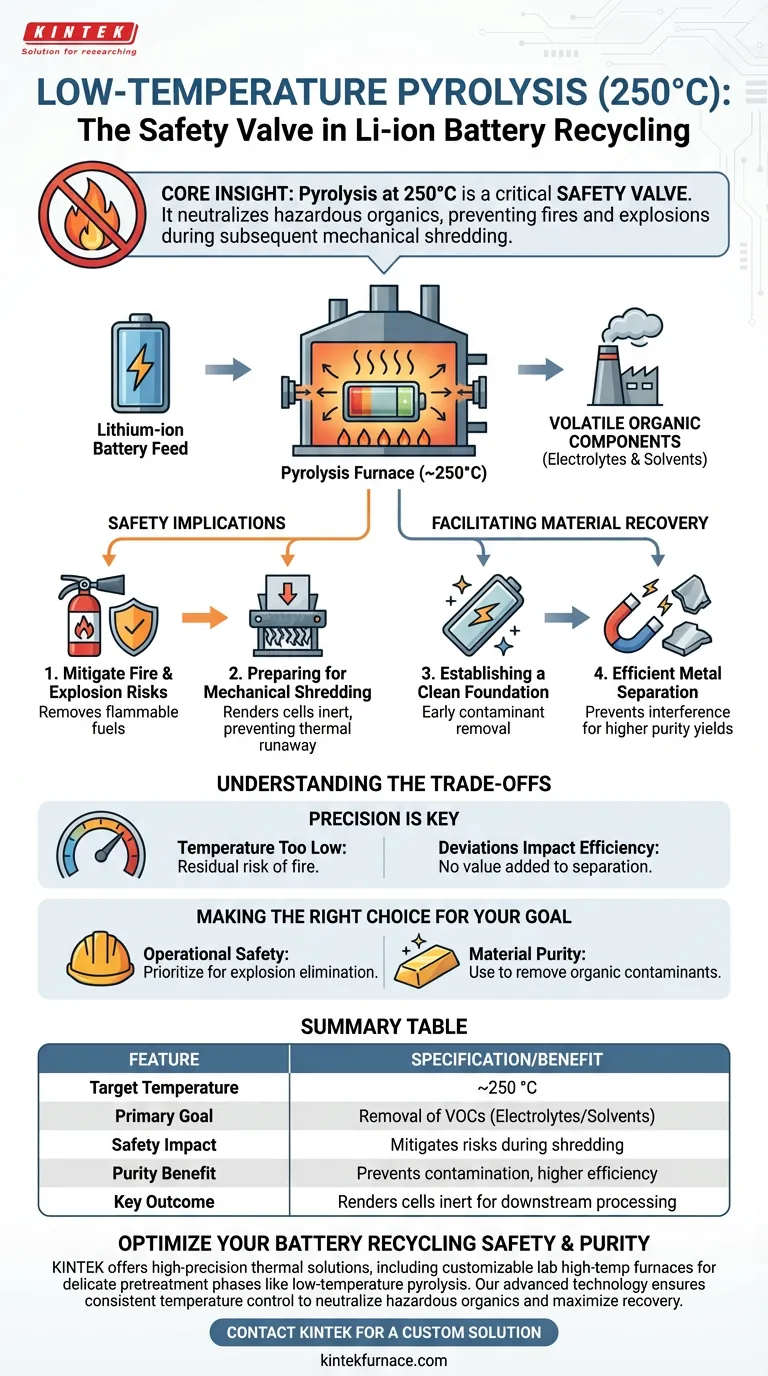
The primary function of low-temperature pyrolysis at approximately 250 °C is the targeted removal of volatile organic components, specifically electrolytes and solvents. By applying controlled industrial heat at this specific temperature, the process neutralizes hazardous materials before the batteries undergo physical processing. This step is a prerequisite for ensuring the safety and efficiency of the entire recycling chain.
Core Insight: Pyrolysis at 250 °C acts as a critical safety valve in the recycling process; it eliminates the fuel source for potential fires (organics) to ensure that subsequent mechanical shredding does not trigger explosions.

