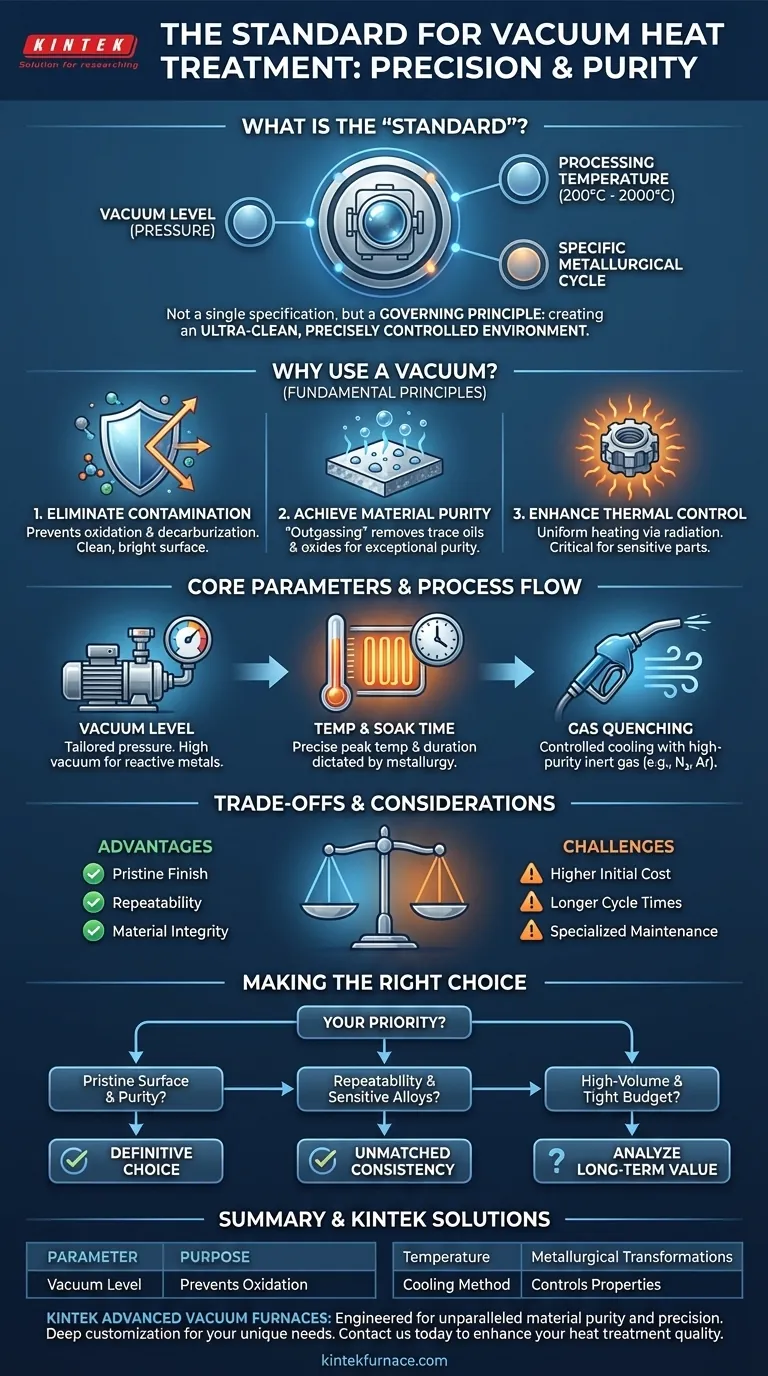
While there is no single universal standard, the "standard" for vacuum heat treatment is defined by a combination of three critical parameters: the vacuum level (pressure), the processing temperature, and the specific metallurgical cycle required for the material. Temperatures typically range from 200°C to 2000°C, and the precise vacuum and thermal profile are tailored to achieve outcomes like hardening, annealing, or tempering without surface contamination.
The standard for vacuum heat treatment is not a single specification but a governing principle: using a vacuum to create an ultra-clean, precisely controlled environment. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions, enabling superior control over a material's final metallurgical properties.

