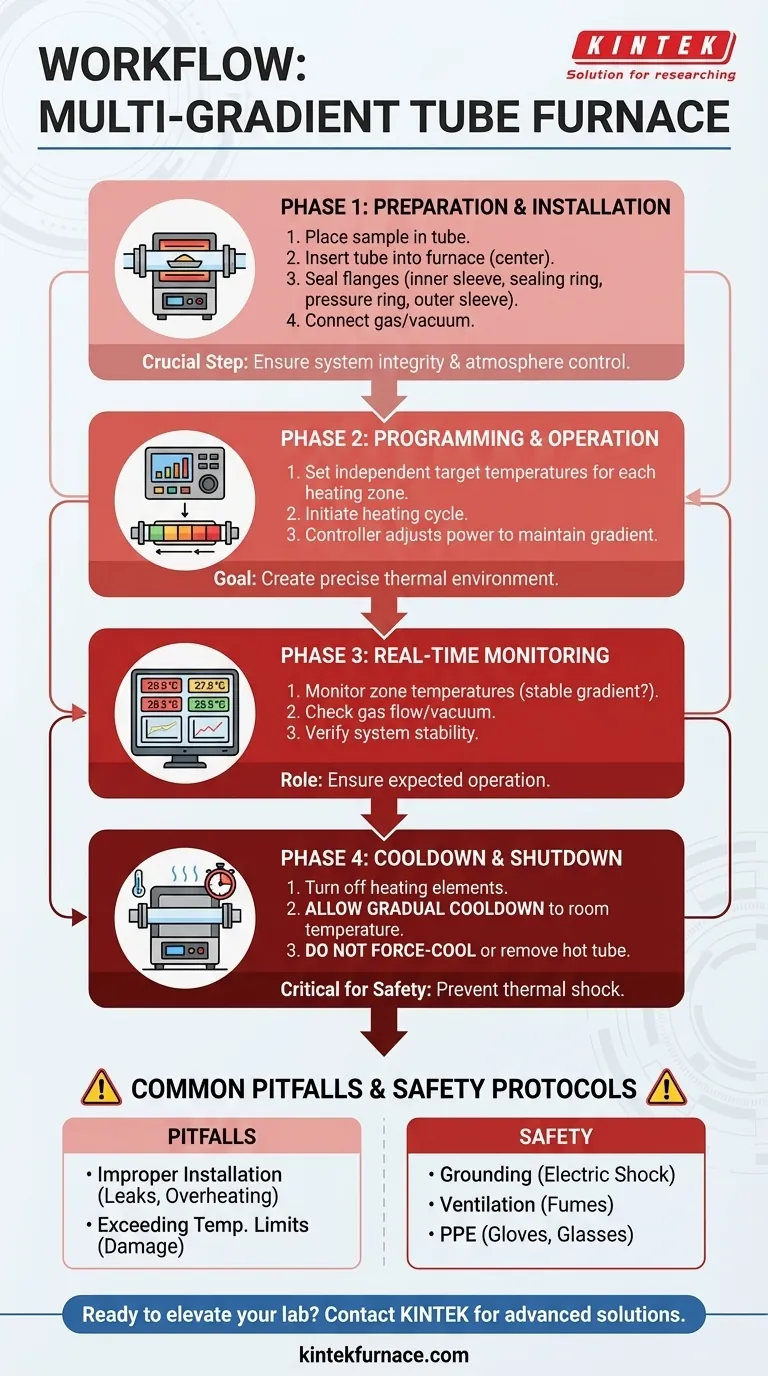
The typical workflow for a multi-gradient experimental tube furnace involves a precise sequence of setup, programming, operation, and shutdown. You begin by installing the furnace tube and placing your sample, then seal the system to control the atmosphere. Next, you program the independent temperature setpoints for each heating zone to create the desired thermal gradient, initiate the heating cycle, and allow the automated control system to maintain it. The process concludes with a controlled cooldown and shutdown phase.
A multi-gradient furnace is a powerful tool for process optimization, but its effective use hinges on a methodical workflow. The key is understanding that you are not just heating a sample, but carefully engineering a precise thermal environment across multiple distinct zones.
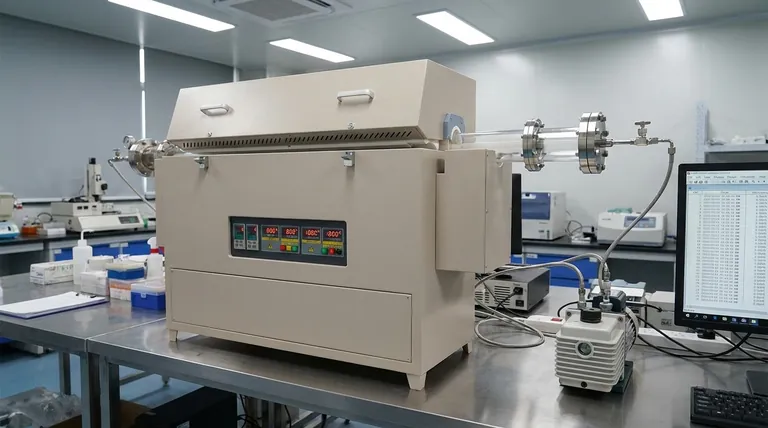

Deconstructing the Multi-Gradient Furnace
To master the workflow, you must first understand the core principles of the equipment. A multi-gradient furnace is not a simple oven; it's a sophisticated system designed for precision.