The Mechanics of Organic Removal
Targeting Volatile Components
The specific temperature setpoint of approximately 250 °C is chosen to address the chemical properties of the battery's internal components.
At this temperature, the process effectively targets and volatilizes organic substances, most notably the liquid electrolytes and solvents used in lithium-ion cells.
Utilizing Industrial Heating
The process relies on specialized industrial heating equipment to maintain a consistent thermal environment.
Maintaining this temperature stability is crucial to ensure the complete removal of these organics without triggering unwanted reactions in other battery materials.
Safety Implications for Downstream Processing
Mitigating Fire and Explosion Risks
The most immediate operational benefit of this pyrolysis step is a drastic reduction in safety hazards.
Lithium-ion batteries contain flammable components that can ignite when physically breached. By removing these fuels thermally first, the risk of fire and explosion is significantly minimized.
Preparing for Mechanical Shredding
Once the organics are removed, the battery cells are rendered inert and safe for mechanical processing.
This allows the subsequent shredding machinery to operate without the threat of thermal runaway events that would otherwise occur if electrolytes were still present.
Facilitating Material Recovery
Establishing a Clean Foundation
Beyond safety, this pretreatment phase plays a vital role in the quality of the final output.
By stripping away organic contaminants early, the process establishes a clean foundation for the rest of the recycling line.
Efficient Metal Separation
The removal of solvents and electrolytes prevents these sticky or liquid substances from interfering with physical separation.
This ensures that the separation of valuable metals in later stages is far more efficient and yields higher purity results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Temperature Precision
While highly effective, this process relies heavily on maintaining the specific temperature of 250 °C.
If the temperature drops too low, organic components may remain, leaving a residual risk of fire during shredding. Conversely, deviations in the process could impact energy efficiency without adding value to the separation logic.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your recycling line, consider how this step aligns with your operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Operational Safety: Prioritize this pyrolysis step to eliminate explosion hazards before any mechanical crushing or shredding begins.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Use this thermal treatment to remove organic contaminants that would otherwise complicate the separation of high-value metals.
The successful recycling of lithium-ion batteries relies on this thermal pretreatment to transform a hazardous device into a safe, separable resource.
Summary Table:
| Process Feature | Specification/Benefit |
|---|---|
| Target Temperature | Approximately 250 °C |
| Primary Goal | Removal of volatile organic compounds (Electrolytes/Solvents) |
| Safety Impact | Mitigates fire and explosion risks during mechanical shredding |
| Purity Benefit | Prevents contamination for higher efficiency metal separation |
| Key Outcome | Renders battery cells inert for downstream processing |
Optimize Your Battery Recycling Safety and Purity
Are you looking to enhance the safety and efficiency of your lithium-ion battery recycling operations? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—including customizable lab high-temp furnaces designed specifically for delicate pretreatment phases like low-temperature pyrolysis. Our thermal solutions ensure the consistent temperature control needed to neutralize hazardous organics and maximize material recovery.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique processing needs and discover how our advanced furnace technology can transform your recycling line.
Contact Us for a Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Vladimír Marcinov, Zita Takáčová. Overview of Recycling Techniques for Lithium-Ion Batteries. DOI: 10.15255/kui.2023.030
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
People Also Ask
- Why is rapid water quenching necessary for Ce2(Fe, Co)17 alloys? Unlock Peak Magnetocaloric Performance
- How do MFCs and Precursor Bottles Work in AP-ALD? Master Precision Vapor Draw for Atomic Coatings
- How does a graphite furnace work? Achieve Ultra-Trace Element Analysis
- How does a constant temperature forced air drying oven contribute to the pore activation process of biomass carbon?
- Why is high-purity argon necessary for PVC dechlorination? Ensure Precise Reaction Control & Safety
- What are the key considerations when choosing a continuous furnace? Optimize Your High-Volume Production
- How is mechanochemical grinding used in lithium battery recovery? Unlock Efficient Solid-State Material Repair
- What is the mechanism of bed powder in LLZO sintering? Optimize Lithium Stability and Phase Purity



















