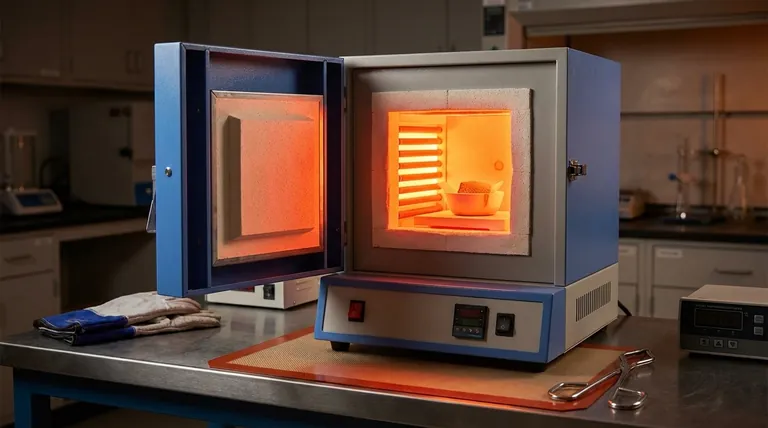
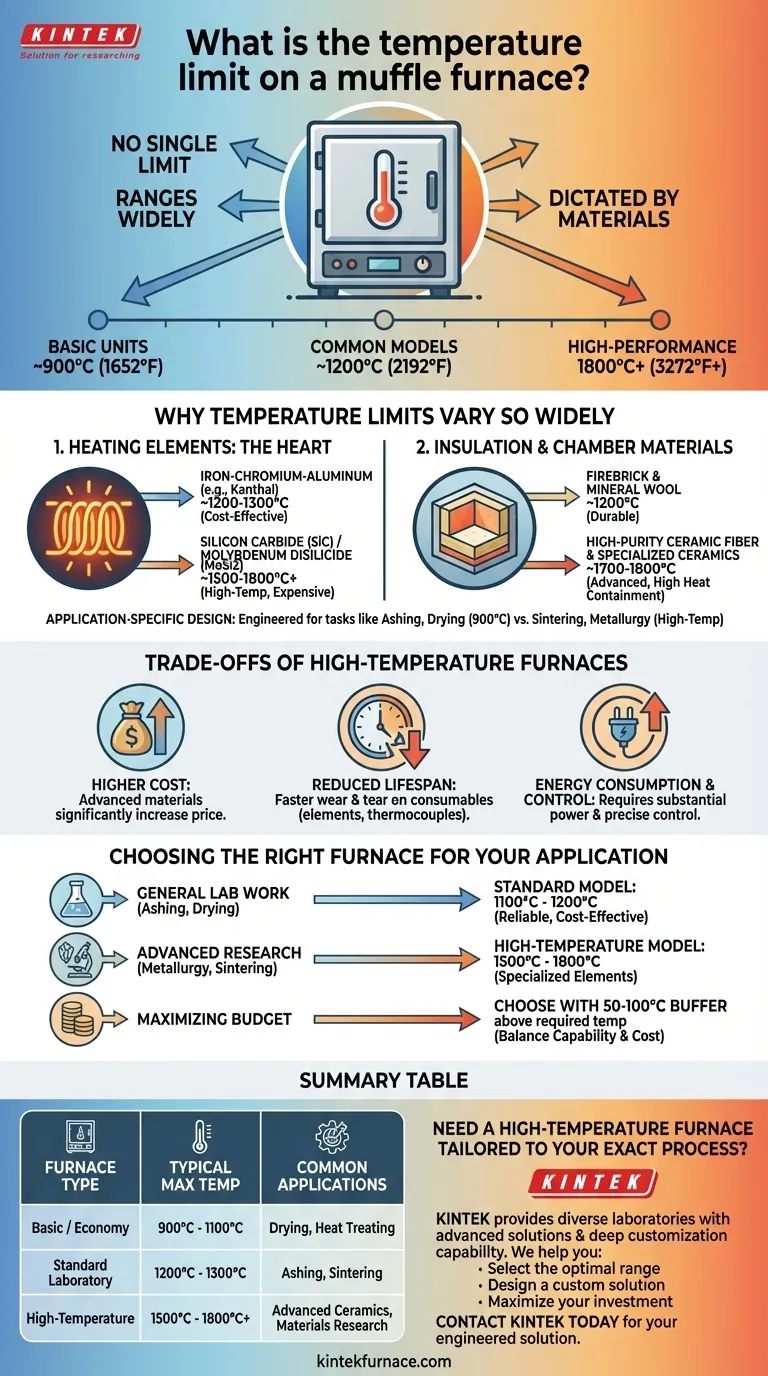
In short, there is no single temperature limit for a muffle furnace. While many common models operate up to 1200°C (2192°F), the maximum temperature can range from around 900°C for basic units to over 1800°C (3272°F) for specialized, high-performance models. The specific limit is dictated entirely by the furnace's construction and intended application.
