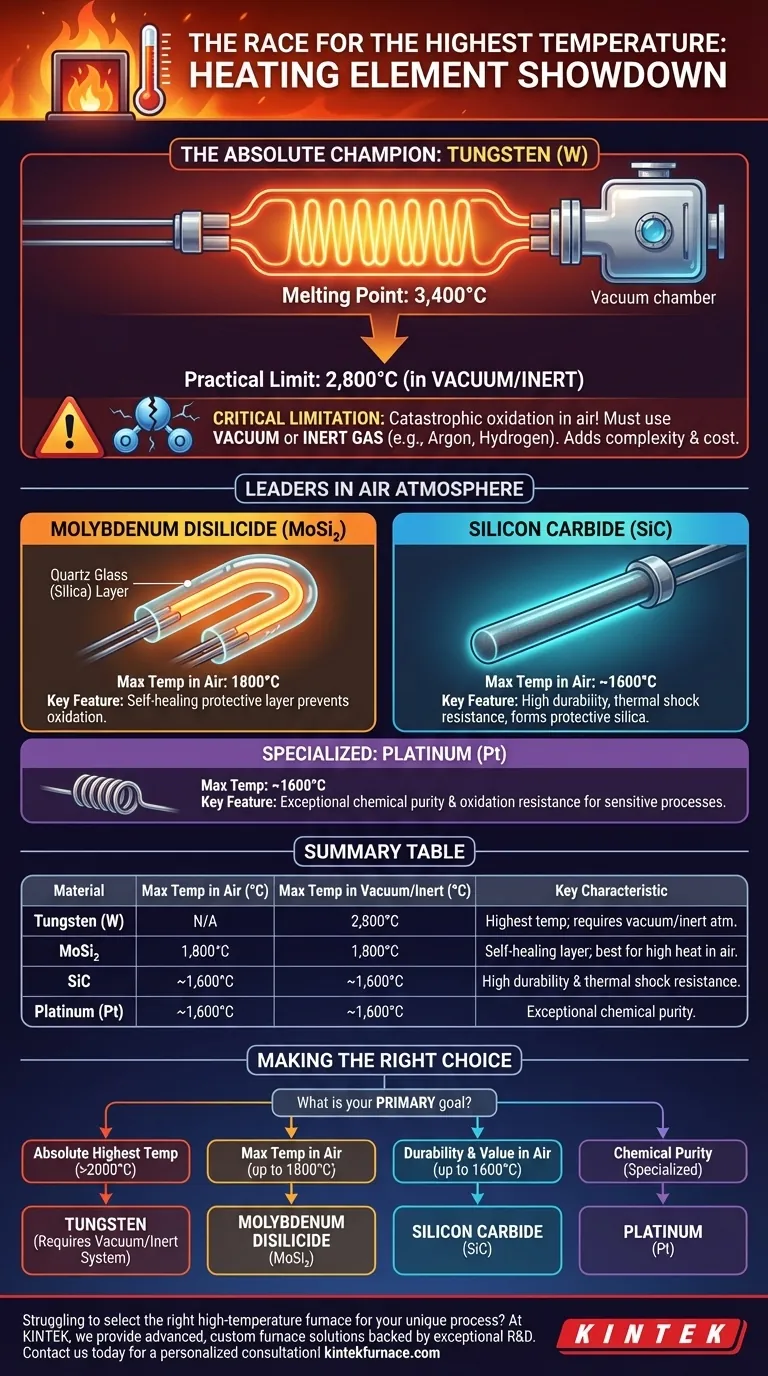
In the realm of electric heating, tungsten stands alone as the material capable of reaching the highest temperatures. With a melting point of 3,400°C (6,152°F), specialized furnaces using tungsten heating elements can achieve practical, stable operating temperatures up to 2,800°C (5,072°F).
While tungsten achieves the highest possible temperatures, its extreme reactivity with oxygen is its critical limitation. This means the choice of a heating element is less about the absolute maximum temperature and more about the required operating atmosphere for your process.

The Absolute Maximum: Understanding Tungsten
Tungsten's unique properties make it the only choice for the most extreme temperature applications, but these properties come with strict operational requirements.
