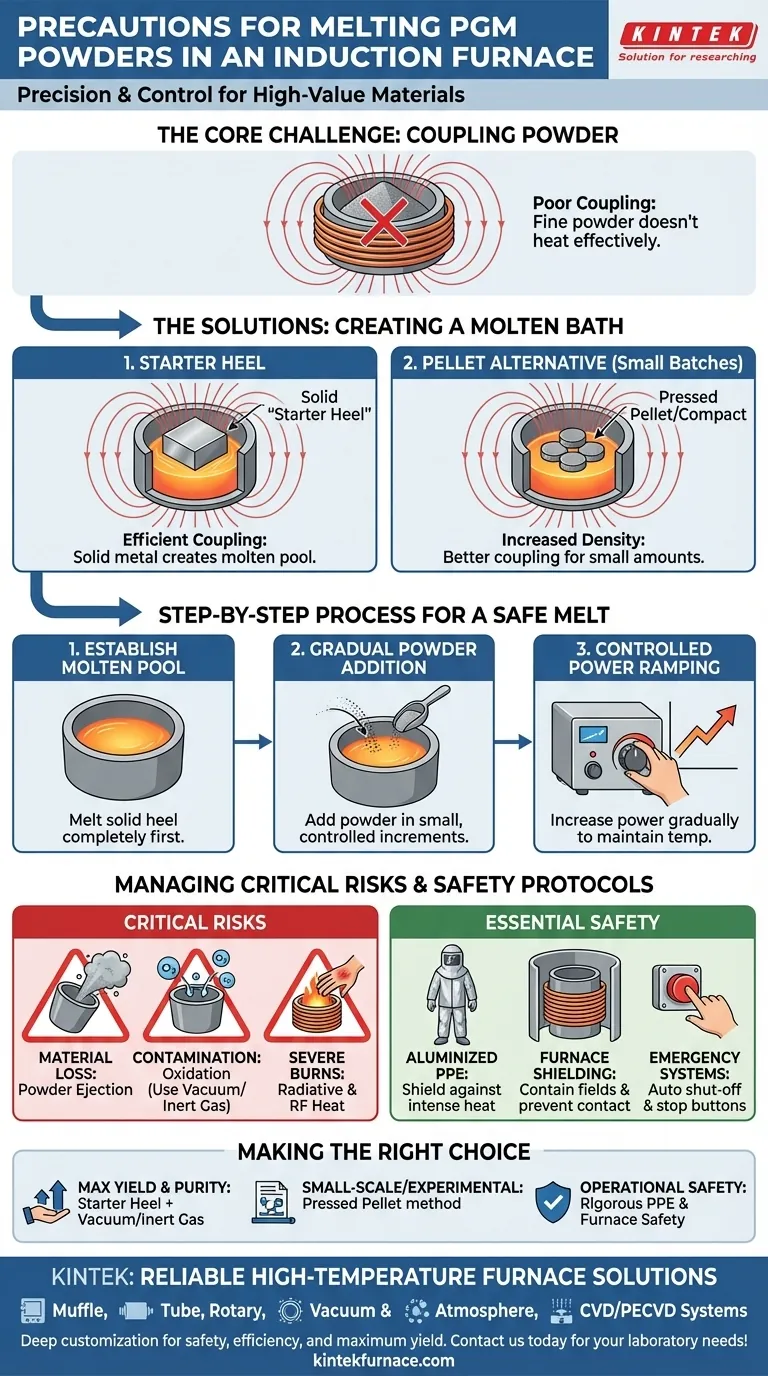
Melting Platinum Group Metal (PGM) powders in an induction furnace demands absolute precision. The primary precautions involve using a solid "starter heel" to initiate the melt, adding the powder slowly and incrementally, and ramping up the furnace power gradually. These steps are critical to prevent the electromagnetic field from ejecting the fine, non-conductive powder from the crucible, which would result in significant material loss.
The core challenge of melting PGM powders is their initial inability to couple with an induction field. The solution is not to heat the powder directly, but to first create a molten bath that the powder can be safely dissolved into.
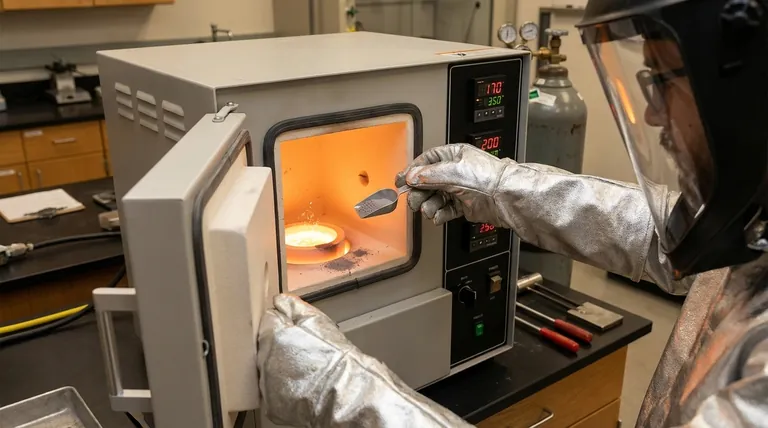

The Core Challenge: Coupling Powder with an Induction Field
Induction heating works by inducing electrical eddy currents within a conductive material. Fine powders, with high surface area and poor particle-to-particle contact, are poor conductors and do not couple effectively with the magnetic field.