The Power of Multiple Heating Zones
The defining feature is its set of independent heating zones arranged along the length of the furnace tube. Each zone has its own resistance heating elements and a dedicated temperature sensor, typically a thermocouple.
This design allows you to set a different temperature for each zone, creating a stable and predictable temperature gradient along the sample. This is essential for experiments like crystal growth, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or studying material phase transitions.
The Control System: The Brains of the Operation
A sophisticated control system orchestrates the entire process. It reads the temperature from each thermocouple in real-time.
The controller constantly compares this real-world temperature to your programmed setpoint for that zone. It then precisely adjusts the electrical power sent to the heating elements to eliminate any deviation, ensuring the target gradient is maintained.
How Heat Reaches Your Sample
The furnace transfers energy to your sample through three mechanisms:
- Conduction: Direct heat transfer from the hot inner tube wall to the sample holder.
- Convection: Heat transfer via the movement of gas inside the tube, if an atmosphere is present.
- Radiation: Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves emitted from the hot heating elements and furnace walls.
The Core Workflow: A Step-by-Step Guide
Executing a successful experiment requires discipline and attention to detail at every stage. Follow this four-phase process for repeatable and safe results.
Phase 1: Preparation and Installation
This is the most critical hands-on phase. Errors here can compromise your experiment or damage the equipment.
First, place your experimental material inside the quartz or corundum furnace tube. Then, carefully slide the tube into the furnace, ensuring it is centered and does not touch the internal heating elements.
Next, seal the tube ends using the stainless steel flanges. The assembly order is critical: install the inner flange sleeve, the sealing ring, the pressure ring, and finally the outer flange sleeve. Tighten the screws evenly to prevent leaks or stress on the tube.
Finally, connect your gas lines or vacuum pump to the flange ports to create the desired experimental atmosphere.
Phase 2: System Programming and Operation
With the physical setup complete, you can program the heating profile. In the control system interface, you will enter the target temperature for each individual heating zone.
Once all parameters are set, you can begin the heating process. The furnace will start delivering power to the elements to ramp up to the programmed temperatures.
Phase 3: Real-Time Monitoring
During the experiment, the control system works automatically. Your main role is to monitor the system to ensure it is operating as expected.
Keep an eye on the real-time temperature display for each zone to confirm the gradient is stable and matches your intended profile. Also, monitor any gas flow rates or vacuum pressures.
Phase 4: Cooldown and Shutdown
Once the experimental duration is complete, you will turn off the heating elements via the control system.
Never force-cool the furnace or remove the tube while it is hot. The system must be allowed to cool down gradually to room temperature. Rapid temperature changes can cause thermal shock, cracking the furnace tube and potentially ruining your sample.
Common Pitfalls and Safety Protocols
Objectivity requires acknowledging risks. Misuse of a tube furnace can lead to failed experiments, equipment damage, or serious injury.
Pitfall: Improper Tube and Flange Installation
An uncentered tube can overheat and break. Improperly sealed flanges will lead to atmosphere leaks, contaminating your experiment and potentially creating a safety hazard if flammable or toxic gases are used. Always double-check your setup.
Pitfall: Exceeding Temperature Limits
Every furnace and furnace tube has a maximum rated temperature. Exceeding this limit will cause irreversible damage to the heating elements and the tube itself. Always operate within the manufacturer's specified limits.
Non-Negotiable: Safety First
- Grounding: Ensure the furnace is connected to a properly grounded power supply to prevent the risk of electric shock.
- Ventilation: Operate the furnace in a well-ventilated area, especially when using process gases, to prevent the buildup of hazardous fumes. Keep flammable materials away.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear high-temperature gloves and safety glasses when handling parts of the furnace, even when it appears cool.
Applying This to Your Experiment
Your specific goal will determine which part of the workflow you need to focus on most.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis (e.g., CVD): Your main concern is the precision of the temperature gradient and the integrity of your gas atmosphere. Meticulous flange sealing and programming are paramount.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: You will be running many cycles with varied parameters. Efficiency in the setup and shutdown phases becomes critical to maximizing your experimental throughput.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Repeatability is key. Document every setting in your workflow, from tube position to temperature ramp rates, to ensure your results can be reliably reproduced.
By treating the furnace not as a black box but as a precise instrument, you empower yourself to achieve reliable and insightful experimental outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Workflow Phase | Key Steps | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation & Installation | Install tube, place sample, seal flanges, connect gas/vacuum | Ensure system integrity and atmosphere control |
| Programming & Operation | Set zone temperatures, initiate heating cycle | Create and maintain precise thermal gradient |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Monitor temperatures, gas flow, vacuum | Verify stability and adjust as needed |
| Cooldown & Shutdown | Turn off heat, allow gradual cooldown | Prevent thermal shock and damage |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with precision high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for material synthesis, process optimization, or fundamental research. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your workflow and deliver reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How are multi zone tube furnaces used in ceramics, metallurgy and glass research? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing
- What steps are involved in the installation of a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Precision and Safety for Your Lab



