Unmatched Melting Point
Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal, which is the fundamental reason it can serve as a heating element at temperatures where others would fail.
Practical Operating Limits
A furnace's maximum operating temperature is always set well below the element's melting point. This gap ensures a reasonable service life and prevents catastrophic failure, which is why tungsten elements are typically rated for use up to 2,800°C.
The Critical Requirement: Atmosphere Control
Tungsten oxidizes catastrophically at high temperatures. If heated in the presence of air (oxygen), it will burn out almost instantly.
Therefore, tungsten elements must be operated in a vacuum or a protective, inert atmosphere (like argon) or a reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen). This adds significant complexity and cost to the furnace design.
High-Temperature Leaders for Use in Air
For applications that must run in an air atmosphere, a different class of materials is required. These elements cannot match tungsten's peak temperature but are the champions for high-heat processes in normal air.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂)
These ceramic-based elements are the go-to choice for the highest temperatures in air, capable of operating up to 1800°C (3272°F).
Their key feature is the ability to form a protective, self-healing layer of quartz glass (silica) on their surface when heated. This layer prevents oxygen from reaching and destroying the underlying material.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide is another ceramic heating element known for its durability and excellent performance in air, with typical maximum operating temperatures around 1600°C (2912°F).
Like MoSi₂, it forms a protective silica layer. SiC is often valued for its high mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock.
Platinum Group Metals
Metals like platinum and rhodium are sometimes used as heating elements in specialized laboratory furnaces. While their maximum temperature is lower than MoSi₂, they offer exceptional resistance to oxidation and chemical contamination, which is critical for high-purity processes like glass manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element is an engineering decision that involves balancing performance, cost, and complexity. No single material is best for every situation.
Atmosphere vs. Temperature
This is the most fundamental trade-off. If you need to exceed ~1800°C, you have no choice but to use tungsten and invest in the vacuum or controlled atmosphere system required to protect it.
Cost and Brittleness
High-temperature ceramic elements like MoSi₂ and SiC are significantly more expensive than common metallic elements (like Nichrome). They are also brittle at room temperature and require careful handling and specialized mounting techniques to avoid breakage.
System Complexity
A tungsten furnace is inherently a complex and expensive system due to the need for a vacuum-tight chamber, pumps, and gas management systems. Furnaces using MoSi₂ or SiC elements can be simpler and less costly as they do not require this atmospheric control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will dictate the ideal material.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest temperature (above 2000°C): Tungsten is your only viable option, but you must build your process around a vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature in an air atmosphere (up to 1800°C): Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂) is the industry standard for top-tier performance in air.
- If your primary focus is durability and reliability in air (up to 1600°C): Silicon carbide (SiC) provides a robust and often more economical solution for a vast range of industrial processes.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity in a specialized process: Precious metals like platinum are chosen for their inertness, despite a lower temperature ceiling and higher material cost.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element is a balance between your target temperature, operating atmosphere, and overall system budget.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temp in Air (°C) | Max Temp in Vacuum/Inert (°C) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten (W) | Not Applicable | 2,800°C | Highest temperature; requires vacuum/inert atmosphere |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | 1,800°C | 1,800°C | Self-healing protective layer; best for high heat in air |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | ~1,600°C | ~1,600°C | High durability and thermal shock resistance |
| Platinum (Pt) | ~1,600°C | ~1,600°C | Exceptional chemical purity and oxidation resistance |
Struggling to select the right high-temperature furnace for your unique process?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, high-temperature furnace solutions. Our diverse product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities. We work with you to precisely match the heating element and furnace system to your specific temperature, atmosphere, and application requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Let our experts help you achieve your extreme temperature goals. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- Why might a vacuum furnace maintain vacuum during cooling? Protect Workpieces from Oxidation and Control Metallurgy
- How are parts loaded into a vacuum furnace? Ensure Precision and Efficiency in Your Process
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What additional processes can a vacuum heat treatment furnace carry out? Unlock Advanced Material Processing



















