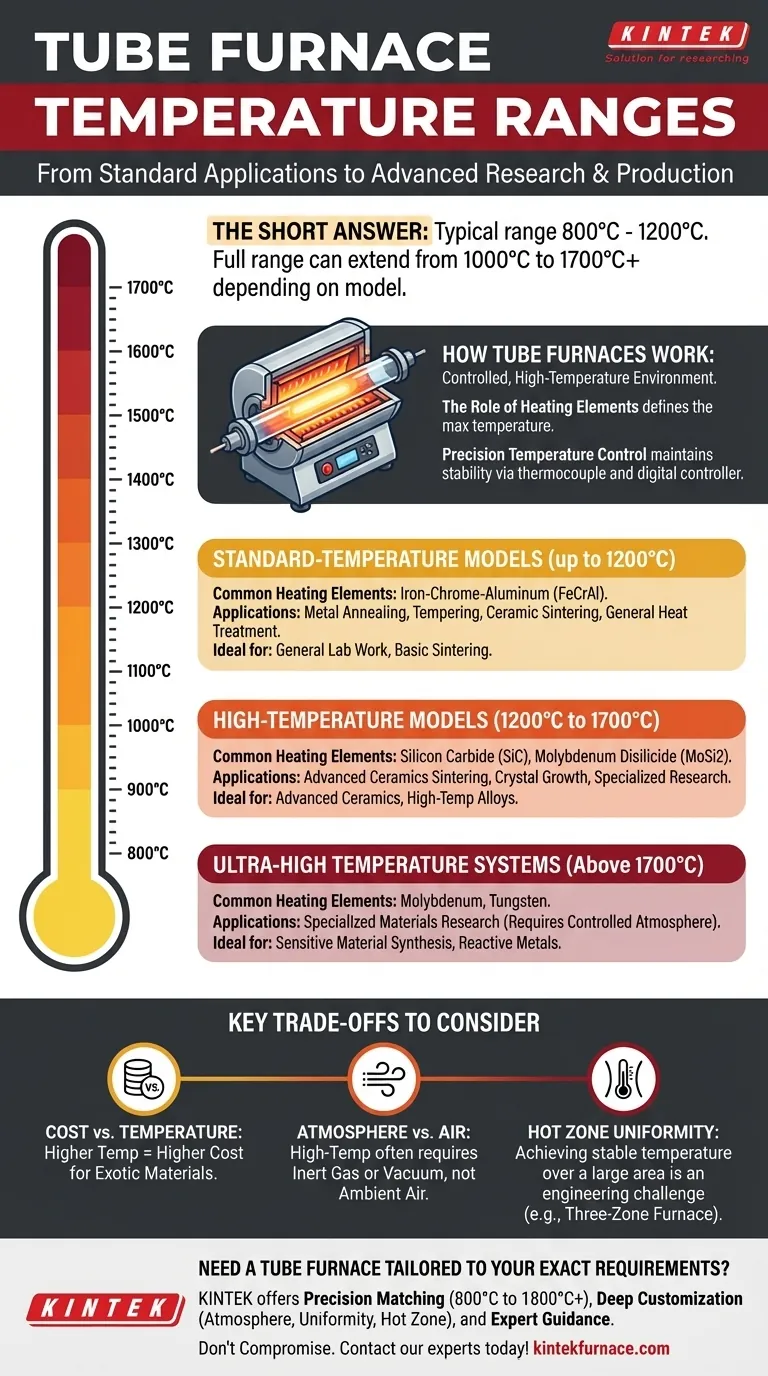
The short answer is that a typical tube furnace operates between 800°C and 1200°C, but the full range is much wider. Depending on the model and its heating elements, a tube furnace's maximum temperature can extend from around 1000°C for basic models to over 1700°C for high-temperature systems.
The term "tube furnace" describes a category of equipment, not a single specification. The functional temperature range is dictated entirely by the materials used in its construction, particularly the heating elements, and must be matched to your specific scientific or industrial process.

How Tube Furnaces Work
A tube furnace is a type of electric heating device that creates a controlled, high-temperature environment within a cylindrical cavity. A process tube, typically made of alumina, quartz, or mullite, is placed inside this heated chamber.
