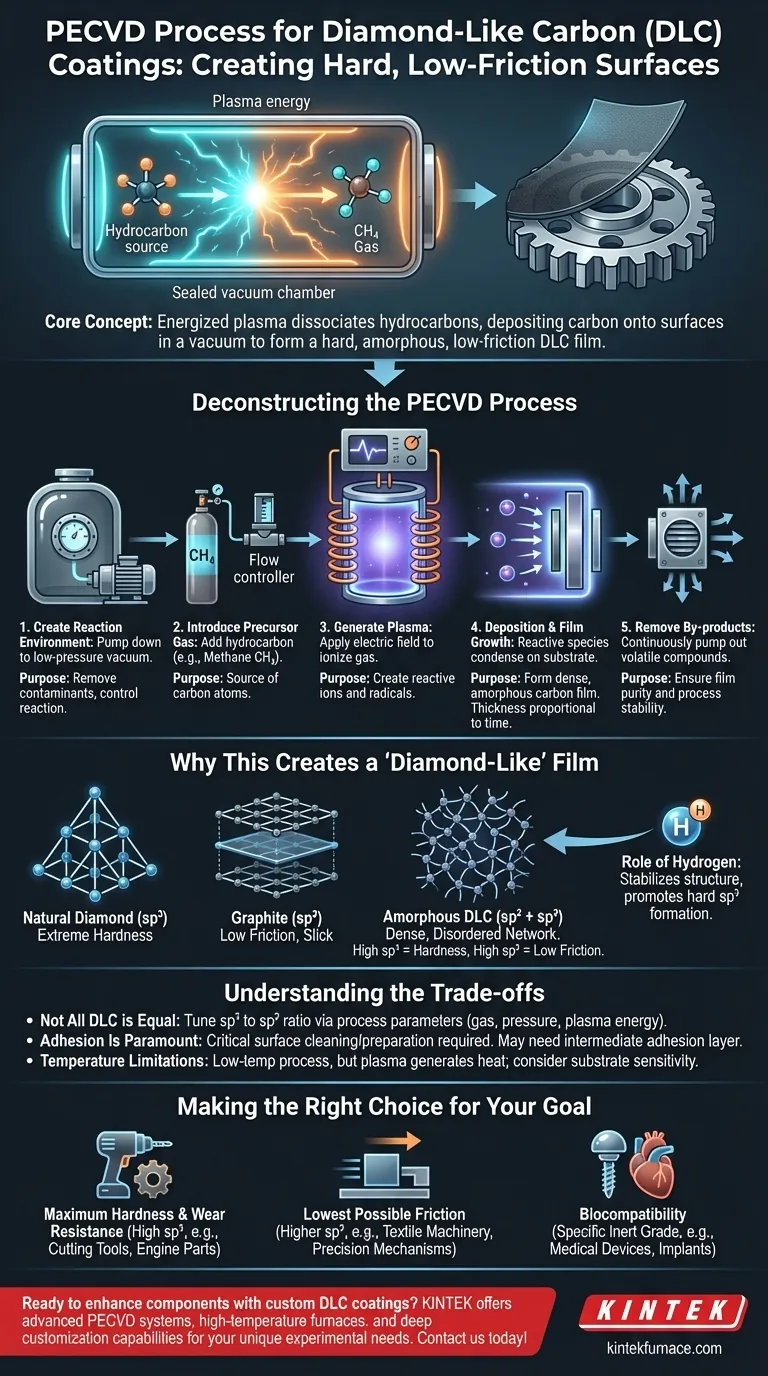
At its core, the process for creating diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings using Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) involves using an energized gas, or plasma, to break down a hydrocarbon source. These dissociated carbon and hydrogen atoms then deposit onto a component's surface inside a vacuum chamber, forming a thin, hard, and slick amorphous film. The coating's thickness is directly proportional to the deposition time.
While the goal is to create a coating with the properties of diamond, the challenge is doing so without the extreme heat and pressure required to form natural diamond. PECVD elegantly solves this by using a low-temperature plasma to assemble a unique carbon structure that mimics diamond's hardness while offering superior low-friction properties.

Deconstructing the PECVD Process for DLC
The PECVD method is a sequence of highly controlled steps performed within a specialized vacuum system. Each stage plays a critical role in determining the final properties of the DLC film.
