In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven that specializes in heating materials within a completely isolated chamber. Its primary purpose is to heat a sample to a precise temperature without allowing it to come into direct contact with the heating elements or any contaminating byproducts of combustion.
The core value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its ability to do so cleanly. By creating a protective barrier—the "muffle"—it ensures that the results of sensitive processes like material testing or ashing are completely untainted.
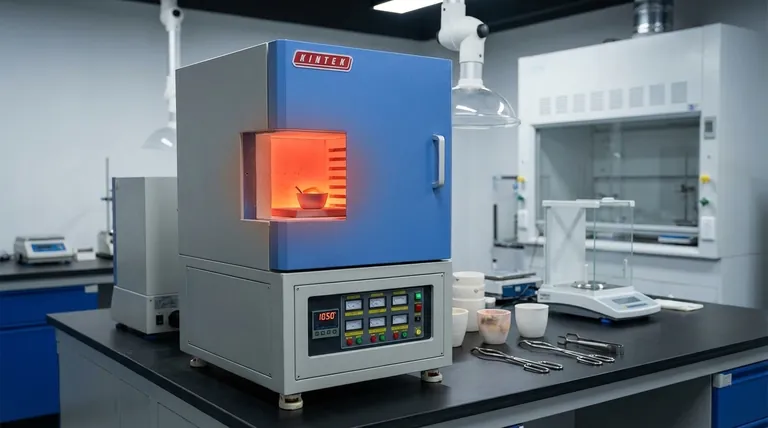

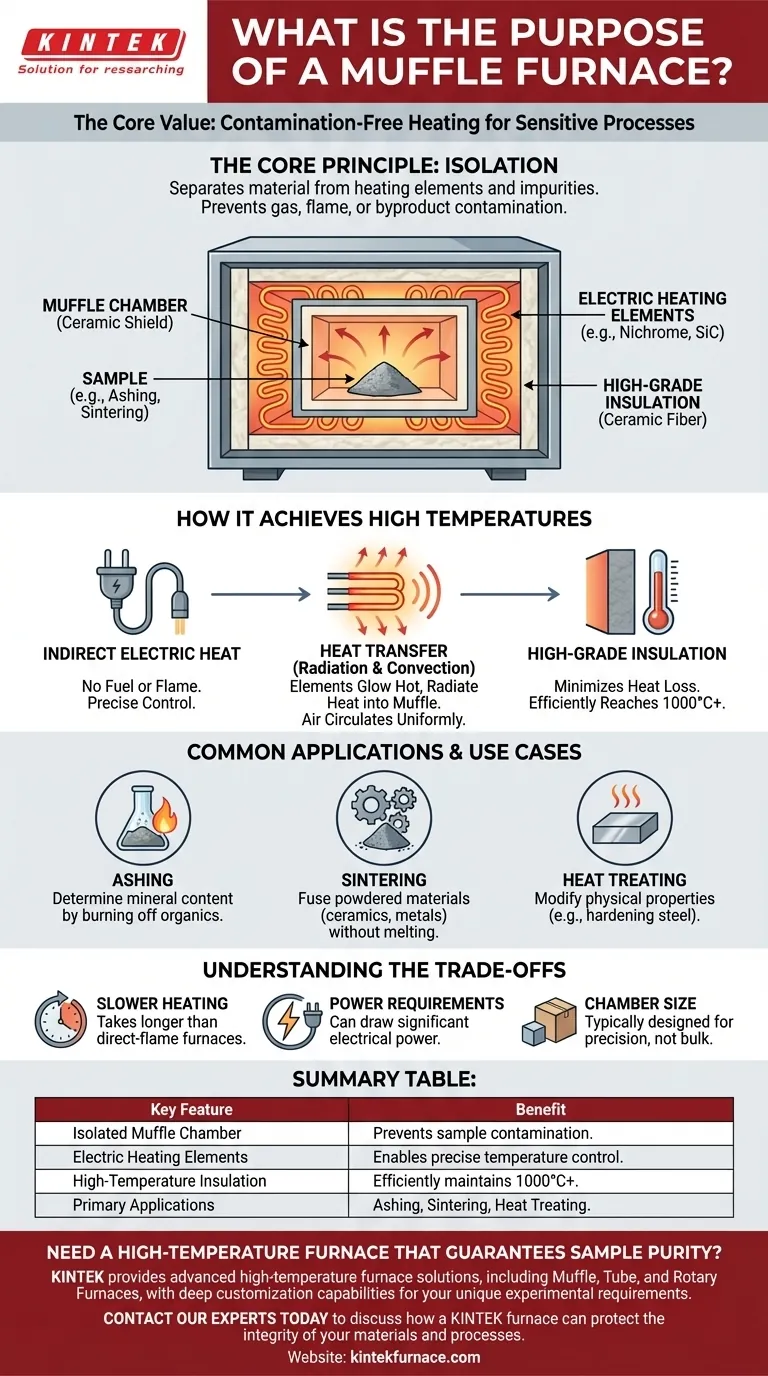
The Core Principle: Contamination-Free Heating
The defining feature of this furnace is the "muffle" itself, which is an insulated inner chamber that separates the material being heated from the rest of the furnace.