The Role of Heating Elements
The maximum achievable temperature of a tube furnace is determined by its heating elements. Different materials are used for different temperature tiers, as each has a maximum service temperature before it degrades. This is the single most important factor defining a furnace's capability.
Precision Temperature Control
Regardless of the maximum temperature, precision is maintained by a control system. A thermocouple inside the furnace measures the real-time temperature and sends this data to a digital controller, which then adjusts the power to the heating elements to maintain a stable, programmed setpoint.
Understanding the Temperature Tiers
Tube furnaces are not one-size-fits-all. They are engineered for specific temperature brackets based on their intended applications.
Standard-Temperature Models (up to 1200°C)
This is the most common and versatile category. These furnaces often use iron-chrome-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy heating elements.
Their operating range, often peaking around 1200°C, is ideal for a wide array of laboratory and industrial tasks, including metal annealing, tempering, ceramic sintering, and general material heat treatment.
High-Temperature Models (1200°C to 1700°C)
To achieve temperatures above 1200°C, furnaces must use more robust heating elements, such as silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
These systems are required for more demanding processes, including the sintering of advanced ceramics, crystal growth, and specialized materials research that requires temperatures between 1200°C and 1700°C.
Ultra-High Temperature Systems (Above 1700°C)
Reaching temperatures beyond 1700°C requires highly specialized equipment, often incorporating molybdenum or tungsten elements and requiring a controlled, non-oxidizing atmosphere (vacuum or inert gas) to prevent element failure. These are less common and built for very specific research applications.
Key Trade-offs to Consider
Choosing a furnace is about more than just hitting a peak temperature. You must balance capability with cost and practical limitations.
Cost vs. Temperature
There is a direct and steep correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its cost. The exotic materials required for heating elements and insulation at higher temperatures are significantly more expensive. Over-specifying your temperature needs is a costly mistake.
Atmosphere vs. Air
Many high-temperature material processes cannot be performed in ambient air. You must determine if your process requires an inert atmosphere (like argon) or a vacuum. A standard furnace may not have the sealed flanges and ports necessary for atmospheric control.
Hot Zone Uniformity
The "hot zone" is the area within the furnace tube that maintains a uniform temperature. Achieving a long, stable hot zone is a significant engineering challenge, especially at higher temperatures. For processes requiring consistent heat over a large sample, a three-zone furnace with multiple controllers may be necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace requires you to clearly define your process requirements first.
- If your primary focus is general lab work, annealing, or basic sintering: A standard furnace with a maximum temperature of 1200°C is almost always the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced ceramics or high-temperature alloys: You will need a high-temperature model capable of reaching 1500°C to 1700°C with appropriate heating elements.
- If your primary focus is sensitive material synthesis or working with reactive metals: Your decision must prioritize atmosphere control (vacuum or inert gas) just as much as the temperature range.
Ultimately, your selection should be guided by the specific temperature, atmosphere, and uniformity your process demands.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Tier | Typical Max. Temperature | Common Heating Elements | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Up to 1200°C | Iron-Chrome-Aluminum (FeCrAl) | Annealing, Tempering, General Material Heat Treatment |
| High-Temperature | 1200°C to 1700°C | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Advanced Ceramics Sintering, Crystal Growth |
| Ultra-High Temperature | Above 1700°C | Molybdenum, Tungsten | Specialized Materials Research (Requires Controlled Atmosphere) |
Need a Tube Furnace Tailored to Your Exact Requirements?
Choosing the wrong temperature range or configuration can lead to costly inefficiencies or process failures. At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide you with the perfect high-temperature solution.
- Precision Matching: Our product line—including Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces—is designed to cover the full spectrum from 800°C to 1800°C+.
- Deep Customization: We excel at modifying our standard models to meet your unique needs for temperature uniformity, atmosphere control (vacuum/inert gas), and hot zone length.
- Expert Guidance: Our team will help you navigate the trade-offs between cost, temperature, and atmosphere to ensure you get a furnace that perfectly aligns with your scientific or industrial goals.
Don't compromise your research or production quality. Contact our experts today for a free consultation and let us engineer a solution that drives your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