Step 1: Creating the Reaction Environment
The entire process begins by placing the components to be coated (the "substrates") into a sealed reaction chamber and pumping it down to a low-pressure, near-vacuum state. This removes contaminants and allows for precise control over the reaction.
Step 2: Introducing the Precursor Gas
Once the vacuum is established, a specific hydrocarbon gas is introduced into the chamber. Methane (CH₄) is a common choice, as it serves as the source for the carbon atoms that will form the coating.
Step 3: Generating the Plasma
A high-frequency electric field is applied across the gas in the chamber. This powerful energy field ionizes the gas, stripping electrons from the atoms and creating a glowing, reactive state of matter known as plasma.
Step 4: Deposition and Film Growth
Within the plasma, the hydrocarbon gas molecules are broken apart into highly reactive carbon and hydrogen ions and radicals. These energetic species are drawn to the substrate's surface, where they condense and recombine to form a dense, amorphous carbon film. The film grows at a relatively constant rate, making its thickness predictable and controllable.
Step 5: Removing By-products
As the film forms, volatile by-products from the chemical reactions are continuously pumped out of the chamber. This ensures the purity of the growing film and the stability of the process.
Why This Creates a "Diamond-Like" Film
The term "diamond-like" refers to the coating's properties, not its crystal structure. The PECVD process creates a unique atomic arrangement that gives DLC its valuable characteristics.
The Mix of sp² and sp³ Bonds
Natural diamond consists of carbon atoms in a pure sp³ hybridization, forming an incredibly hard and rigid lattice. Graphite, another form of carbon, consists of sp² hybridized atoms, which form slick, flat sheets.
DLC is an amorphous material, meaning it lacks a uniform crystal structure. It is a dense, disordered network containing a significant fraction of both diamond-like sp³ bonds and graphite-like sp² bonds. The sp³ bonds provide high hardness, while the sp² bonds contribute to the coating's low-friction, slick surface.
The Role of Hydrogen
The hydrogen from the precursor gas is incorporated into the amorphous carbon network. This hydrogen plays a crucial role in stabilizing the structure and saturating "dangling" carbon bonds, which helps promote the formation of the hard sp³ configuration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PECVD process for DLC is not without its considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
Not All DLC is Created Equal
"DLC" is not a single material but a family of coatings. By adjusting process parameters like gas composition, pressure, and plasma energy, engineers can tune the ratio of sp³ to sp² bonds. This allows for optimization but also means properties can vary significantly between different DLC types.
Adhesion Is Paramount
A coating is only as good as its bond to the substrate. Proper surface cleaning and preparation are absolutely critical to ensure the DLC film adheres strongly and does not flake or delaminate under stress. In some cases, a thin intermediate "adhesion layer" of another material is deposited first.
Temperature Limitations
PECVD is considered a "low-temperature" process compared to other methods like traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), making it suitable for many metals and even some polymers. However, the plasma still generates heat, which can be a limiting factor for extremely temperature-sensitive substrates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of the PECVD process allows DLC coatings to be tailored for a vast range of applications, from automotive parts and consumer electronics to biomedical implants.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: You will need a DLC variant with a high percentage of sp³ bonds, ideal for cutting tools, engine components, and other high-wear surfaces.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction: A coating with a higher sp² (graphitic) content is more suitable, making it perfect for sliding components in textile machinery or precision mechanisms.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility for medical devices: A specific, highly inert, and certified grade of DLC is required to ensure it is safe for use in biomedical implants.
Ultimately, mastering the PECVD process allows you to engineer a custom carbon surface perfectly suited to your specific performance demands.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Create Reaction Environment | Pump chamber to vacuum | Remove contaminants, control reaction |
| Introduce Precursor Gas | Add hydrocarbon gas (e.g., methane) | Provide carbon source for coating |
| Generate Plasma | Apply electric field to ionize gas | Create reactive species for deposition |
| Deposition and Film Growth | Ions condense on substrate | Form hard, amorphous carbon film |
| Remove By-products | Pump out volatile compounds | Ensure film purity and process stability |
Ready to enhance your components with custom DLC coatings? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced PECVD systems and high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're targeting wear resistance, low friction, or biocompatibility, we can help optimize your process. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















