At its core, a muffle furnace is an instrument designed to heat materials to extremely high temperatures within a completely isolated chamber. Its primary purpose is to separate the material being heated from the byproducts of combustion and other contaminants, ensuring the heating process itself does not alter the sample's chemical composition.
The fundamental value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to generate intense heat, but its power to do so in a pristine, controlled environment. This isolation is what enables accurate chemical analysis and high-purity material processing.
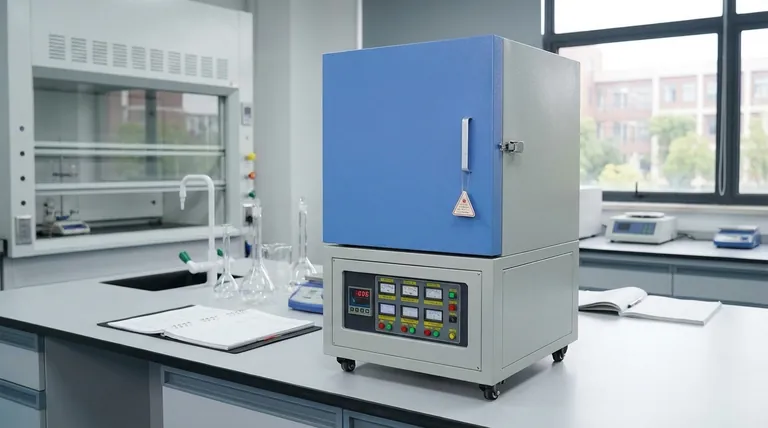

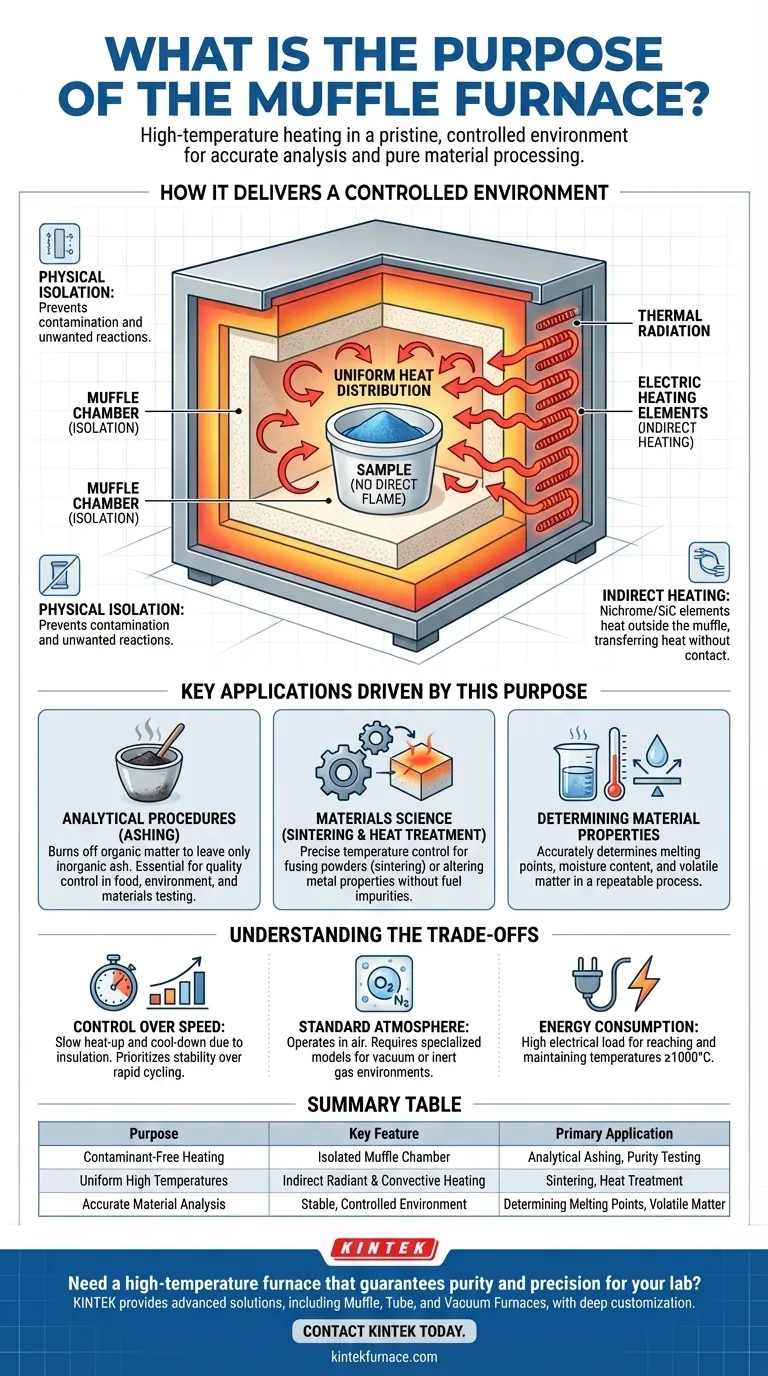
How a Muffle Furnace Delivers a Controlled Environment
To understand the purpose of a muffle furnace, you must first understand its unique design. Unlike a conventional furnace that might expose materials to a direct flame, a muffle furnace relies on separation and indirect heating.
