The primary technical role of a muffle furnace in this context is the thermal activation of waste material. By subjecting dyeing sludge to controlled high temperatures—specifically around 400 °C—the furnace effectively eliminates moisture and volatile organic matter. This process chemically alters the sludge, activating its pozzolanic properties and transforming it into a viable supplementary cementitious material capable of replacing standard cement.
The muffle furnace serves as the critical reaction vessel that converts hazardous industrial waste into a stabilized construction resource. By precisely controlling the thermal environment, it ensures the destruction of impurities while optimizing the material's chemical reactivity for use in concrete systems.
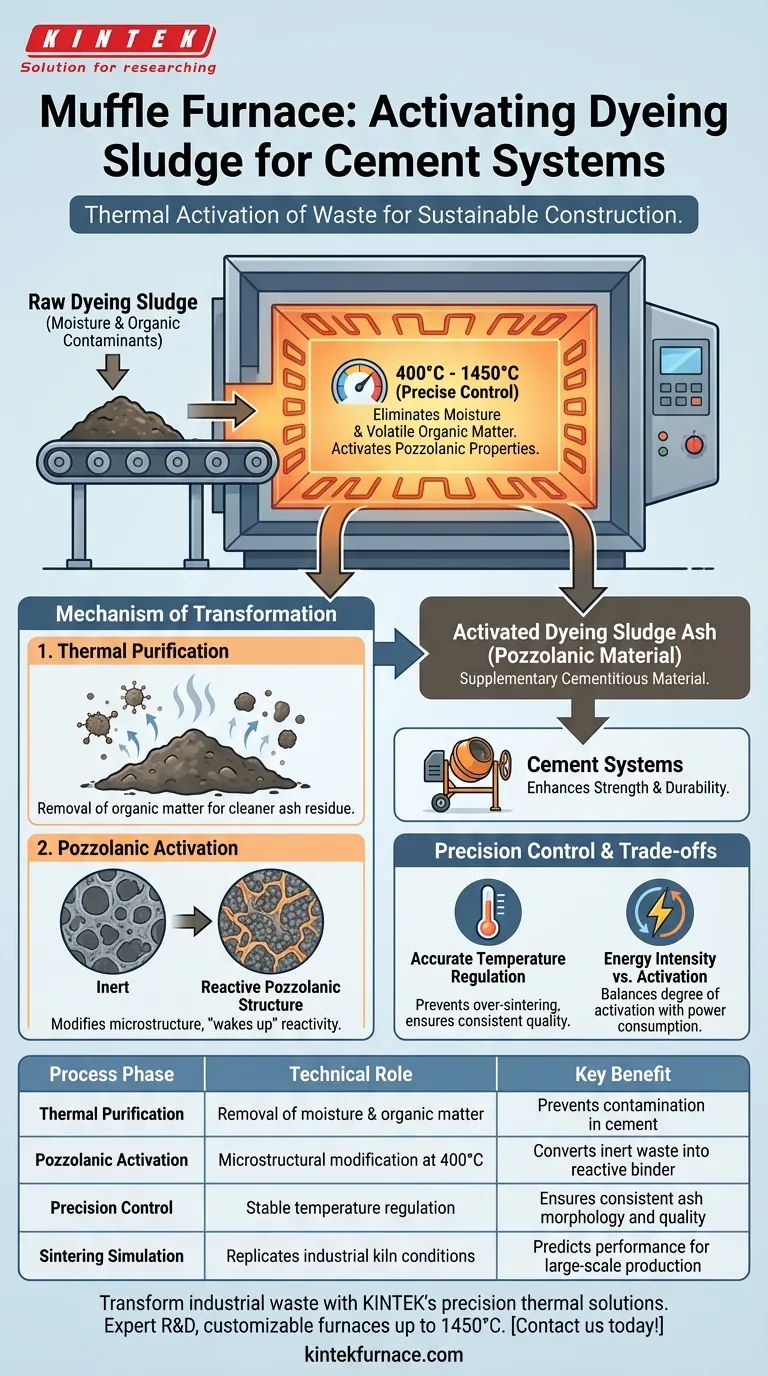
The Mechanism of Transformation
Thermal Purification
The raw dyeing sludge contains significant amounts of moisture and organic contaminants that would be detrimental to concrete performance. The muffle furnace provides a consistent thermal environment to incinerate these impurities.
