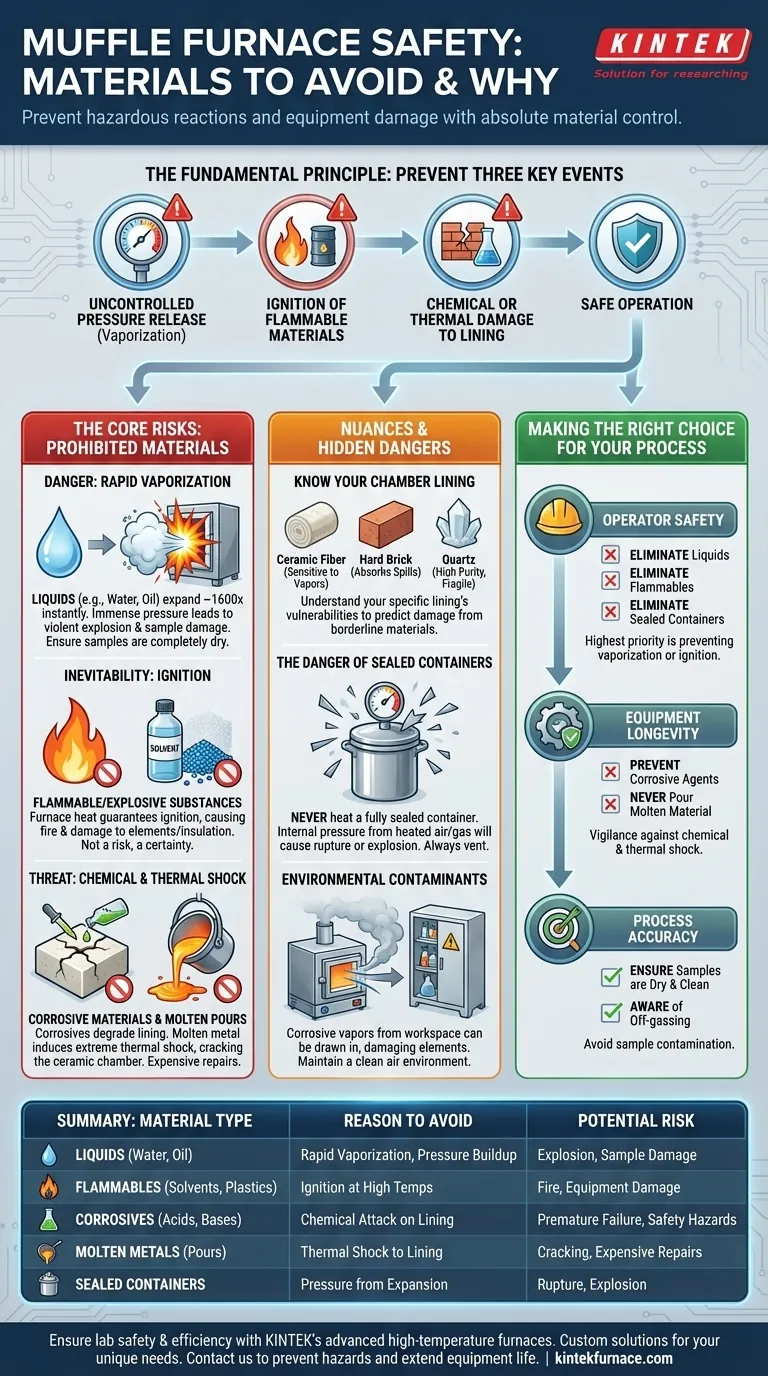
Operating a muffle furnace demands absolute control over the materials you introduce. To prevent hazardous reactions and equipment damage, you must strictly avoid placing any liquids (like water or oil), flammable or explosive substances, or materials that cannot withstand the programmed temperatures. Furthermore, never pour molten metals or other liquids directly into the furnace chamber, as this can cause catastrophic failure.
