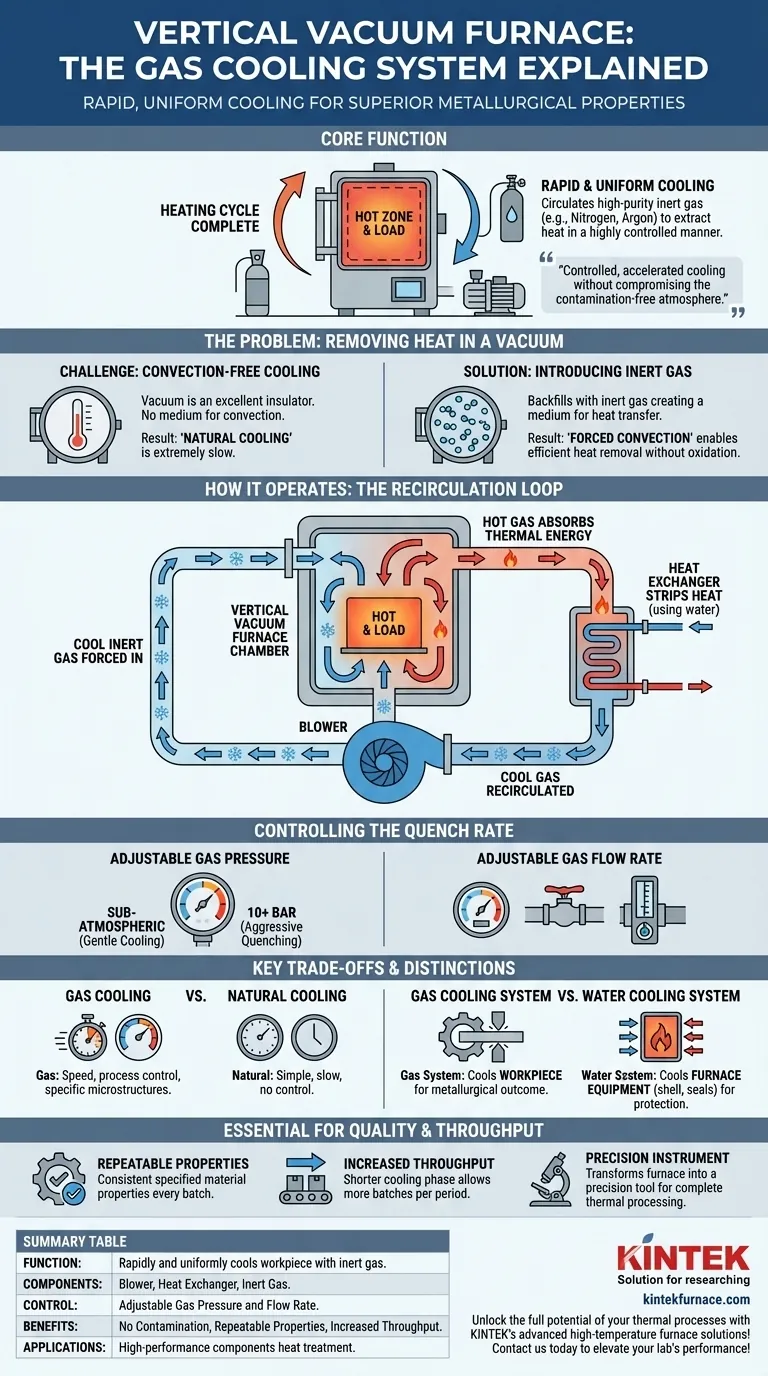
At its core, the function of a gas cooling system in a vertical vacuum furnace is to rapidly and uniformly cool the workpiece, or "load," after the heating cycle is complete. It achieves this by circulating a high-purity inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, through the heated chamber to extract heat in a highly controlled manner.
After heating a material in the protective environment of a vacuum, you must cool it down to lock in desired properties. The gas cooling system provides a method for controlled, accelerated cooling without compromising the contamination-free atmosphere that the vacuum provides.
