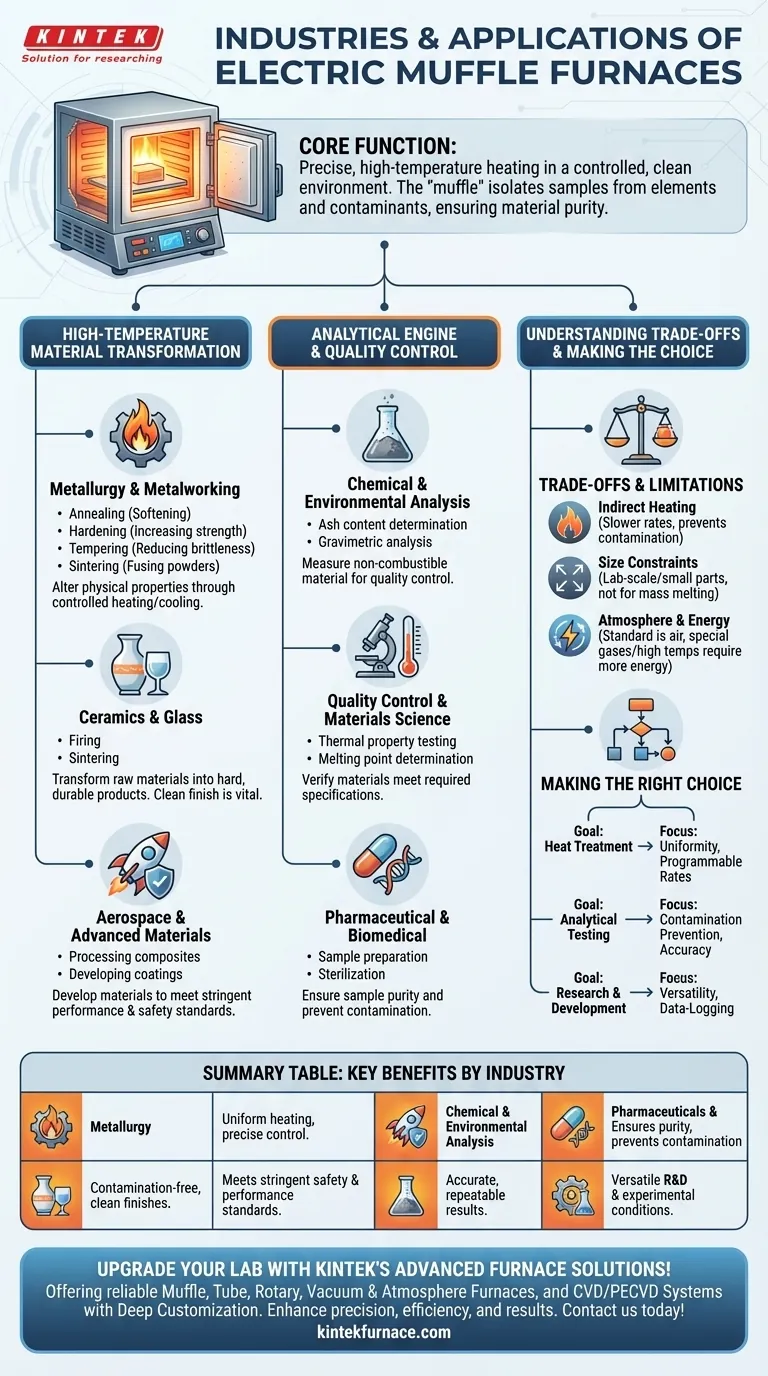
Electric muffle furnaces are a cornerstone technology used in any industry that requires precise, high-temperature heating in a controlled, clean environment. The most common sectors include materials science, metallurgy, analytical chemistry, and ceramics, but their applications extend to pharmaceuticals, environmental testing, and advanced research and development labs.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach extreme temperatures, but its capacity to do so within an isolated chamber—the "muffle." This protects the sample from the heating elements and fuel byproducts, making it indispensable for processes requiring absolute material purity and precise analysis.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Material Transformation
Many industries use muffle furnaces to fundamentally change the physical or chemical properties of a material through controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Metallurgy and Metalworking
In metallurgy, heat treatment is critical for altering the characteristics of metals and alloys. Muffle furnaces provide the uniform, controllable environment needed for these processes.
