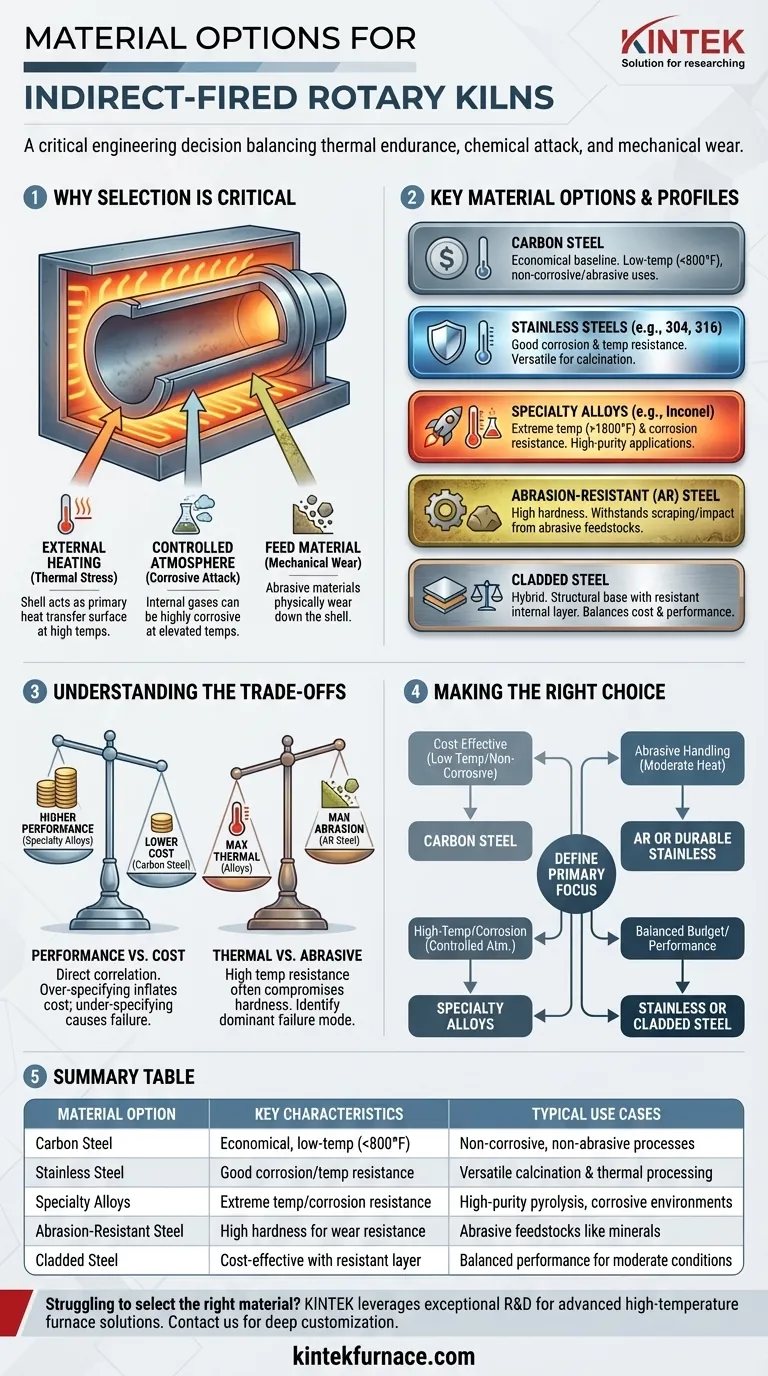
For indirect-fired rotary kilns, the primary material options for the kiln shell are carbon steel, stainless steel, specialty alloys, cladded steel, and abrasion-resistant (AR) steel. The final selection depends entirely on the operating temperature, the corrosiveness of the internal atmosphere, and the abrasiveness of the material being processed.
The choice of material for an indirect-fired kiln is not a simple menu selection; it is a critical engineering decision. The right material must balance thermal endurance against chemical attack and mechanical wear to ensure the integrity and efficiency of your entire process.
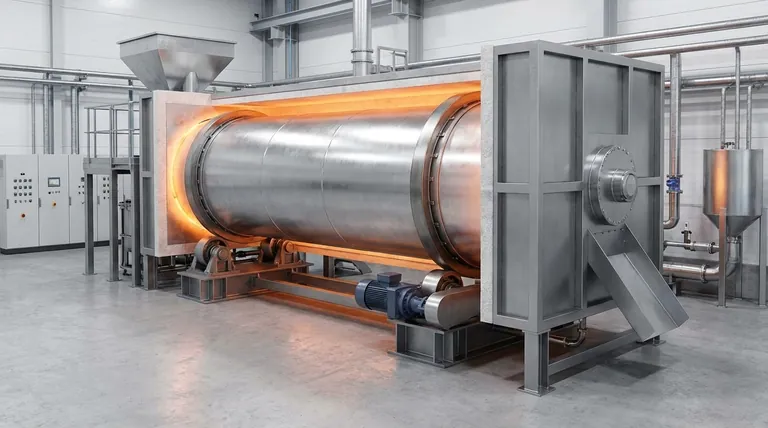

Why Material Selection is Critical for Indirect-Fired Kilns
An indirect-fired kiln operates by being enclosed within a furnace and heated externally. This fundamental design places unique and severe demands on the kiln's shell material.
