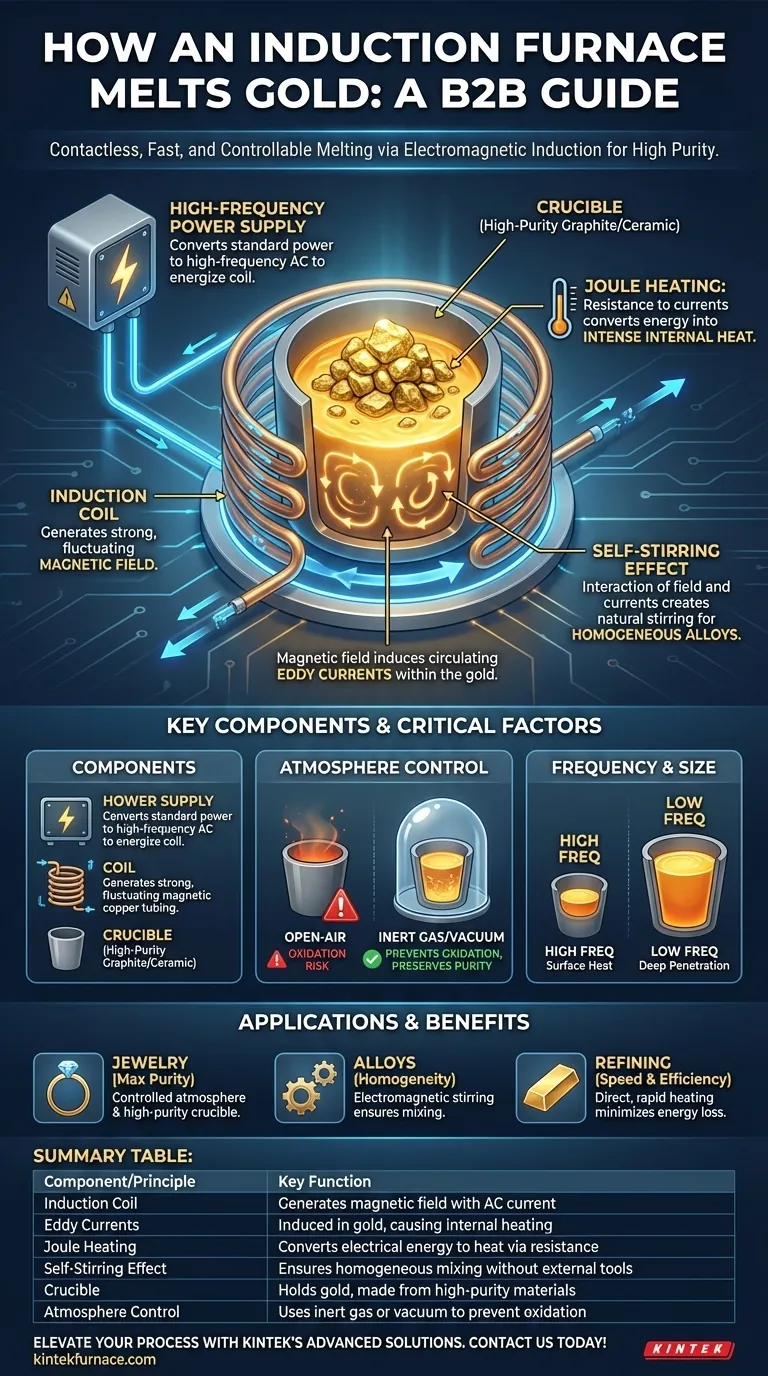
At its core, an induction furnace melts gold by using a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field to generate intense heat directly within the metal itself. This process, known as electromagnetic induction, is entirely contactless, avoiding direct flames or external heating elements. The result is an exceptionally fast, clean, and controllable melting process ideal for precious metals.
The true advantage of induction melting for gold isn't just the heat, but the inherent control it provides. By generating heat inside the gold via eddy currents, the process is naturally clean, self-stirring, and highly efficient, making it the superior method for preserving the value and purity of precious metals.