By maintaining a steady temperature (e.g., 400 °C), the furnace ensures the complete removal of organic matter. This leaves behind a cleaner ash residue that is chemically compatible with cement hydration processes.
Pozzolanic Activation
Beyond simple drying, the furnace facilitates a chemical phase change known as activation. The thermal treatment modifies the microstructure of the sludge.
This heating process "wakes up" the material's pozzolanic reactivity. Without this specific thermal history, the sludge would remain an inert filler; with it, the ash becomes a reactive agent that contributes to the strength and durability of the final cement composite.
The Role of Precision Control
Accurate Temperature Regulation
While the preparation of sludge ash typically targets moderate temperatures like 400 °C, the muffle furnace is engineered for high-precision control across a vast range.
High-end furnaces can reach ultra-high temperatures (1350°C to 1450°C) to simulate industrial cement kilns. This capability ensures that when targeting 400 °C for sludge, the temperature is maintained with absolute stability, preventing temperature spikes that could alter the ash's morphology undesirably.
Simulating Industrial Conditions
The muffle furnace allows researchers to replicate the conditions of large-scale production in a lab setting.
It enables the study of solid-phase reactions and sintering processes. This ensures that the resulting dyeing sludge ash will perform predictably when scaled up for use in actual construction projects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
The quality of the final ash is heavily dependent on maintaining the correct temperature window.
If the temperature is too low, organic impurities may remain, weakening the cement bond. If the temperature is uncontrolled or excessive, it may lead to over-sintering, which could reduce the surface area and reactivity of the ash particles.
Energy Intensity
While effective, the use of a muffle furnace represents a significant energy input in the material preparation cycle.
Operators must balance the degree of activation achieved against the energy cost of the thermal treatment. The goal is to find the minimum temperature required (e.g., the cited 400 °C) to achieve maximum pozzolanic activity without unnecessary power consumption.
Optimizing the Process for Your Goals
To get the most out of dyeing sludge ash preparation, align your furnace settings with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Waste Remediation: Ensure the furnace dwell time is sufficient at 400 °C to guarantee the total destruction of all organic pollutants and volatile compounds.
- If your primary focus is Cement Strength: Prioritize precise temperature stability to maximize pozzolanic activation without causing particle agglomeration or glassification.
Controlled thermal treatment is the bridge between raw industrial waste and high-performance sustainable construction materials.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Technical Role | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Purification | Removal of moisture & organic matter | Prevents contamination in cement hydration |
| Pozzolanic Activation | Microstructural modification at 400°C | Converts inert waste into reactive binder |
| Precision Control | Stable temperature regulation | Ensures consistent ash morphology and quality |
| Sintering Simulation | Replicates industrial kiln conditions | Predicts performance for large-scale production |
Transform your industrial waste into high-value construction resources with KINTEK's precision thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces designed to reach up to 1450°C with absolute stability. Whether you are optimizing pozzolanic activity or simulating industrial sintering, KINTEK provides the reliability your lab requires. Contact us today to find your perfect high-temp furnace system!
Visual Guide
References
- Dongyang Tian, Shuang Lü. Carbon sequestration and environmental impacts in ternary blended cements using dyeing sludge and papermaking sludge. DOI: 10.1186/s43065-024-00109-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is an industrial muffle furnace required for preheating Fe-C-B-Cr-W alloys? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What industries commonly use electric muffle furnaces? Essential for Precise High-Temp Processing
- How is a laboratory muffle furnace utilized to evaluate SAnMBR sludge? Optimize Biomass Health & Process Stability
- Why is a box-type resistance furnace utilized for long-duration heat preservation of chromium steel? Key Benefits
- How do box furnaces maintain temperature over long periods? Key Components for Stable Heat
- What is the role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in PNCO-impregnated electrode post-treatment? Master Sintering
- Why is a muffle furnace used to bake reinforcement particles? Optimize Aluminum Matrix Composite Quality
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of muffle furnaces? Achieve Contaminant-Free Heating for Sensitive Applications



















