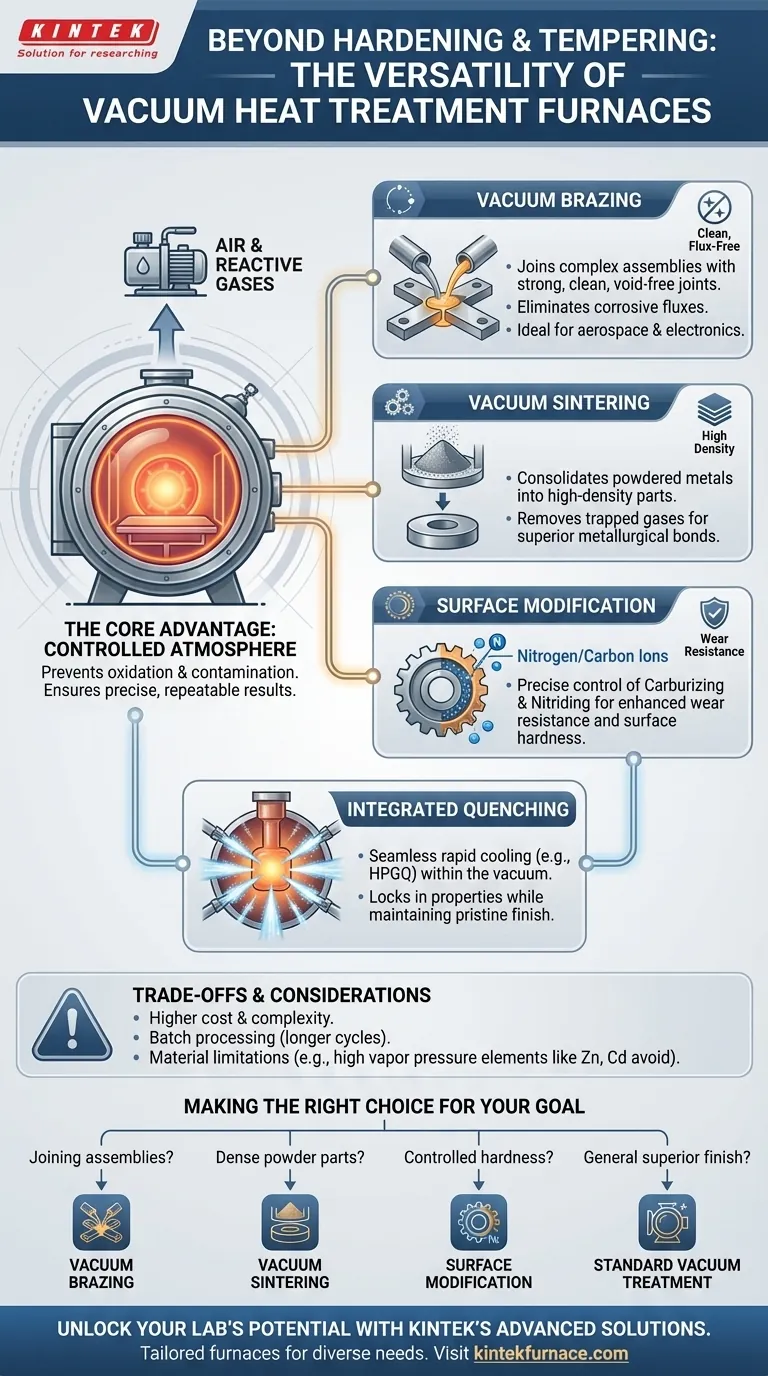
Beyond standard hardening and tempering, a vacuum furnace is a highly versatile tool capable of performing advanced material joining and surface modification processes. It can execute vacuum brazing for creating strong, clean joints; vacuum sintering for consolidating powdered metals into dense parts; and surface treatments like carburizing and nitriding for enhanced wear resistance.
A vacuum furnace's primary advantage is not just the heat, but the highly controlled, contamination-free environment it creates. This allows it to perform multiple sensitive processes in a single cycle, enhancing the quality, strength, and finish of the final component by completely preventing oxidation.

The Core Advantage: A Controlled Atmosphere
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is the removal of air and other reactive gases. This fundamental capability is what unlocks its process versatility.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
By operating in a near-vacuum, the furnace eliminates oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants. This prevents the formation of oxides (scale) on the material's surface, resulting in a bright, clean finish that often requires no post-process cleaning.
