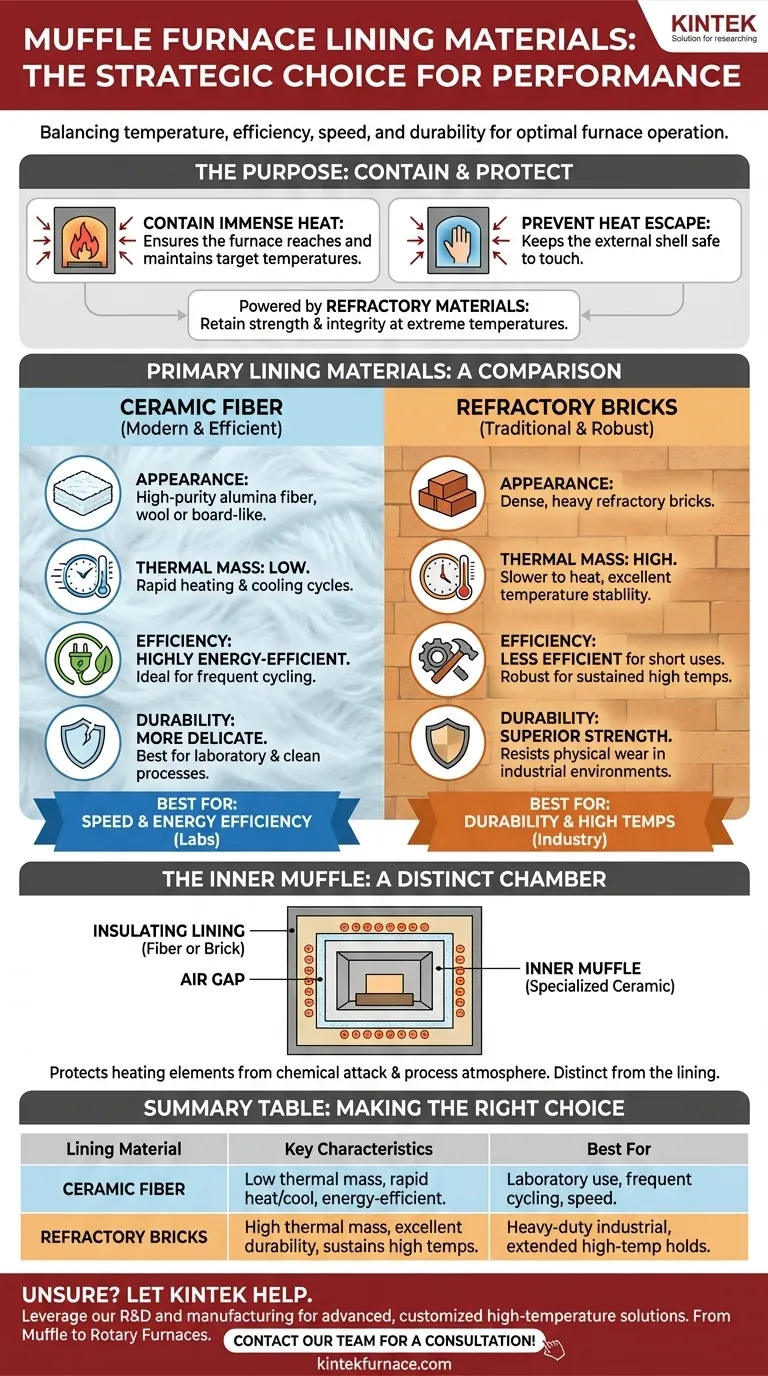
In short, the lining of a muffle furnace is made from refractory materials designed to withstand extreme temperatures. The two most common materials used for this purpose are high-purity ceramic fiber insulation and dense refractory bricks, with the choice depending on the furnace's specific performance requirements.
The selection of a furnace lining is not about a single "best" material. It is a strategic engineering choice that balances the need for maximum temperature, energy efficiency, operational speed, and long-term durability.

The Purpose of a Muffle Furnace Lining
A furnace lining has two primary responsibilities: containing immense heat within the chamber and preventing that heat from escaping. An effective lining allows the furnace to reach and maintain target temperatures efficiently while keeping the external shell safe to touch.
The Principle of Refractory Materials
The materials used for this task are known as refractories. A refractory material is one that retains its physical strength and chemical integrity at very high temperatures. The entire design of a high-temperature furnace hinges on the quality and properties of its refractory lining.
Primary Lining Materials: Fiber vs. Brick
Modern muffle furnaces are typically constructed using one of two primary types of refractory linings: lightweight ceramic fiber or dense refractory bricks.
Modern Construction: Ceramic Fiber Insulation
Most contemporary muffle furnaces use a lining made of high-purity alumina fiber. This material, which looks like a dense wool or board, is an exceptional insulator.
These furnaces are often built with a double-layer shell. The inner lining of alumina fiber contains the heat, while an air gap and the outer steel cabinet provide structural integrity and operator safety.
The low thermal mass of ceramic fiber allows the furnace to heat up and cool down very quickly, making it highly energy-efficient for processes that require frequent cycling.
Traditional Construction: Refractory Bricks
For heavy-duty industrial applications or furnaces designed to reach extreme temperatures (up to 1800°C), the lining is often constructed from refractory bricks.
These dense, heavy bricks are extremely durable and can withstand significant physical wear and tear. Their high thermal mass means they take longer to heat up but also retain heat for a long time.
This structure is exceptionally robust, but it is generally heavier and less responsive to rapid temperature changes compared to fiber-lined furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between a fiber or brick lining involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs. There is no universally superior option; the right choice depends entirely on the intended use.
Thermal Mass and Efficiency
Ceramic fiber has a very low thermal mass. This is its greatest advantage, enabling rapid heating and cooling cycles that save both time and energy.
Refractory bricks have a high thermal mass. This makes them slower to heat but excellent at holding a stable temperature for extended periods, though they are less efficient for short, repeated uses.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Refractory bricks offer superior mechanical strength and are more resistant to physical damage. This makes them suitable for harsh industrial environments where loads might be placed directly on the furnace hearth.
Ceramic fiber is more delicate and can be damaged by physical abrasion or impact. It is best suited for laboratory or clean process environments.
The Inner Muffle Chamber
Crucially, the insulating lining is distinct from the muffle itself. The muffle is an inner, sealed chamber that protects the heating elements from the sample's atmosphere (and vice versa).
This inner chamber is often made of a specialized ceramic chosen for its resistance to chemical attack from aggressive gases or vapors that may be released during a process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these materials allows you to select a furnace that is optimized for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy efficiency: Choose a modern furnace with a high-purity ceramic fiber lining for its rapid heating and cooling capabilities.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and sustained high temperatures: A furnace with a dense refractory brick lining offers unmatched robustness for heavy industrial use.
- If your primary focus is processing samples that release fumes: Ensure the furnace contains a dedicated ceramic muffle to protect the heating elements and ensure process purity.
Ultimately, knowing the function of each material transforms your purchase from a simple choice into an informed engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Lining Material | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Fiber | Low thermal mass, rapid heating/cooling, energy-efficient, lightweight | Laboratory use, frequent cycling, processes requiring speed and efficiency |
| Refractory Bricks | High thermal mass, excellent durability, sustains high temperatures, robust | Heavy-duty industrial applications, extended high-temperature holds |
Unsure which muffle furnace lining is right for your application?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Let our experts help you select or customize a furnace with the ideal lining material for your specific needs in temperature, efficiency, and durability. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















