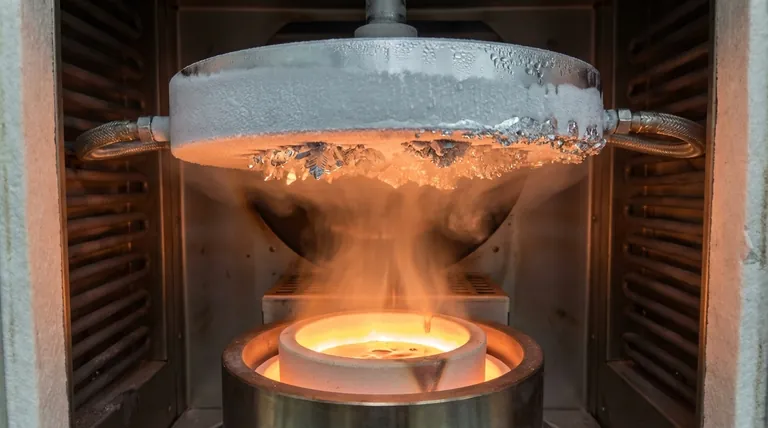
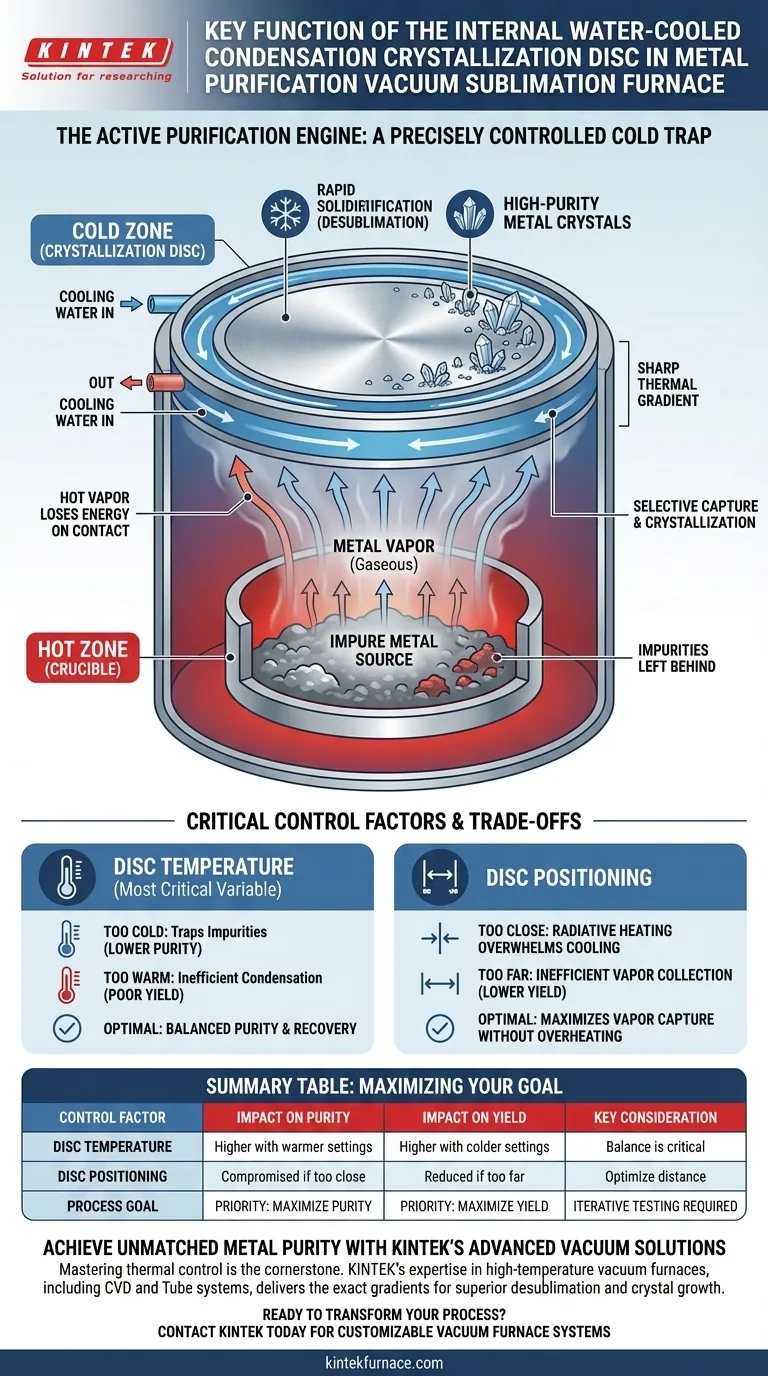
In short, the internal water-cooled condensation crystallization disc serves as a precisely controlled cold trap. Its key function is to force hot, gaseous metal vapor to rapidly solidify back into high-purity crystals upon contact, effectively separating the desired metal from less volatile impurities left behind in the crucible.