The Solution: The Starter Heel
A starter heel is a solid piece of the same metal or a compatible parent alloy. This solid piece is placed in the crucible first.
Because it is a dense, conductive mass, the heel couples efficiently with the induction field and melts, creating a molten pool. This pool serves as the medium for melting the powder.
Alternative for Small Batches: Pressing Pellets
For very small quantities, an effective alternative is to press the PGM powder into a dense pellet or compact.
By mechanically compacting the powder, you increase its density and electrical continuity. This allows the pellet to couple with the induction field more effectively than loose powder, sometimes eliminating the need for a separate starter heel.
A Step-by-Step Process for a Safe Melt
A successful melt is defined by control. The goal is to transfer energy into the material without physically displacing it.
1. Establish the Molten Pool
Begin by placing the starter heel in the center of the crucible. Apply power to melt the heel completely, establishing a stable molten bath.
2. Gradual Powder Addition
Once the heel is fully molten, begin adding the PGM powder in small, controlled increments. Do not dump the entire charge in at once.
Adding the powder slowly allows it to be assimilated into the hot liquid metal without overwhelming the bath or floating on top.
3. Controlled Power Ramping
As you add powder, the overall temperature of the melt may drop. Increase the power gradually to compensate.
Sudden power spikes can intensify the electromagnetic stirring effect of the field, which can easily eject the lightweight, un-melted powder from the crucible.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Risks
While efficient, induction melting of powders carries inherent risks that must be managed through process control and proper safety protocols.
Risk of Material Loss
The single greatest operational risk is blowing powder out of the crucible. PGMs are exceptionally valuable, and even minor losses are costly. This is a direct consequence of adding powder too quickly or applying power too aggressively.
Risk of Contamination and Oxidation
PGMs are often melted for high-purity applications. Melting in a standard atmosphere can introduce oxygen and other contaminants.
For this reason, high-purity melts must be performed under a vacuum or in an inert gas atmosphere (like argon). This protects the molten metal from reacting with air, ensuring the final product's integrity.
Risk of Severe Burns
Induction furnaces generate intense heat. Radiative heat can cause severe burns even from a distance.
Additionally, the high-frequency currents in the coil can cause severe RF (Radio-Frequency) burns if an operator gets too close or if the coil is unshielded.
Essential Safety Protocols
Beyond the melting process itself, a strict safety posture is non-negotiable.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Operators must wear aluminized protective gear. This reflective material is specifically designed to shield against the intense radiative heat produced during melting. Standard flame-retardant clothing is not sufficient.
Furnace and Electrical Safety
The induction coil must be properly shielded to contain the magnetic field and prevent accidental contact and RF burns.
Ensure the furnace is equipped with modern safety features, including emergency stop buttons and automatic shut-off systems for thermal or electrical faults. All equipment must meet current industry safety regulations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific approach should be tailored to the scale and goals of your melt.
- If your primary focus is maximum yield and purity: The starter heel method within a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere is the definitive process.
- If your primary focus is small-scale or experimental melts: Pressing the powder into a dense pellet is a highly effective and efficient starting point.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Rigorous adherence to PPE standards, especially aluminized gear, and ensuring furnace safety systems are functional is the absolute baseline for any operation.
Mastering this process transforms a difficult task into a reliable and highly efficient manufacturing step.
Summary Table:
| Precaution | Purpose | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Use Starter Heel | Initiate melt safely | Solid conductive mass creates molten pool for powder dissolution |
| Add Powder Gradually | Prevent ejection | Small increments avoid overwhelming bath and material loss |
| Ramp Power Slowly | Control temperature | Gradual increases reduce electromagnetic stirring risks |
| Use Vacuum/Inert Gas | Prevent contamination | Protects PGM purity from oxidation in high-purity applications |
| Wear Aluminized PPE | Ensure operator safety | Shields against intense radiative heat and RF burns |
Need reliable high-temperature furnace solutions for your PGM melting processes? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we tailor solutions to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring safety, efficiency, and maximum yield. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity



