A muffle furnace's temperature capability is not a generic feature but a direct result of its design. The limit is determined by the specific materials used for its internal heating elements and insulation, which are chosen to meet the demands of different scientific and industrial processes.

Why Temperature Limits Vary So Widely
The term "muffle furnace" describes a category of equipment, not a single specification. The significant variation in maximum temperature from one model to another stems directly from the materials used in its core components.
The Critical Role of Heating Elements
The heating elements are the heart of the furnace, and their material composition is the primary factor limiting the maximum temperature.
Different materials have different physical limits. For example, common iron-chromium-aluminum alloys (like Kanthal) are cost-effective but typically max out around 1200°C-1300°C.
To achieve higher temperatures, manufacturers must use more exotic and expensive materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), which can operate reliably at 1500°C to 1800°C and beyond.
The Importance of Insulation and Chamber Materials
A furnace can only get as hot as its insulation can contain. The chamber, or "muffle," must withstand the extreme heat without degrading.
Lower-temperature furnaces often use durable firebrick and mineral wool insulation. These are effective and robust for applications up to about 1200°C.
High-temperature models require advanced, high-purity ceramic fiber insulation and specialized ceramic chambers to prevent heat loss, ensure temperature uniformity, and withstand the thermal stress of reaching 1700°C or 1800°C.
Application-Specific Design
Furnaces are engineered for specific tasks, which dictates their temperature range. A furnace designed for simple ashing or drying may only need to reach 900°C.
In contrast, a furnace built for sintering advanced ceramics, growing crystals, or conducting metallurgical research must be capable of reaching and sustaining much higher temperatures. This tailored design approach is why you see such a broad range of specifications on the market.
Understanding the Trade-offs of High-Temperature Furnaces
Selecting a furnace with a higher temperature rating involves more than just a higher number on a spec sheet. It comes with critical trade-offs that impact cost, maintenance, and operation.
The Direct Impact on Cost
The single biggest trade-off is cost. The advanced materials required for high-temperature heating elements and insulation are significantly more expensive than their standard counterparts. A 1700°C furnace can cost several times more than a 1200°C model of the same size.
Reduced Lifespan of Consumables
Operating a furnace near its maximum rated temperature accelerates the wear and tear on its components. Heating elements and thermocouples are consumables with a finite lifespan. The hotter you run the furnace, and the more frequently you do it, the faster they will degrade and require replacement.
Energy Consumption and Control
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1700°C or 1800°C requires a substantial amount of electrical power. This not only increases operational costs but also places greater demands on your facility's electrical infrastructure. Furthermore, precise temperature control becomes more challenging at these extremes.
Choosing the Right Furnace for Your Application
To make an informed decision, you must match the furnace's capabilities to your specific process requirements. Over-specifying a furnace leads to unnecessary expense, while under-specifying it makes your work impossible.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing, drying, or basic heat treating: A standard 1100°C or 1200°C model is almost always sufficient, reliable, and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research, metallurgy, or ceramic sintering: You must invest in a high-temperature model (1500°C to 1800°C) with the appropriate heating elements to meet your process demands.
- If your primary focus is maximizing your budget: Choose a furnace with a maximum temperature that provides a 50-100°C buffer above your highest required process temperature, but no more, to balance capability with cost.
Understanding that the temperature limit is a function of material science empowers you to select the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Basic / Economy | 900°C - 1100°C | Drying, Loss on Ignition, Basic Heat Treating |
| Standard Laboratory | 1200°C - 1300°C | Ashing, Sintering, General Lab Work |
| High-Temperature | 1500°C - 1800°C+ | Advanced Ceramics, Metallurgy, Materials Research |
Need a High-Temperature Furnace Tailored to Your Exact Process?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
We can help you:
- Select the optimal temperature range to avoid over-spending or under-performing.
- Design a custom solution with the right heating elements and insulation for your specific application.
- Maximize your investment with a furnace that provides the perfect balance of capability, cost, and longevity.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your high-temperature needs and get a solution engineered for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















