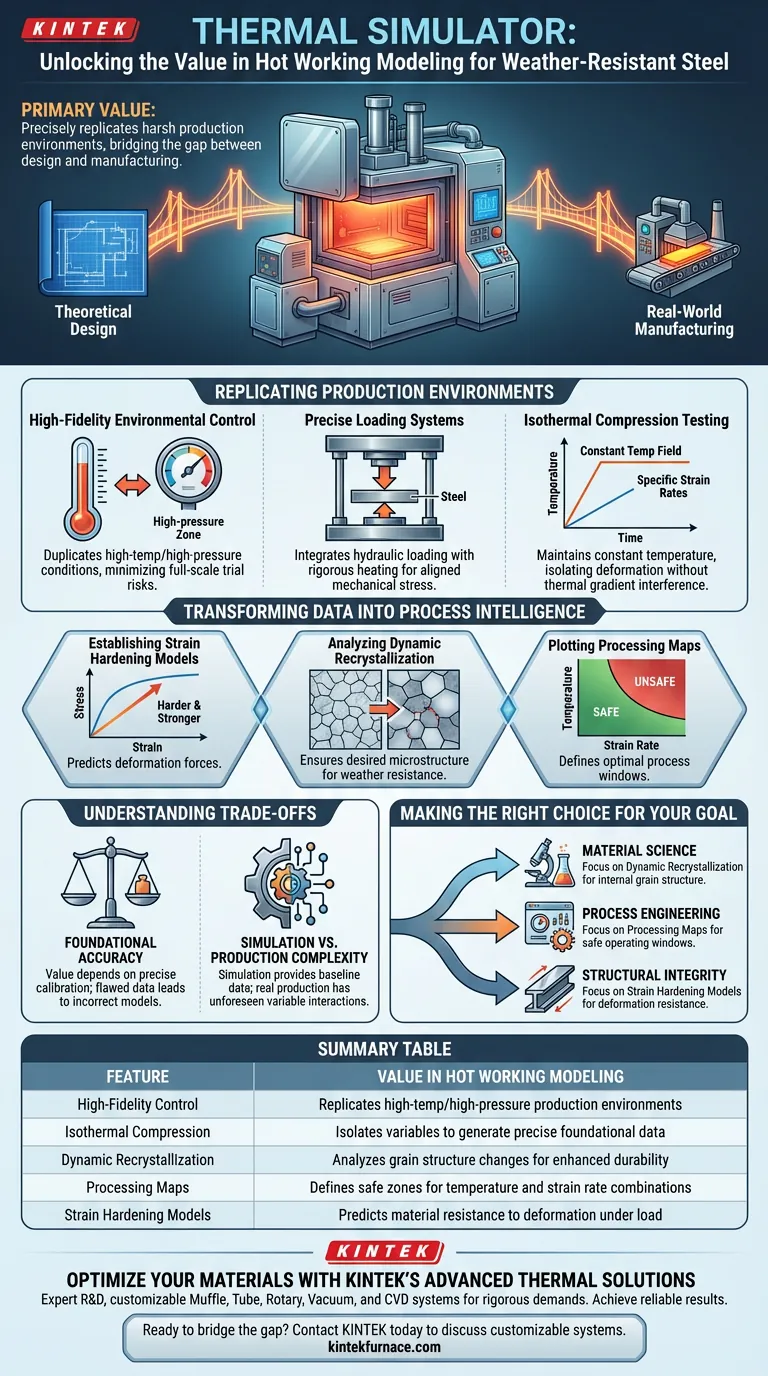
The primary value of a thermal simulator lies in its ability to precisely replicate the harsh environments of actual steel production. By integrating high-precision heating control with hydraulic loading systems, these simulators bridge the gap between theoretical design and real-world manufacturing. They perform isothermal compression tests to generate the foundational data needed to understand how weather-resistant steel behaves under extreme heat and pressure.
Thermal simulators provide the empirical foundation necessary for optimizing weather-resistant steel processing. By isolating variables like temperature and strain rate, they generate the data required to predict dynamic recrystallization and build robust strain hardening models.