The Problem: Removing Heat in a Vacuum
The Challenge of Convection-Free Cooling
A vacuum is an excellent insulator because it lacks a medium, like air, to transfer heat through convection.
While this is beneficial for efficient heating, it makes cooling extremely slow. Simply turning off the heating elements results in "natural cooling," a gradual process that is often too slow to achieve the specific metallurgical properties required for high-performance components.
The Solution: Introducing an Inert Gas
The gas cooling system solves this problem by temporarily introducing a medium for heat transfer back into the furnace chamber.
By backfilling the chamber with an inert gas, the system creates an environment where heat can be efficiently removed from the workpiece via forced convection, all while preventing the oxidation and contamination that would occur with exposure to air.
How the Gas Cooling System Operates
The Recirculation Loop
The system operates on a closed loop. A powerful blower forces the cool, inert gas into the furnace's hot zone.
The gas flows over the hot workpiece, absorbing its thermal energy. This now-hot gas is then drawn out of the chamber and directed through a heat exchanger.
The Role of the Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger is critical. It uses a separate cooling medium, typically water, to strip the heat from the inert gas.
Once cooled, the inert gas is recirculated by the blower back into the furnace chamber to absorb more heat from the load. This continuous cycle enables rapid and consistent cooling.
Controlling the Quench Rate
The speed of cooling, or "quenching," is precisely controlled. Engineers can adjust the gas pressure—from sub-atmospheric levels for gentle cooling to high pressures (up to 10 bar or more) for aggressive quenching.
Adjusting the gas flow rate via valves provides another layer of control, allowing the cooling profile to be tailored perfectly to the material's requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Distinctions
Gas Cooling vs. Natural Cooling
Natural cooling is simple but extremely slow and offers no control over the cooling rate.
Gas cooling provides the speed and process control necessary for advanced heat treatment, enabling the creation of specific microstructures that determine a material's final hardness, strength, and durability.
Gas Cooling vs. Water Cooling: A Critical Distinction
It is crucial not to confuse the gas cooling system with the furnace's water cooling system.
The gas cooling system cools the workpiece inside the furnace to achieve a desired metallurgical outcome. The water cooling system cools the furnace equipment itself—such as the shell, seals, and power feedthroughs—to protect it from damage during operation.
Why This System is Essential for Quality and Throughput
Achieving Repeatable Material Properties
The primary benefit of a controlled gas quench is process repeatability. It ensures that every part in a batch, and every batch over time, achieves the same specified material properties without deviation.
Increasing Production Throughput
By drastically shortening the cooling phase of the thermal cycle, the gas cooling system allows for more batches to be processed in a given period. This directly translates to higher productivity and efficiency for the manufacturing operation.
Applying This to Your Process
Choosing the right cooling method depends entirely on your process goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific metallurgical properties (e.g., hardness in tool steel): A gas cooling system is non-negotiable for providing the controlled, rapid quench required.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production throughput: The system's ability to shorten cycle times is essential for an efficient operation.
- If your process involves materials that are not sensitive to cooling rates: A simple natural cool-down in vacuum might suffice, though this is rare in modern applications.
Ultimately, the gas cooling system transforms the vacuum furnace from a simple heating chamber into a precision instrument for complete thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Function | Rapidly and uniformly cools the workpiece after heating using inert gas circulation. |
| Key Components | Blower, heat exchanger, inert gas (e.g., nitrogen, argon). |
| Cooling Control | Adjustable gas pressure and flow rate for precise quench rates. |
| Benefits | Prevents contamination, achieves repeatable material properties, increases throughput. |
| Applications | Ideal for heat treatment of high-performance components requiring specific metallurgical outcomes. |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions!
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precision-engineered equipment like Vertical Vacuum Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can tailor solutions to meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior cooling control, enhanced material properties, and increased productivity.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment? Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity



















