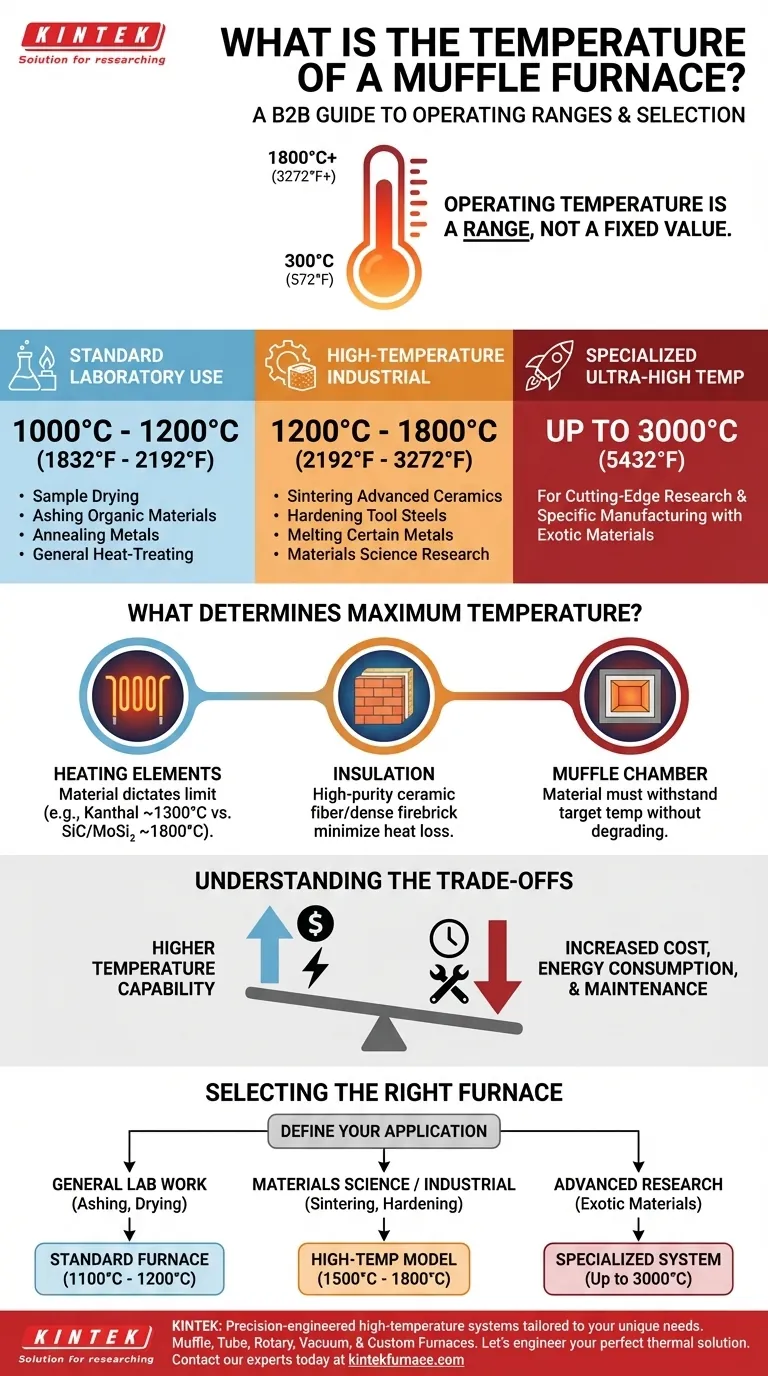
To be precise, a muffle furnace does not have one single temperature. Its operating temperature is a range that depends entirely on the model and its intended application, but most common furnaces operate between 300°C and 1800°C (572°F to 3272°F). Standard laboratory models typically max out around 1200°C, while more advanced industrial and research-grade furnaces can reach 1800°C or even higher.