Common applications include annealing (softening metal), hardening (increasing strength), tempering (reducing brittleness), and sintering (fusing metal powders into a solid mass).
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
The ceramics industry relies on muffle furnaces for firing and sintering. These processes transform clay and other raw materials into hard, durable finished products.
Because the muffle separates the product from combustion contaminants, it ensures a clean finish, which is vital for technical ceramics, dental prosthetics, and artistic pottery.
Aerospace and Advanced Materials
In high-stakes industries like aerospace, the properties of every component must be exact. Muffle furnaces are used to develop and process advanced materials, composites, and coatings.
The precise temperature control ensures these materials meet the stringent performance and safety standards required for flight.
The Analytical Engine: Quantitative and Qualitative Testing
The second major use case is analysis, where the furnace is used as a tool to measure how a material behaves or what it is made of.
Chemical and Environmental Analysis
A primary analytical technique is ash content determination, also known as gravimetric analysis. A sample is heated to a high temperature to burn off all organic and volatile substances.
The remaining non-combustible material (ash) is then weighed. This is crucial for quality control in the food, pharmaceutical, plastics, and coal industries to determine the amount of inorganic filler or impurities.
Quality Control and Materials Science
Labs use muffle furnaces to test a material's thermal properties. This includes determining its melting point, thermal degradation behavior, or its reaction to simulated extreme heat conditions.
This testing is fundamental for verifying that raw materials and finished products meet required specifications.
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Research
In pharmaceutical and biomedical fields, sample purity is paramount. Muffle furnaces are used for preparing samples for analysis where any contamination could invalidate the results.
They are also used in drug testing and the sterilization of specific lab equipment that can withstand high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every heating task. Understanding its specific design reveals its limitations.
The "Muffle" Defines the Use Case
The key is indirect heating. The heating elements heat the chamber, which in turn heats the sample. This prevents contamination but can result in slower heating rates compared to direct-fired furnaces where the flame directly contacts the material.
Constraints on Size and Scale
Electric muffle furnaces are typically designed for laboratory-scale work or the processing of small parts. They are not intended for melting tons of steel or large-scale industrial production, which requires much larger, fuel-fired furnaces.
Atmosphere and Energy
While excellent for preventing contamination from fuel, a standard muffle furnace operates in an air atmosphere. If a process requires a specific inert gas (like argon) or a vacuum, a specialized and more complex furnace is necessary. Furthermore, reaching temperatures above 1000°C electrically requires significant energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment (e.g., annealing metals): Prioritize a furnace with excellent temperature uniformity and programmable heating/cooling rates to achieve specific material properties.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing (e.g., ashing): Your chief concern is preventing sample contamination and ensuring temperature accuracy to get repeatable, reliable results.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Opt for a versatile furnace with a wide temperature range and data-logging capabilities to track and replicate experimental conditions.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is chosen whenever the integrity of the material and the precision of the process are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Annealing, hardening, tempering, sintering | Uniform heating, precise temperature control |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing, sintering | Contamination-free environment, clean finishes |
| Aerospace & Advanced Materials | Processing composites, coatings | Meets stringent safety and performance standards |
| Chemical & Environmental Analysis | Ash content determination, gravimetric analysis | Accurate, repeatable results for quality control |
| Pharmaceuticals & Biomedical | Sample preparation, sterilization | Ensures material purity, prevents contamination |
| General R&D & Quality Control | Thermal property testing, material behavior analysis | Versatile for various experimental conditions |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs—whether for metallurgy, ceramics, or analytical testing. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your precision, efficiency, and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