Replicating Production Environments
High-Fidelity Environmental Control
To understand how weather-resistant steel will perform during manufacturing, you must duplicate the conditions it faces. A thermal simulator replicates the high-temperature and high-pressure environments encountered in actual production lines. This allows for testing without the cost or risk of full-scale trial runs.
Precise Loading Systems
The simulator utilizes advanced hydraulic loading systems combined with rigorous heating controls. This integration ensures that the mechanical stress applied to the sample aligns perfectly with the thermal conditions.
Isothermal Compression Testing
The core function of the simulator is performing isothermal compression tests. By maintaining a constant temperature field while applying specific strain rates, engineers can isolate how the material deforms without the interference of fluctuating thermal gradients.
Transforming Data into Process Intelligence
Establishing Strain Hardening Models
The data gathered from the simulator is critical for creating strain hardening models. These models predict how the steel becomes harder and stronger as it is deformed, a key factor in determining the forces required for shaping the metal.
Analyzing Dynamic Recrystallization
Hot working causes the internal grain structure of steel to change and reform, a process known as dynamic recrystallization. The simulator provides the data needed to analyze this behavior, ensuring the final product achieves the desired microstructural properties for weather resistance.
Plotting Processing Maps
Perhaps the most practical output is the creation of processing maps. These maps use the simulator's data to define safe and unsafe processing zones, guiding engineers on the optimal combinations of temperature and strain rate to avoid defects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Foundational Accuracy
While powerful, the value of a thermal simulator is entirely dependent on the accuracy of the foundational data it produces. If the heating control or hydraulic loading is not calibrated precisely, the resulting models for strain hardening or recrystallization will be flawed.
Simulation vs. Production Complexity
It is important to remember that the simulator provides data under controlled conditions. While it replicates the environment, it isolates specific variables to create models. In actual production, unforeseen interactions between variables can occur, meaning simulation data should always be treated as a baseline for optimization rather than an absolute guarantee of full-scale behavior.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a thermal simulator for weather-resistant steel, align your testing strategy with your end goal:
- If your primary focus is Material Science: Prioritize the analysis of dynamic recrystallization behavior to ensure the steel achieves the correct internal grain structure for durability.
- If your primary focus is Process Engineering: Focus on generating data to plot processing maps, which will define the safe operating windows for temperature and pressure during manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Use the simulator to establish rigorous strain hardening models to predict how the material will resist deformation under load.
Accurate simulation converts the unpredictability of hot working into a controllable, data-driven engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Value in Hot Working Modeling |
|---|---|
| High-Fidelity Control | Replicates high-temp/high-pressure production environments |
| Isothermal Compression | Isolates variables to generate precise foundational data |
| Dynamic Recrystallization | Analyzes grain structure changes for enhanced durability |
| Processing Maps | Defines safe zones for temperature and strain rate combinations |
| Strain Hardening Models | Predicts material resistance to deformation under load |
Optimize Your Materials with KINTEK’s Advanced Thermal Solutions
Precision in hot working modeling starts with superior equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science and process engineering. Whether you are analyzing dynamic recrystallization or establishing complex strain hardening models, our customizable lab high-temperature furnaces provide the stability and control you need to achieve reliable results.
Ready to bridge the gap between simulation and production? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our customizable systems can enhance your research and manufacturing efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Jianwei Cheng. Research on hot deformation characterization of a new weathering steel through processing map and microstructural observation. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-86619-2
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the core role of a high-pressure autoclave in the synthesis of LTA zeolites? Achieve Precise Crystal Growth
- What is the primary role of high-purity hydrogen in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallic Coating Protection
- What role does a nitrogen curtain protection system play in copper tube welding? Ensure Peak Joint Integrity
- What is the function of a high-temperature sintering furnace in ceramic membrane production? Engineered Performance
- What is the significance of preheating UHPC molds? Ensure Safety & Longevity with High-Temp Furnaces
- What role does an oscillating heating stage play in WO3 thin film growth? Control Kinetics and Crystal Orientation
- Why must the casting dispersion be treated in a 100°C drying oven? Ensure Perfect Film Morphology
- What core parameters does a sessile drop furnace provide for quartz glass? Master High-Temp Material Evaluation