The Principle of Isolation
The defining feature is the "muffle," an inner chamber typically made of high-temperature ceramic. This chamber completely encloses the sample.
This design physically isolates the material from the heating elements and any external atmospheric contaminants. This is the key to preventing unwanted chemical reactions or cross-contamination.
The Mechanism of Indirect Heating
The furnace operates using electric heating elements, such as nichrome or silicon carbide wires, that line the walls outside the muffle chamber.
When electricity passes through these elements, they generate intense heat. This heat is then transferred into the sealed chamber, warming the sample without any direct contact.
Achieving Uniform Heat Distribution
Heat enters the chamber through two primary methods: thermal radiation and thermal convection.
Radiant heat travels directly from the hot chamber walls to the sample, while convection circulates the hot air inside the sealed space. This dual-action ensures a stable, even temperature throughout the chamber, which is critical for obtaining repeatable and reliable results.
Key Applications Driven by This Purpose
The ability to heat a sample without contaminating it makes the muffle furnace indispensable for several specific tasks across science and industry.
Analytical Procedures (Ashing)
A primary use is ashing, which involves heating a sample to burn away all organic matter, leaving only the inorganic residue (ash).
Because the environment is clean, scientists can be confident that the final weight of the ash is an accurate measure of the sample's inorganic content. This is vital for quality control in food science, environmental analysis, and materials testing.
Materials Science (Sintering and Heat Treatment)
In materials science, processes like sintering (fusing powdered materials together with heat) and heat treatment (altering a metal's physical properties) demand precise temperature control in a non-reactive environment.
The muffle furnace provides the necessary high heat without introducing impurities from fuel, which could weaken the final product.
Determining Material Properties
Researchers use muffle furnaces to accurately determine properties like melting points, moisture content, and the percentage of volatile matter. The controlled, repeatable heating process is essential for these standardized tests.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the muffle furnace is a specialized tool with specific characteristics. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Control Over Speed
The heavy insulation required to maintain high temperatures means that muffle furnaces often heat up and cool down more slowly than other types of furnaces. The priority is stability and precision, not rapid cycling.
Standard Atmospheric Conditions
A standard muffle furnace operates in the presence of air. While it isolates the sample from fuel byproducts, it does not create a vacuum or an inert gas environment. Specialized models are required for processes that must exclude oxygen.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1000°C or higher is an energy-intensive process. These furnaces represent a significant electrical load, which is a practical consideration for any laboratory.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use a muffle furnace depends entirely on whether your application requires a pure, high-temperature environment.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: For tasks like ashing or elemental analysis, the isolation provided by a muffle furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: For sintering, annealing, or creating high-purity ceramics and alloys, the furnace's clean, uniform heat is essential.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or low-temperature heating: A standard laboratory oven is a more efficient and appropriate tool.
The muffle furnace is the definitive instrument when your work demands high heat without compromise.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Feature | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Contaminant-Free Heating | Isolated Muffle Chamber | Analytical Ashing, Purity Testing |
| Uniform High Temperatures | Indirect Radiant & Convective Heating | Sintering, Heat Treatment |
| Accurate Material Analysis | Stable, Controlled Environment | Determining Melting Points, Volatile Matter |
Need a high-temperature furnace that guarantees purity and precision for your lab?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements for ashing, sintering, and materials testing.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our robust and reliable furnaces can enhance your analytical results and material processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















