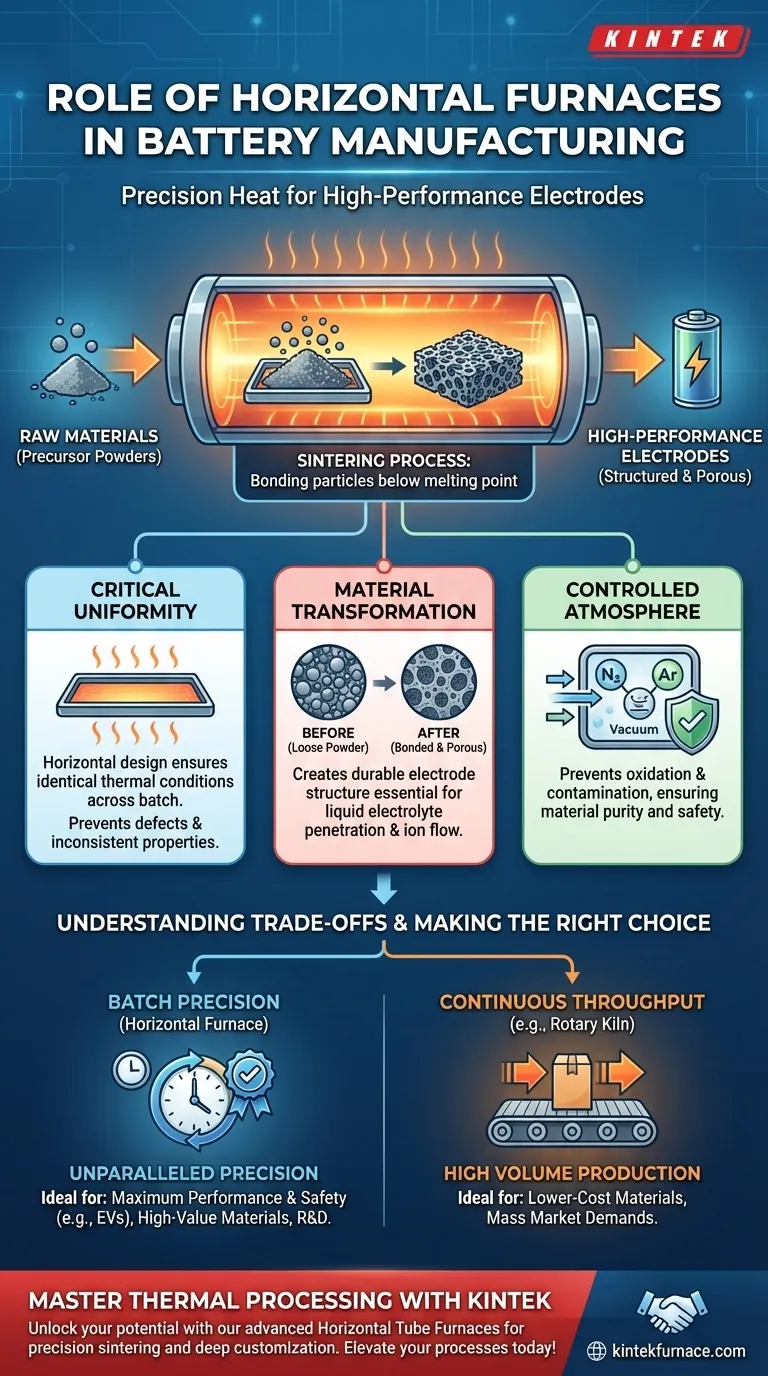
At its core, the role of a horizontal furnace in battery manufacturing is to provide an environment of extremely precise and uniform heat. This controlled thermal processing is essential for specific manufacturing steps, most notably the sintering of active materials used in battery electrodes, which directly dictates the final performance, quality, and safety of the battery cell.
A horizontal furnace is not merely an oven; it is a precision instrument. Its primary purpose is to execute a specific thermal profile—a carefully controlled sequence of heating, holding, and cooling—to create the exact microscopic material structures required for efficient and reliable battery operation.

The Critical Role of Thermal Processing
The creation of advanced battery materials is a process of transformation. Raw chemical powders are converted into highly engineered structures, and heat is the primary tool used to drive this change. The quality of that heat application is what separates low-grade materials from high-performance ones.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal treatment process that uses heat to bond particles of a material together, increasing its strength and density. Critically, this occurs at a temperature below the material's melting point.
Imagine pressing loose snow together to form a solid snowball. Sintering achieves a similar outcome at a microscopic level for ceramic or metallic powders, using heat and pressure to fuse the particles into a solid, yet often porous, mass.
Creating High-Performance Electrodes
Both the cathode and anode materials in a lithium-ion battery undergo a thermal process like sintering or calcination. This step is what transforms a simple mixture of precursor powders into a crystalline structure with the desired properties.
This process creates a porous, yet structurally sound, electrode material. This porosity is essential for the liquid electrolyte to penetrate the electrode, allowing lithium ions to move freely during charging and discharging. The furnace's precision ensures this structure is consistent every time.
Ensuring Uniformity and Purity
The "horizontal" design of these furnaces is key to achieving temperature uniformity. Components are laid out on a flat plane, ensuring every part of the batch is exposed to nearly identical thermal conditions.
This uniformity prevents hot or cold spots, which could lead to inconsistent material properties, defects, and ultimately, a higher rate of battery cell failure. The controlled atmosphere inside the furnace also prevents unwanted chemical reactions and contamination, ensuring material purity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, horizontal furnaces are part of a larger ecosystem of thermal processing equipment, and choosing the right tool involves understanding its specific advantages and limitations.
Batch Precision vs. Continuous Throughput
Horizontal furnaces are typically batch furnaces. They process a set quantity of material in a single, highly controlled cycle. This provides unparalleled precision and is ideal for high-value materials where quality control is paramount.
The trade-off is throughput. For lower-value materials or different process steps, manufacturers might use continuous furnaces, like rotary kilns, which process a constant flow of material. While offering much higher volume, they may not achieve the same level of temperature uniformity as a batch horizontal furnace.
Atmosphere Control
Many advanced material processes require a specific atmosphere—such as a vacuum or an inert gas like argon—to prevent oxidation.
While standard horizontal furnaces operate with controlled air or gas flows, a vacuum furnace is a specialized variant used when even trace amounts of oxygen could compromise the material. This is common in manufacturing components for medical or aerospace applications where material purity is the absolute priority.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a horizontal furnace is driven by the specific quality and performance targets of the final product. Understanding your primary objective is key to evaluating its role in your process.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and safety: The precision sintering offered by a horizontal furnace is non-negotiable for creating the reliable and highly consistent electrode microstructures required for applications like electric vehicles.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: You must weigh the batch precision of a horizontal furnace against the high throughput of a continuous system, making a choice based on the specific quality demands of your target market.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A smaller-scale horizontal tube furnace is an indispensable laboratory tool for developing new materials and optimizing thermal processes before scaling up to mass production.
Ultimately, mastering the application of heat through precision equipment like the horizontal furnace is fundamental to manufacturing the next generation of high-performance batteries.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role in Battery Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides precise and uniform heat for sintering active materials in electrodes. |
| Key Benefits | Ensures consistent material structure, high purity, and improved battery safety and performance. |
| Common Applications | Sintering of cathode and anode materials, calcination, and R&D processes. |
| Trade-offs | Batch processing offers high precision but lower throughput compared to continuous furnaces. |
Unlock the full potential of your battery manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precision high-temperature furnaces, including Horizontal Tube Furnaces ideal for sintering and thermal processing in battery production. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing performance, safety, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems can elevate your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















