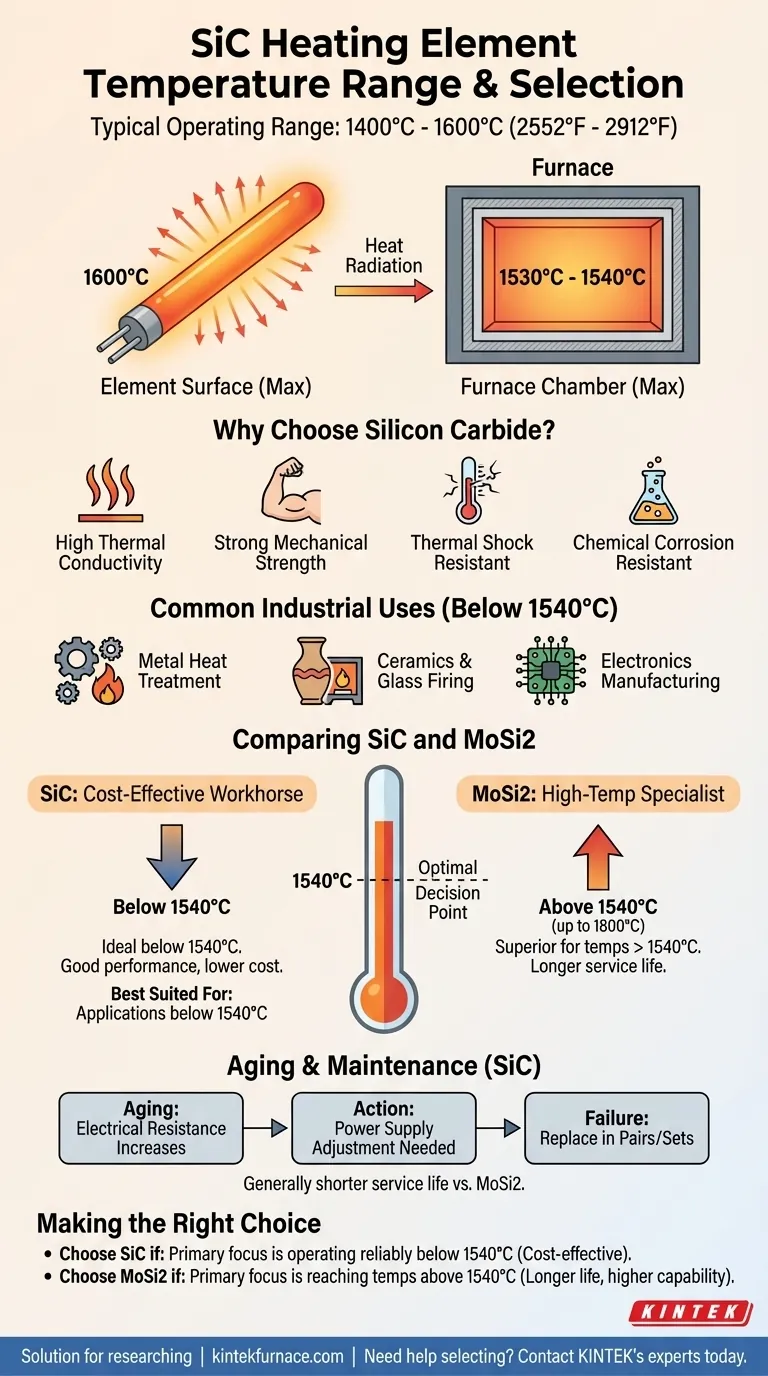
At a glance, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements operate in a typical range of 1400°C to 1600°C (2552°F to 2912°F). However, this is the maximum temperature of the element's surface. The resulting maximum temperature inside the furnace chamber is often lower, typically around 1530°C to 1540°C.
The decision to use SiC heating elements is not just about reaching a peak temperature. It is a strategic choice best suited for applications below 1540°C, where they provide a balance of cost-effectiveness and performance.

Understanding the Operating Range of SiC Elements
To properly select a heating element, you must look beyond the maximum temperature rating and understand how it performs in a real-world system.
The Difference Between Element and Furnace Temperature
A critical distinction exists between the temperature of the heating element itself and the ambient temperature of the furnace it is heating.
The element surface can reach up to 1600°C, but to achieve this, it radiates heat into the chamber. This transfer results in a maximum furnace temperature of approximately 1530°C to 1540°C.
Key Properties of Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide is not chosen for its heat resistance alone. It possesses a combination of properties that make it a reliable choice for demanding industrial environments.
These include excellent thermal conductivity, high mechanical strength, and strong resistance to both thermal shock and chemical corrosion.
Common Industrial Applications
The robust nature of SiC elements makes them suitable for a wide variety of high-temperature processes.
Common uses include heat treatment of metals, firing of advanced ceramics and glass, and the manufacturing of electronic components where precise and stable high temperatures are required.
Understanding the Trade-offs: SiC vs. MoSi2
Choosing SiC involves understanding its limitations, especially when compared to its main alternative for very high temperatures, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
When to Choose SiC: The Cost-Effective Workhorse
SiC elements are the ideal choice when your process requires temperatures up to the 1540°C range and cost is a significant consideration.
They provide excellent performance and reliability for a vast number of applications without needing the extreme temperature capabilities of more expensive alternatives.
When MoSi2 is the Better Choice
For processes that must operate above 1540°C, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) becomes the superior option.
MoSi2 elements can operate at temperatures up to 1800°C, offering a clear advantage for the most demanding high-temperature sintering and melting applications.
The Impact of Aging and Maintenance
SiC elements have a distinct operational lifespan that must be factored into maintenance planning.
Over time, the electrical resistance of SiC elements increases as they age. This requires adjustments to the power supply to maintain output. Furthermore, when a single element fails, they typically must be replaced in pairs or as a complete set to ensure balanced heating. This results in a generally shorter service life compared to MoSi2 elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the specific temperature profile and operational demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is operating reliably below 1540°C: SiC elements offer a robust and cost-effective solution for your heating needs.
- If your primary focus is reaching temperatures above 1540°C: Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements are the correct choice, providing a longer service life and higher temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term maintenance: Be aware that the shorter lifespan and set-based replacement of SiC may make MoSi2 a more economical choice over the long term, despite its higher initial cost.
Choosing the right heating element depends on a clear understanding of your specific temperature requirements and operational priorities.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Typical Element Temperature Range | 1400°C to 1600°C (2552°F to 2912°F) |
| Maximum Furnace Temperature | Approximately 1530°C to 1540°C |
| Key Properties | High thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, thermal shock and chemical corrosion resistance |
| Best Suited For | Applications below 1540°C, such as heat treatment, ceramics firing, and electronics manufacturing |
| Comparison with MoSi2 | SiC is cost-effective up to 1540°C; MoSi2 is better for temperatures above 1540°C up to 1800°C |
| Maintenance Considerations | Electrical resistance increases with age; elements often replaced in pairs or sets, leading to shorter service life vs. MoSi2 |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your high-temperature processes? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely match your unique experimental needs—ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency. Let our experts help you achieve superior results. Contact us today for a tailored consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