The 'Muffle' Explained
The muffle is a box-like enclosure, typically made of high-temperature ceramic. It acts as a shield, preventing any gases, flames, or other impurities from the heat source from reaching the sample inside.
Why Isolation Matters
In many scientific and industrial applications, even the slightest contamination can ruin an experiment or process. For example, when determining the inorganic ash content of a sample, any soot from a flame would add mass and produce an inaccurate result. The muffle ensures analytical purity.
How a Muffle Furnace Achieves High Temperatures
A muffle furnace operates using indirect electric heat, which allows for precise and uniform temperature control.
Electric Heating Elements
The furnace does not use fuel or flame. Instead, high-resistance wires or rods (made of materials like nichrome or silicon carbide) are lined along the chamber walls. When electricity passes through them, they glow hot.
Heat Transfer via Radiation and Convection
These glowing elements transfer heat into the muffle chamber primarily through thermal radiation. The air inside the chamber then circulates via thermal convection, distributing the heat evenly to ensure the entire sample reaches a uniform temperature.
The Role of High-Grade Insulation
Thick layers of ceramic fiber insulation surround the muffle. This insulation is critical for minimizing heat loss, allowing the furnace to reach and maintain very high temperatures (often over 1000°C) efficiently and safely.
Common Applications and Use Cases
The muffle furnace's unique properties make it indispensable for specific, high-purity tasks.
Ashing
Ashing is a process used to determine the non-combustible mineral content of a sample. The furnace burns off all organic material, leaving only the ash behind for analysis. A clean environment is non-negotiable for this.
Sintering
Sintering involves heating powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) to fuse them into a solid piece without melting them. A controlled, contamination-free atmosphere is crucial for ensuring the final material's purity and structural integrity.
Heat Treating
This involves modifying the physical properties of a material, such as hardening or softening steel. The precise temperature control and uniform heating of a muffle furnace are ideal for achieving consistent and predictable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is a specialized tool and not always the best choice.
Slower Heating Cycles
Because the heat is transferred indirectly, muffle furnaces can sometimes take longer to reach the target temperature compared to a direct-flame furnace.
Electrical Power Requirements
These furnaces are entirely electric and can draw significant power, which can be a cost and infrastructure consideration for any facility.
Chamber Size Limitations
Laboratory-grade muffle furnaces are designed for precision, not necessarily volume. Their internal chambers are often smaller than those found in large, industrial furnaces designed for bulk processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating method depends entirely on whether purity and control are more important than speed and volume.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: A muffle furnace is essential for tasks like ashing or trace element analysis where any contamination would invalidate results.
- If your primary focus is precise material modification: The superior temperature uniformity of a muffle furnace is ideal for heat treating, annealing, or sintering sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is rapid, bulk heating: A direct-fire or conventional furnace may be more efficient, provided sample contamination from combustion is not a concern.
Ultimately, you choose a muffle furnace when the integrity of your sample cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Isolated Muffle Chamber | Prevents sample contamination from heating elements |
| Electric Heating Elements | Enables precise temperature control and uniformity |
| High-Temperature Insulation | Efficiently maintains temperatures often exceeding 1000°C |
| Primary Applications | Ashing, Sintering, Heat Treating, Annealing |
Need a high-temperature furnace that guarantees sample purity?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for contamination-free heating, sintering, or heat treatment.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can protect the integrity of your materials and processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















