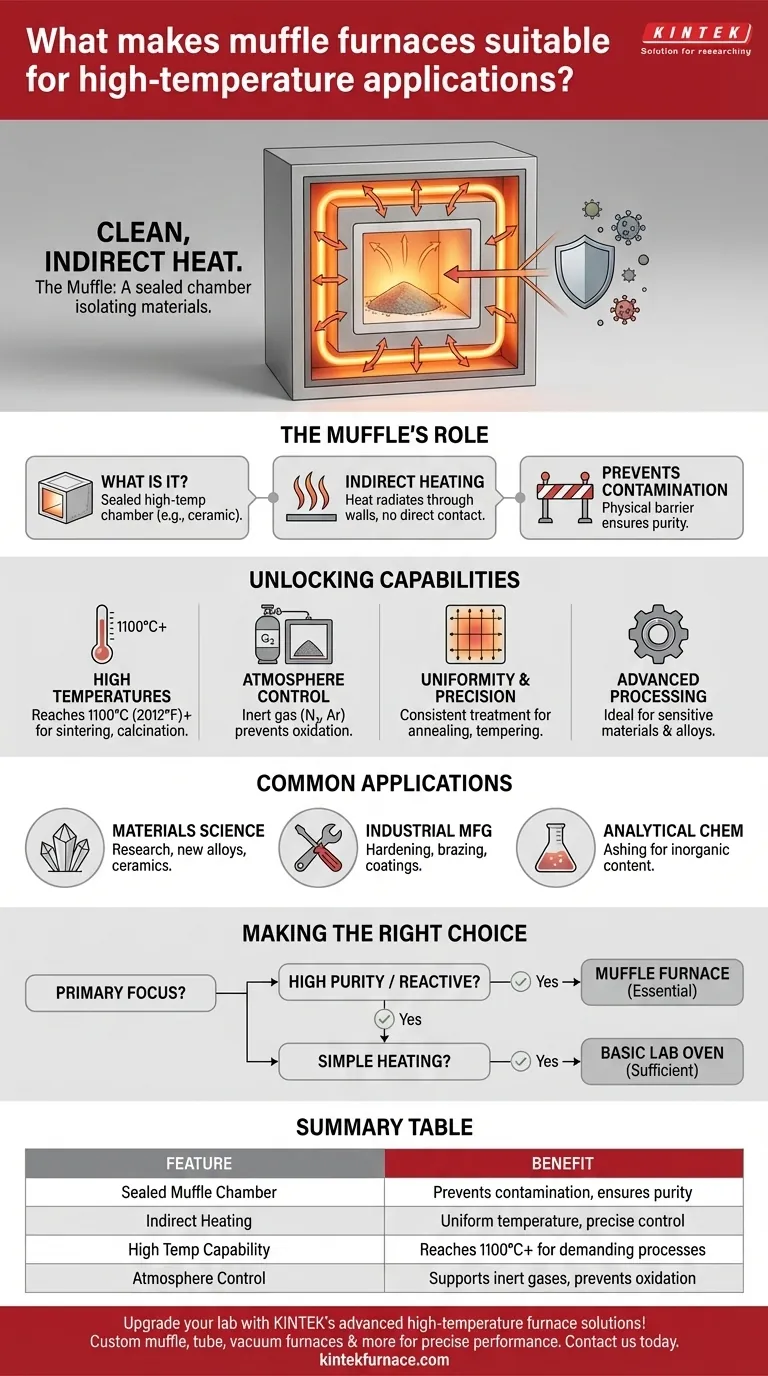
At its core, a muffle furnace is suitable for high-temperature applications because of its unique design. It uses a sealed internal chamber, the "muffle," to isolate materials from the heating elements and external atmosphere. This indirect heating method not only allows it to reach very high temperatures but also prevents contamination, ensuring the purity of the process.
The defining advantage of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its ability to provide clean heat. Its design fundamentally separates the material being processed from the source of the heat, enabling high-purity results that are impossible in a standard furnace.

The Defining Feature: The Role of the Muffle
A muffle furnace's capabilities are rooted in its core component: the muffle itself. Understanding this chamber is key to understanding its value.
What is a Muffle?
A muffle is a sealed, enclosed chamber made of a material resistant to high temperatures, often a type of ceramic. This chamber sits inside the furnace and holds the materials to be heated.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
The heating elements of the furnace heat the outside of the muffle. The heat then radiates through the muffle's walls to uniformly heat the materials inside. The material never comes into direct contact with the heating elements or any combustion byproducts.
Preventing Contamination
This separation is critical. In many high-temperature processes, direct exposure to heating elements or fuel combustion can introduce impurities. The muffle acts as a physical barrier, ensuring that the sample remains in a pure, controlled environment.
Unlocking Advanced Material Processing
The muffle design enables several capabilities essential for modern science and industry.
Achieving High Temperatures
Muffle furnaces are engineered to reach temperatures of 1100°C (2012°F) or higher, often with rapid heat-up times. This makes them ideal for tasks that demand intense thermal energy, such as sintering, calcination, and assaying metals.
Atmosphere Control for Sensitive Materials
Because the muffle is a sealed chamber, the internal atmosphere can be precisely controlled. Air can be removed and replaced with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon. This is vital for preventing oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions when heat-treating special alloys, superalloys, or refractory metals.
Ensuring Uniformity and Precision
The design promotes exceptional temperature uniformity throughout the chamber. This precise and even heating is crucial for processes like annealing, tempering, and firing ceramics, where consistent thermal treatment is necessary to achieve the desired material properties.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The unique combination of high, clean, and controlled heat makes muffle furnaces indispensable across various fields.
Materials Science and Research
Researchers use muffle furnaces for creating high-purity materials, testing thermal resistance, and developing new alloys and ceramics.
Industrial Manufacturing
Applications are widespread, including hardening metal tools, brazing components, creating enamel coatings on cookware, and producing technical ceramics for the electronics and aerospace industries.
Analytical Chemistry
In analytical labs, muffle furnaces are used for ashing—the process of burning off organic substances to determine the inorganic content of a sample. The contamination-free environment ensures the accuracy of the results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct tool, consider the specific requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity results: The muffle furnace is essential, as its isolation prevents contamination from the heating elements or combustion.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals or materials: The ability to introduce a controlled, inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation makes it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is simply heating a non-sensitive material: A more basic laboratory oven may be a sufficient and more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing a muffle furnace is a decision to prioritize the quality and purity of the heating environment over simply achieving a high temperature.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed Muffle Chamber | Prevents contamination and ensures material purity |
| Indirect Heating | Allows uniform temperature distribution and precise control |
| High Temperature Capability | Reaches up to 1100°C or higher for demanding processes |
| Atmosphere Control | Supports inert gases to prevent oxidation and unwanted reactions |
| Common Applications | Includes sintering, ashing, annealing, and material testing |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, rotary furnaces, vacuum & atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures precise performance for materials science, industrial processes, and analytical applications. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable, contamination-free heating can enhance your results and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