The Demands of External Heating
The kiln shell itself acts as the primary heat transfer surface, conducting thermal energy from the external furnace to the material inside. This means the shell must maintain its structural integrity at extremely high and sustained operating temperatures.
Material failure due to thermal stress is a primary concern, making high-temperature strength a non-negotiable property for most applications.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
A key advantage of indirect kilns is their ability to maintain a specific, controlled atmosphere around the material. This is crucial for pyrolysis, calcination of high-value materials, or any process requiring an inert environment.
However, this internal atmosphere can be highly corrosive at elevated temperatures. The shell material must therefore resist chemical attack from the process gases to prevent degradation and contamination.
The Impact of the Feed Material
The physical and chemical characteristics of the material being processed directly influence the choice of kiln shell. Abrasive materials like silica sand or certain minerals will mechanically wear down the shell's interior surface over time.
Furthermore, some materials can have chemical reactions with the shell material at high temperatures, leading to corrosion or product contamination.
A Breakdown of Key Material Options
Each material category offers a specific profile of resistance to heat, corrosion, and abrasion. The choice involves matching this profile to your specific process conditions.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is the most economical option and serves as the baseline material. It is suitable for low-temperature applications (typically below 800°F or 425°C) where the material and internal atmosphere are non-corrosive and non-abrasive.
Stainless Steels
This category, including alloys like 304, 316, and 310, represents a significant step up in performance. Stainless steels offer good resistance to both corrosion and higher temperatures, making them a versatile choice for many calcination and thermal processing applications.
Specialty Alloys
For the most demanding conditions, specialty alloys like Inconel, Hastelloy, or other nickel-based alloys are required. These materials are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures (often exceeding 1800°F or 980°C) and aggressive chemical environments.
They are the standard for high-purity processing, pyrolysis, and applications involving highly corrosive substances where long-term reliability is paramount.
Abrasion-Resistant (AR) Steel
When the primary challenge is mechanical wear from abrasive feedstocks, AR steel is the preferred choice. This hardened steel is designed to withstand scraping and impact, extending the kiln's service life when processing abrasive minerals or particles.
Cladded Steel
Cladding offers a hybrid solution to balance cost and performance. This involves fabricating the kiln shell from a structural base metal, like carbon steel, and bonding a thin internal layer of a more resistant material, such as a specialty alloy.
This provides the required corrosion or heat resistance on the process-facing surface without the full cost of a solid alloy shell.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is an exercise in balancing competing factors. An ideal material for one metric is often a compromise on another.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between material performance and cost. The price increases significantly as you move from carbon steel to stainless steel and then to specialty alloys. Over-specifying a material unnecessarily inflates project costs, while under-specifying leads to premature failure and costly downtime.
Thermal Strength vs. Abrasive Resistance
Materials with the highest temperature resistance, like certain specialty alloys, may not possess the best hardness for resisting abrasion. Conversely, a very hard AR steel may have a limited operating temperature. You must identify the dominant failure mode—thermal stress, corrosion, or abrasion—and prioritize the material property that counters it.
Fabrication and Maintenance
Specialty alloys are often more difficult and expensive to weld, machine, and repair than carbon or stainless steels. This can impact not only the initial fabrication cost but also the complexity and cost of any future modifications or field repairs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision must be guided by the specific demands of your application. Begin by defining your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a low-temperature, non-corrosive process: Carbon steel is the most logical starting point.
- If your primary focus is handling abrasive minerals with moderate heat: Prioritize AR steel or a durable stainless steel grade.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (pyrolysis, calcination) in a controlled atmosphere: Specialty alloys are essential for process integrity and long-term reliability.
- If your primary focus is balancing budget with moderate corrosion and heat resistance: Stainless steel or cladded steel options provide a practical and effective compromise.
Ultimately, a thorough analysis of your process chemistry, temperature, and material characteristics will lead to an informed and defensible material selection.
Summary Table:
| Material Option | Key Characteristics | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Economical, low-temperature use (<800°F) | Non-corrosive, non-abrasive processes |
| Stainless Steel | Good corrosion/temp resistance (e.g., 304, 316) | Versatile calcination and thermal processing |
| Specialty Alloys | Extreme temp/corrosion resistance (e.g., Inconel) | High-purity pyrolysis, corrosive environments |
| Abrasion-Resistant Steel | High hardness for wear resistance | Abrasive feedstocks like minerals |
| Cladded Steel | Cost-effective with resistant internal layer | Balanced performance for moderate conditions |
Struggling to select the right material for your indirect-fired rotary kiln? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—ensuring optimal performance, durability, and efficiency for your lab. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your process and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- How do vibrational feeder specifications impact rotary kiln efficiency? Optimize Your Lab's Material Flow & Stability
- What role does gas flow and combustion play in a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer for Efficiency and Quality
- What supporting equipment is needed for a rotary kiln system? Essential Components for Efficient Thermal Processing
- What distinguishes direct from indirect rotary kilns? Choose the Right Kiln for Your Material
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















