standard furnaces and are typically rated for up to 1200°C or 1300°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are used in higher-temperature models, enabling operation up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are reserved for the most demanding applications, allowing furnaces to reach 1700°C to 1800°C and sometimes higher.
Insulation and Chamber Materials
To reach and maintain these extreme temperatures efficiently, the heating chamber must be exceptionally well-insulated.
Materials like high-purity ceramic fiber and dense refractory firebricks are used to line the chamber. The quality and thickness of this insulation determine the furnace's heat retention, energy efficiency, and outer surface temperature.
Common Temperature Tiers and Their Applications
The required temperature dictates the type of furnace you need. These can be grouped into two main categories based on their capabilities and intended use.
Standard Models (Up to 1200°C)
This is the most common range for general laboratory and workshop tasks. Furnaces in this tier are workhorses for a variety of thermal processes.
Common applications include ashing organic materials, sintering low-temperature powders, heat treating steel tools, and general materials testing.
High-Temperature Models (1300°C to 1800°C)
These are specialized furnaces built for advanced research and industrial production where extreme heat is necessary.
They are used for processes like sintering advanced ceramics, melting specific glass and metal alloys, crystal growth, and high-temperature materials research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace isn't just about finding the highest temperature. You must consider the practical implications and limitations associated with higher heat.
Higher Temperature Equals Higher Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its price. The specialized heating elements (like MoSi2) and advanced insulation required for 1800°C operation are significantly more expensive than the materials used in a 1200°C furnace.
Slower Heat-Up and Cool-Down Rates
The massive thermal insulation required to safely contain extreme heat also means these furnaces have significant thermal mass. As a result, high-temperature models can take several hours to reach their setpoint and even longer to cool down, impacting workflow and turnaround time.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with an air atmosphere. If your process requires an inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum to prevent oxidation, you need a furnace specifically designed for atmosphere control. These models are more complex and costly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To select the correct furnace, match its capabilities directly to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing or basic analysis: A standard model rated for 1100°C or 1200°C offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is heat treating specialized steels or alloys: A mid-range furnace capable of reaching 1300°C will provide the necessary capability without the cost of a top-tier model.
- If your primary focus is sintering technical ceramics or advanced materials research: You must invest in a high-temperature model rated for 1700°C or 1800°C, built with the appropriate elements and insulation.
Ultimately, choosing the right muffle furnace means selecting a tool engineered for the specific temperature and precision your work demands.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Heating Elements | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Kanthal (FeCrAl) | Ashing, sintering low-temp powders, heat treating steel tools |
| 1300°C to 1800°C | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Sintering advanced ceramics, crystal growth, high-temp research |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