Ensuring Process Purity and Repeatability
A vacuum creates an inert baseline. This means any gases introduced for specific processes (like nitrogen for nitriding) are the only reactive agents present. This allows for extremely precise, computer-controlled, and repeatable results cycle after cycle.
Key Processes Enabled by a Vacuum Environment
While used for standard annealing and tempering, the vacuum environment is critical for several other advanced manufacturing processes.
Vacuum Brazing
Brazing is a process that joins two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint.
Performing this in a vacuum produces exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joints. It eliminates the need for corrosive fluxes, which can become trapped and compromise the integrity of the assembly. This is critical for aerospace and electronic components.
Vacuum Sintering
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder by applying heat below its melting point.
Vacuum sintering is essential for creating high-density components with minimal porosity from powdered metals or ceramics. The vacuum removes trapped gases from the powder, leading to superior metallurgical bonds and enhanced mechanical properties in the final part.
Surface Modification Processes
These processes alter the chemistry of a part's surface to improve its physical properties, primarily hardness and wear resistance.
In a vacuum furnace, processes like vacuum carburizing (adding carbon) and nitriding (adding nitrogen) are precisely controlled. The vacuum ensures that the introduced gas is pure and reacts predictably with the surface, allowing for exact control over case depth and hardness.
Integrating Quenching Within a Single Cycle
Many heat treatments require a rapid cooling step, or quench, to lock in the desired material properties. Modern vacuum furnaces integrate this step seamlessly.
The Role of Quenching
Quenching "freezes" the crystalline structure of the metal that was altered by heat. The speed and medium of the quench determine the final hardness and ductility of the component.
Common Quenching Methods
Vacuum furnaces can be equipped with various quenching systems. While older systems may use oil or water, modern furnaces increasingly rely on high-pressure gas quenching (HPGQ).
Using an inert gas like nitrogen or argon to quench allows the entire hardening and cooling cycle to occur within the sealed, controlled vacuum environment, maintaining the part's pristine surface finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnace systems, with their associated pumps, seals, and control systems, represent a significant capital investment compared to traditional atmosphere furnaces. They also require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance.
Batch Processing and Cycle Times
Vacuum furnaces are inherently batch-processing tools. The time required to pump down the chamber, run the thermal cycle, and cool the load can be longer than continuous belt-furnace operations, making them less suitable for certain high-volume, low-margin parts.
Material Limitations
Certain materials are not suitable for vacuum processing. Elements with a high vapor pressure, such as zinc, cadmium, lead, and magnesium, can "outgas" or vaporize in a vacuum at high temperatures. This can damage the furnace and contaminate future loads.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The versatility of a vacuum furnace allows it to be tailored to specific manufacturing objectives.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, high-purity assemblies: Vacuum brazing is the ideal choice as it eliminates flux entrapment and post-braze cleaning.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, near-net-shape parts from powders: Vacuum sintering will provide superior density and mechanical properties compared to atmospheric methods.
- If your primary focus is achieving highly controlled surface hardness: Vacuum carburizing or nitriding offers unmatched precision by ensuring a pure process atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment with a superior finish: Standard vacuum annealing, hardening, and tempering will prevent any surface oxidation or discoloration.
By understanding its full range of capabilities, you can leverage a vacuum furnace as a multi-process solution that enhances both product quality and operational efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Brazing | Creates strong, clean joints without corrosive fluxes |
| Vacuum Sintering | Produces high-density parts from powdered metals |
| Surface Modification (e.g., Carburizing, Nitriding) | Enhances wear resistance with precise control |
| Integrated Quenching | Maintains surface finish in a controlled vacuum |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored vacuum heat treatment furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing process efficiency and material quality. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can elevate your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What gases in the air can dissolve into molten metal and cause defects? Prevent Porosity and Embrittlement
- What role does a reduction furnace play in the activation of CuO-Fe3O4 catalysts? Master Catalyst Engineering
- What industries commonly use vacuum chamber furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and More
- Why are vacuum furnaces important in aerospace? Essential for High-Strength, Pure Components
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven necessary for drying degraded LTGP samples? Ensure Pure Surface Analysis Results
- How does vacuum sintering help in material purification? Achieve Superior Purity and Performance
- How does a vacuum furnace prevent heat transfer and contamination? Achieve Ultimate Material Purity
- How does a radiant heating system within a vacuum furnace influence brazed joints? Expert Tips for Superior Quality



