A muffle furnace's temperature is not a fixed value but a specified range. The core challenge is not finding "the" temperature, but understanding which temperature range aligns with your specific scientific or industrial process, from basic ashing to advanced material sintering.

Deconstructing the Muffle Furnace Temperature Range
The term "muffle furnace" describes a broad category of equipment. The maximum achievable temperature is the primary factor that distinguishes one model from another.
The Standard for Laboratory Use
Most general-purpose muffle furnaces found in laboratories have a maximum temperature between 1000°C and 1200°C (1832°F to 2192°F).
This range is more than sufficient for a wide array of common applications, including sample drying, ashing organic materials, annealing metals, and general heat-treating processes.
High-Temperature Industrial Models
For more demanding applications, high-temperature furnaces are required. These models are designed to reliably operate in the range of 1200°C to 1800°C (2192°F to 3272°F).
These furnaces are essential for processes like sintering advanced ceramics, hardening tool steels, melting certain metals, and conducting materials science research that requires extreme heat.
Specialized Ultra-High Temperature Systems
In rare cases, highly specialized furnaces are engineered to exceed 1800°C. Some advanced models, used in cutting-edge research and specific manufacturing, can reach temperatures as high as 3000°C (5432°F). These are not typical muffle furnaces and are built for very specific tasks.
What Determines a Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
A furnace's temperature capability is not arbitrary; it's a direct result of its engineering and the materials used in its construction.
The Role of Heating Elements
The material of the heating elements is the single biggest factor. Different materials have different maximum service temperatures. For example, Kanthal (FeCrAl) elements are common up to ~1300°C, while silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) elements are needed to reach 1600°C-1800°C.
The Importance of Insulation
To reach and hold extreme temperatures efficiently, the furnace chamber must be exceptionally well-insulated. Materials like high-purity ceramic fiber and dense firebrick are used to minimize heat loss and protect the outer casing and electronics.
The "Muffle" Chamber
The muffle itself—the inner chamber that isolates the workload from the heating elements—must be made of a material that can withstand the target temperature without degrading. This ensures a clean, non-contaminated heating environment for the sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace with the highest possible temperature is not always the best strategy. There are critical trade-offs to consider.
Cost vs. Capability
There is a direct and steep correlation between maximum temperature and cost. A furnace capable of 1800°C can be many times more expensive than a 1200°C model due to the exotic materials required for its elements and insulation.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining higher temperatures requires exponentially more electrical power. An 1800°C process will have significantly higher operational costs than one at 1100°C.
Lifespan and Maintenance
Operating a furnace consistently at its maximum rated temperature will accelerate the degradation of its heating elements and insulation. This leads to more frequent, and often costly, maintenance and replacement.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Choosing a furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific goal. Over-specifying is costly, while under-specifying makes your work impossible.
- If your primary focus is general lab work (ashing, drying, basic heat treating): A standard furnace with a maximum temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C is sufficient and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is materials science or specific industrial processes (sintering ceramics, tool hardening): You will likely need a high-temperature model capable of reaching at least 1500°C to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is advanced research with exotic materials: You may require a specialized, ultra-high temperature system (up to 3000°C), which is a significant and highly specific investment.
Ultimately, the right choice is the furnace that reliably meets your required process temperature without unnecessary expense.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Typical Temperature Range | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Laboratory | 1000°C - 1200°C | Ashing, drying, annealing, general heat treatment |
| High-Temperature Industrial | 1200°C - 1800°C | Sintering ceramics, hardening tool steels, materials research |
| Specialized Systems | Up to 3000°C | Advanced research with exotic materials |
Struggling to match a furnace to your exact temperature requirements? KINTEK's expertise is your solution. We don't just sell furnaces; we deliver precision-engineered high-temperature systems tailored to your unique experimental needs.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced solutions. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you need a standard 1200°C lab furnace or a custom 1800°C+ system for sintering, we ensure it precisely fits your process, budget, and performance goals.
Let's engineer the perfect thermal solution for you. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