The fundamental principle of muffle furnace safety is to prevent three key events: uncontrolled pressure release from vaporization, ignition of flammable materials, and chemical or thermal damage to the furnace's interior lining. Every material choice must be evaluated against these three risks.

The Core Risks: Why Certain Materials Are Prohibited
A muffle furnace is not simply an oven; it is a high-energy environment where seemingly benign materials can become hazardous. Understanding the underlying "why" behind the rules is critical for safe operation.
The Danger of Rapid Vaporization
Any liquid introduced into a hot furnace will vaporize almost instantly. Water, for example, expands to over 1,600 times its original volume when it turns to steam.
This rapid expansion creates immense pressure inside the furnace chamber. If the pressure cannot vent quickly enough, it can lead to a violent explosion, potentially ejecting the door and hazardous materials.
This risk also applies to samples that are not completely dry. Trapped moisture within a seemingly solid sample can cause it to crack, shatter, or explode.
The Inevitability of Ignition
A muffle furnace operates at temperatures far exceeding the autoignition point of virtually all flammable and explosive materials.
Placing substances like oils, solvents, or certain plastics into the furnace is not a fire risk; it is a guarantee of ignition. This can cause a fire or deflagration that damages the heating elements, insulation, and control systems.
The Threat of Chemical and Thermal Shock
The interior of a muffle furnace is typically lined with a specialized refractory ceramic. While durable against heat, this material is vulnerable to chemical attack and sudden temperature changes.
Corrosive substances, whether solid or in vapor form, can etch and degrade the furnace lining, compromising its structural integrity and leading to premature failure.
Pouring molten metal or other liquids into the chamber induces extreme thermal shock. The drastic and localized temperature difference will crack the ceramic lining, rendering the furnace unsafe and requiring expensive repairs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Beyond the obvious prohibitions, a true expert considers the subtle interactions between their sample and the furnace environment.
Know Your Furnace Chamber
Not all furnace linings are the same. Ceramic fiber is common and lightweight but can be sensitive to certain chemical vapors. Hard refractory brick is more robust but can absorb spills. Quartz chambers offer high purity and corrosion resistance but are more fragile.
Understanding your specific furnace's lining helps you predict which "borderline" materials or reactions might cause damage over time.
The Hidden Danger of Sealed Containers
Never heat a fully sealed container in a muffle furnace. Even if the contents are safe, the air or any off-gassing inside will expand upon heating.
This creates a pressure vessel. The container will eventually rupture or explode, turning an otherwise safe procedure into a major hazard. All crucibles and containers must be open or have a dedicated vent.
Beyond the Sample: Environmental Contaminants
The rule against corrosives extends to the area around the furnace. A strong ventilation system can draw fumes from nearby chemical storage into the furnace intake, leading to gradual corrosion of the heating elements and chamber.
Always maintain a clean workspace and ensure the air surrounding the furnace is free of volatile and corrosive vapors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal dictates your primary area of focus. Use this checklist to guide your material preparation and operational mindset.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Your highest priority is eliminating materials that can vaporize or ignite, such as liquids, flammables, and anything in a sealed container.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: You must be vigilant about preventing chemical and thermal shock by avoiding all corrosive agents and never pouring any liquid or molten material into the chamber.
- If your primary focus is process accuracy: Ensure your samples are completely dry and clean, and be aware of any potential off-gassing that could contaminate your sample or the furnace atmosphere.
By treating the furnace not just as a heater but as a controlled reaction environment, you ensure safety, longevity, and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Reason to Avoid | Potential Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Liquids (e.g., water, oil) | Rapid vaporization causes pressure buildup | Explosion, sample damage |
| Flammable/explosive substances | Ignition at high temperatures | Fire, equipment damage |
| Corrosive materials | Chemical attack on furnace lining | Premature failure, safety hazards |
| Molten metals | Thermal shock to lining | Cracking, expensive repairs |
| Sealed containers | Pressure buildup from expansion | Rupture, explosion |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can prevent hazards and extend equipment life—get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