The Fundamental Principle: Why Use a Vacuum?
Understanding vacuum heat treatment begins with why the vacuum is necessary. Its primary purpose is to remove the atmosphere—specifically oxygen and water vapor—from the heating chamber to prevent unwanted reactions at high temperatures.
Eliminating Atmospheric Contamination
When heated in the presence of oxygen, most metals will oxidize (form scale) and, in the case of steel, can lose surface carbon (decarburization). A vacuum environment eliminates the reactive gases, ensuring the material's surface remains clean, bright, and free from scale after processing.
Achieving Material Purity
The vacuum does more than just prevent new contamination; it actively cleans the part. Trace contaminants on the material's surface, such as oils or oxides, can vaporize or decompose under heat and vacuum, a phenomenon known as outgassing. This leaves an exceptionally pure surface.
Enhancing Thermal Control
In a vacuum, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation. This allows for highly uniform heating, as parts are not subject to the uneven convection currents found in traditional atmosphere furnaces. This precision is critical for sensitive components and complex geometries.
Core Parameters of a Vacuum Process
A vacuum heat treatment cycle is not just about heating something in a vacuum. It is a carefully orchestrated sequence where each variable is precisely controlled to achieve a specific metallurgical outcome.
Vacuum Level (Pressure)
This is the first critical parameter. The degree of vacuum required depends on the material and its sensitivity to oxidation. While some processes can be run in a low vacuum, others involving highly reactive metals like titanium require a high vacuum to prevent any interaction with remaining trace gases.
Temperature and Soak Time
As with any heat treatment, the peak temperature and the duration it is held (soak time) are dictated by the material's metallurgy. This could be the austenitizing temperature for hardening steel or the stress-relieving temperature for an alloy. The vacuum ensures this stage happens without compromising the material's surface chemistry.
Cooling (Quenching) Method
After soaking at temperature, the material must be cooled at a specific rate to lock in the desired properties. In a vacuum furnace, this is often accomplished by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like nitrogen or argon and circulating it at high velocity. This is known as gas quenching and provides a controlled, clean cooling environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While vacuum heat treatment offers significant advantages, it is essential to understand its practical implications and limitations to determine if it is the right choice for your application.
Initial Equipment Cost
Vacuum furnaces are complex, high-precision machines. Their initial acquisition cost is significantly higher than that of conventional atmosphere furnaces. This represents a major capital investment.
Process Cycle Times
Achieving a high vacuum requires time to pump down the chamber before the heating cycle can begin. This can result in longer overall cycle times compared to some atmospheric processes, potentially impacting throughput.
Maintenance Complexity
The high-vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems on a vacuum furnace require specialized maintenance and expertise. Keeping the furnace leak-free and operating at peak performance is more demanding than with simpler equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on your project's goals and priorities.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and material purity: Vacuum treatment is the definitive choice, as it inherently prevents oxidation and decarburization without secondary cleaning.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and treating sensitive alloys: The precise temperature uniformity and environmental control of a vacuum furnace provide unmatched consistency.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production on a tight budget: The higher initial cost and potentially longer cycle times of vacuum treatment may require a careful cost-benefit analysis against the long-term gains in quality and reduced post-processing.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum heat treatment is a strategic decision to prioritize material integrity and absolute process control.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Typical Range / Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Level | Low to High Vacuum | Prevents oxidation & surface contamination |
| Temperature | 200°C to 2000°C | Achieves specific metallurgical transformations |
| Cooling Method | High-Purity Gas Quenching (e.g., N₂, Ar) | Controls cooling rate for hardening/tempering |
Ready to achieve unparalleled material purity and precision?
KINTEK's advanced high-temperature vacuum furnaces are engineered to deliver the exacting standards discussed in this article. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with robust solutions like our Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, designed for superior thermal control and contamination-free results.
Our strong deep customization capability ensures your furnace is tailored to your unique material and process requirements, whether you're hardening tool steel, annealing sensitive alloys, or processing reactive metals.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your heat treatment quality and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