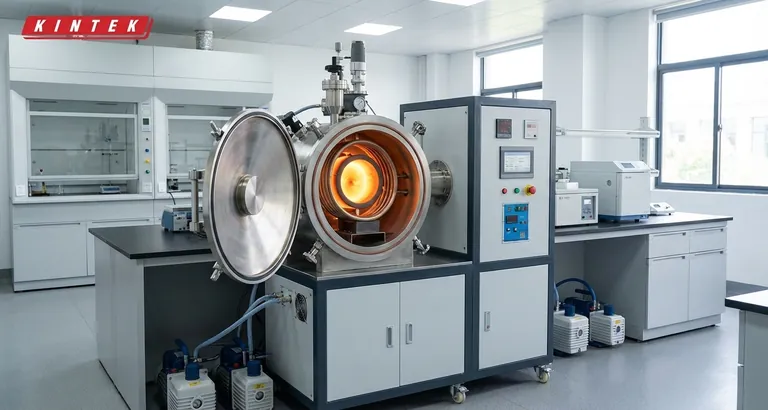

The Core Principle: Heat from Magnetism
The working principle of an induction furnace relies on a fundamental law of physics described by Maxwell's equations. It efficiently converts electrical energy into a magnetic field, and then into heat within the target material.
The Induction Coil and Magnetic Field
The process begins when a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through a copper induction coil. This coil, typically water-cooled to handle the high power, generates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around it.
Generating Eddy Currents in the Gold
When a conductive material like gold is placed inside the crucible within this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents within the gold. These circulating currents are known as eddy currents.
Resistance and Joule Heating
Like any electrical current passing through a conductor, these eddy currents encounter the gold's natural electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy of the eddy currents into intense heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. The heat is generated inside the gold itself, causing it to heat and melt rapidly from the inside out.
The Self-Stirring Effect
A unique and critical benefit of induction is the natural stirring action. The interaction between the powerful magnetic field and the electrical currents flowing through the molten gold creates a force that gently and continuously stirs the liquid metal. This electromagnetic stirring ensures a homogenous temperature and is invaluable for creating perfectly mixed alloys.
Key Components of a Gold Melting System
An induction furnace is a system of specialized components working in concert. For gold, each component's quality is critical to maintaining the purity of the final product.
The High-Frequency Power Supply
This is the engine of the system. It converts standard electrical power into the high-frequency AC required to energize the induction coil and create the necessary magnetic field.
The Water-Cooled Induction Coil
This custom-shaped copper coil is the heart of the furnace. It is precisely engineered to create a concentrated magnetic field that couples efficiently with the gold charge in the crucible.
The Crucible: The Vessel of Purity
The crucible holds the gold and must be able to withstand extreme temperatures without reacting with or contaminating the molten metal. For gold melting, materials like high-purity graphite and specialized ceramics are used. The choice of crucible is a non-negotiable factor in achieving high-purity results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
While highly effective, success with induction melting requires understanding a few key variables.
Atmosphere Control is Crucial
Induction heating can be performed under various atmospheres. For a high-value metal like gold, melting in an open-air environment can lead to some oxidation. Using a controlled atmosphere of inert gas (like Argon) or a vacuum prevents oxidation, protects against impurities, and preserves the total weight and quality of the melt.
Crucible Selection and Lifespan
The intense, rapid heating places significant thermal stress on the crucible. You must use a crucible specifically rated for your furnace and the temperatures you will achieve. Improper selection can lead to crucible failure and a catastrophic loss of the melt.
Frequency and Melt Size
The frequency of the alternating current influences how deeply the eddy currents penetrate the material. Higher frequencies are used for smaller quantities of gold as they concentrate the heat near the surface, while lower frequencies penetrate more deeply and are better for larger melts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the right induction setup depends entirely on your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity for small-batch jewelry work: Prioritize a furnace with excellent atmosphere control (vacuum or inert gas) and use high-purity graphite or ceramic crucibles.
- If your primary focus is creating gold alloys: The natural electromagnetic stirring is your greatest asset, ensuring a completely homogenous final product without the need for mechanical mixing.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency in refining: The direct, rapid heating of induction melting minimizes both energy loss and processing time compared to traditional flame or resistance furnaces.
By understanding these principles, you can leverage induction technology not just to melt gold, but to do so with precision, efficiency, and uncompromising quality.
Summary Table:
| Component/Principle | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Induction Coil | Generates magnetic field with AC current |
| Eddy Currents | Induced in gold, causing internal heating |
| Joule Heating | Converts electrical energy to heat via resistance |
| Self-Stirring Effect | Ensures homogeneous mixing without external tools |
| Crucible | Holds gold, made from high-purity materials |
| Atmosphere Control | Uses inert gas or vacuum to prevent oxidation |
Ready to elevate your gold melting process with precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for laboratories and precious metal applications. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs—ensuring fast, clean, and controllable melting for maximum purity and value preservation. Contact us today to discuss how our induction furnaces can optimize your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