The disc is not merely a passive collection surface; it is the active purification engine of the furnace. By creating a sharp thermal gradient within the vacuum chamber, it selectively captures the target metal and dictates the final purity and yield of the entire process.

The Core Principle: Harnessing a Thermal Gradient
The effectiveness of the crystallization disc is rooted in the physics of phase transitions—specifically, sublimation and desublimation—which are controlled by creating a stark temperature difference within the furnace.
Creating a Cold Zone in a Hot Environment
The process begins by establishing two extreme temperature zones. The crucible at the bottom of the furnace is heated to a high temperature, while the crystallization disc, positioned above it, is kept at a very low temperature by continuously circulating cooling water.
The Journey of Metal Vapor
Under high vacuum and intense heat, the source metal in the crucible does not melt but sublimates, turning directly from a solid into a gas. This metal vapor expands to fill the chamber, carrying with it the kinetic energy from the heat source.
The Moment of Desublimation
When the hot, energetic metal vapor molecules collide with the frigid surface of the water-cooled disc, they experience an immediate and drastic loss of energy. This forces them to transition directly back into a solid state, a process known as desublimation.
How This Process Guarantees Purity
The purification occurs because different materials sublimate at different temperatures. The furnace is calibrated so that only the target metal vaporizes efficiently, leaving heavier, less volatile impurities behind as solids in the crucible. The disc then selectively captures the purified vapor, allowing it to crystallize in a controlled manner.
Understanding the Critical Control Factors
The final quality and quantity of the purified metal are not accidental. They are the direct result of carefully managing the operational parameters of the crystallization disc. The balance between purity and recovery rate is a constant trade-off.
The Impact of Disc Temperature
The temperature of the disc is the most critical variable. If the disc is too cold, it may trap other, more volatile impurities along with the target metal, slightly reducing purity. If it is too warm, the metal vapor will not condense effectively, leading to a poor recovery rate, as much of the vapor fails to solidify on the disc.
The Role of Disc Positioning
The physical placement of the disc in relation to the source material is also crucial. Positioning it too close to the crucible can lead to radiative heating that overwhelms the cooling system. Positioning it too far away can reduce the efficiency of vapor collection, lowering the overall yield as vapor may condense on other, cooler parts of the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal settings for the crystallization disc depend entirely on your end-product requirements. You must decide whether absolute purity or maximum yield is the priority for a given run.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: You should prioritize a meticulously controlled disc temperature, potentially sacrificing a small amount of yield to ensure only the target metal desublimates.
- If your primary focus is maximizing recovery rate: You may use a slightly lower disc temperature to capture the maximum amount of vapor, accepting the possibility of marginally lower final purity.
- If you are developing a new process: You must run iterative tests, adjusting disc temperature and position to find the ideal equilibrium that meets your specific purity and yield targets.
Ultimately, mastering control over the crystallization disc is the key to transforming a raw material into a final product of exceptional quality.
Summary Table:
| Control Factor | Impact on Purity | Impact on Yield | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disc Temperature | Higher purity with precise, warmer settings | Higher yield with colder settings | Balance is critical; too cold traps impurities, too warm reduces condensation. |
| Disc Positioning | Can be compromised if too close (radiative heating) | Reduced if too far (inefficient collection) | Optimize distance to maximize vapor capture without overheating the disc. |
| Process Goal | Priority: Maximize Purity | Priority: Maximize Yield | Requires iterative testing to find the ideal equilibrium for your specific needs. |
Achieve Unmatched Metal Purity with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Solutions
Mastering the precise thermal control of the crystallization disc is the cornerstone of effective vacuum sublimation. Whether your goal is maximum purity for high-value applications or optimal yield for production efficiency, the right furnace technology makes all the difference.
KINTEK's expertise is your advantage. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a range of high-temperature vacuum furnaces, including specialized CVD and Tube systems, all customizable for your unique metal purification needs. Our solutions are engineered to deliver the exact thermal gradients and control required for superior desublimation and crystal growth.
Ready to transform your metal purification process and achieve exceptional product quality?
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our customizable vacuum furnace systems can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















